Spring系统学习--1、IOC和DI
2021-05-01 01:26
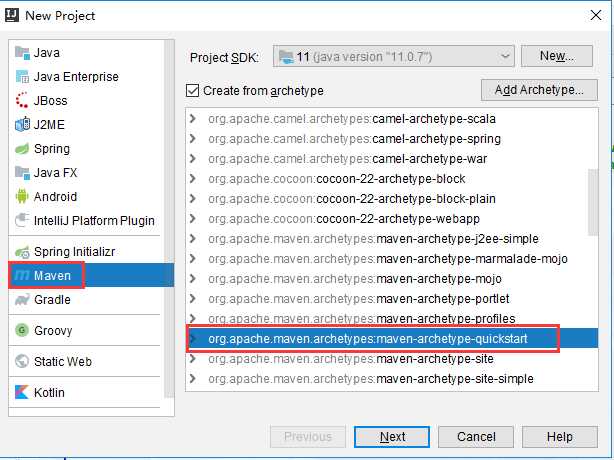
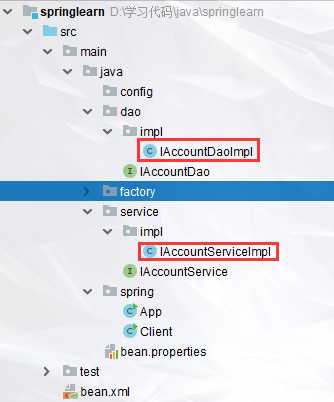
标签:try return 名称 factor 初始化 text 返回 scope end Spring,Spring,Spring,天天用,但是对她太过缺乏“深入”的了解,今天思虑良久,下定决心,我要好好“深入的”了解一下她。 Spring是一个架构性的框架:也就是改变代码结构的框架; 大部分教学视频是使用老掉牙Ecliplse教学Spring的,但是我TM是真的不想用Ecliplse,虽然我电脑上有Ecliplse...如果你要选择Ecliplse那么你可以跟着视频老老实实创建java项目--->导入jar包--->创建XML配置文件,完成spring学习环境的搭建;但是下面我要说的是我是如何使用IDEA开始Spring的学习的: 然后,你会发现项目依赖库下面增加了许多spring相关jar: 然后我们在项目资源文件夹src下面创建spring的配置文件: 这样你就可以愉快的开始spring学习之旅了....简单吧 前提是下面的类已经在对应的路径下创建了: 创建一个类,书写如下代码: 如果我??们xml文件里面bean非常多,在创建容器的时候我们瞬间初始化那么多bean可能会导致卡顿,这个时候我们可以在xml文件里面按照下图:就能实现在调用getBean时才初始化: 如果我们不想通过上面的配置实现懒加载,下面的代码也可以实现在getBean时才创建对象: 注意:上面xml文件里面bean标签内部结构相同的标签可以互换使用: Spring系统学习--1、IOC和DI 标签:try return 名称 factor 初始化 text 返回 scope end 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/luzhanshi/p/11685763.html1.学习环境的准备
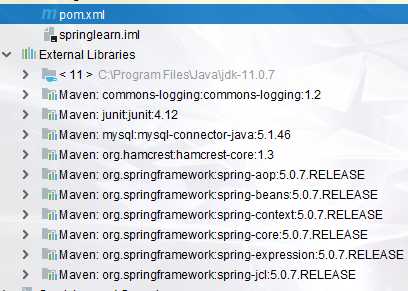
创建完maven项目之后,在pom.xml文件里面添加如下依赖:
dependency>
groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
version>5.0.7.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
dependency>
groupId>commons-logginggroupId>
artifactId>commons-loggingartifactId>
version>1.2version>
dependency>
dependencies>
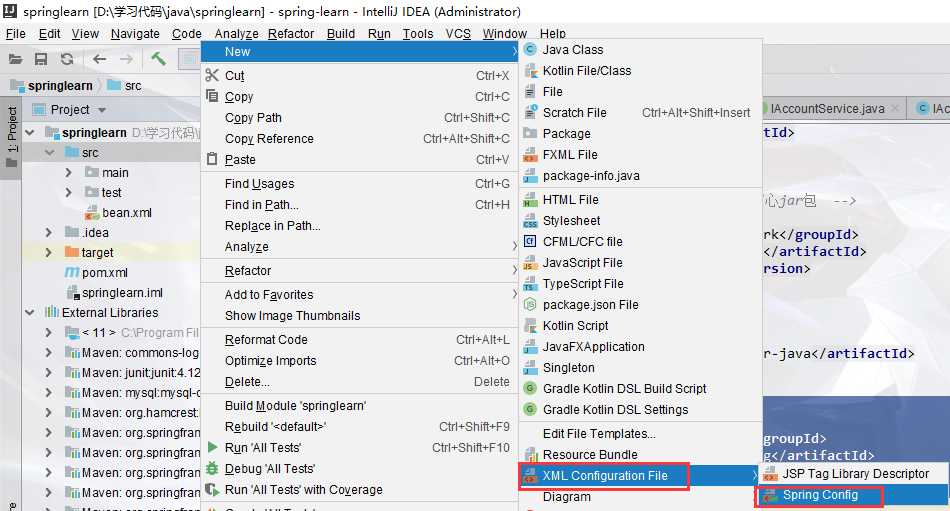
2.IOC入门案例
2.1在bean.xml里面添加如下配置:
bean id="accountService" class="main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl">bean>
bean id="accountDao" class="main.java.dao.impl.IAccountDaoImpl">bean>
2.2获取Spring的核心容器,并且根据bean的id获取对象
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 获取Spring的核心容器,并且根据bean的id获取对象
*
* ApplicationContext:是BeanFactory的孙子接口,创建对象的时候采取的是理解加载的策略.(读取完XML配置文件之后,xml里面所有的bean对象就已经全部创建完成了)
*/
// 1.获取容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 2.根据bean的id获取对象
IAccountService iAccountService=(IAccountService)context.getBean("accountService");
IAccountDao accountDao = context.getBean("accountDao", IAccountDao.class);
System.out.println(iAccountService);
System.out.println(accountDao);
}
}
补充:ApplicationContext子类:
/* * ApplicationContext子类:
* -----ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:
* 她是通过读取类路径下的配置文件创建spring容器;要求配置文件在类路径下
* -----FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
* 她是通过读取文件系统中的配置文件创建spring容器;要求配置文件在文件系统中即可
*/
2.3懒加载
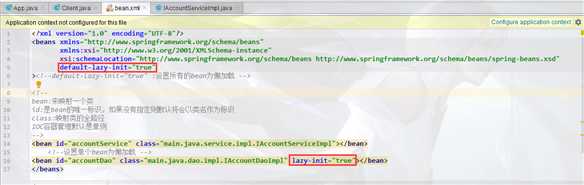
2.4懒加载容器
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 获取Spring的核心容器,并且根据bean的id获取对象
*
* ApplicationContext:是BeanFactory的孙子接口,创建对象的时候采取的是理解加载的策略.(读取完XML配置文件之后,xml里面所有的bean对象就已经全部创建完成了)
* BeanFactory:是springIoc的顶层接口,创建bean对象时,采用延迟加载的策略(当真正要从容器中获取对象时,才会创建,读完配置文件并不创建)
*/
// 1.获取容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 2.获取对象
IAccountService iAccountService = (IAccountService) context.getBean("accountService");
IAccountDao accountDao = context.getBean("accountDao", IAccountDao.class);
System.out.println(iAccountService);
System.out.println(accountDao);
// 1.加载配置文件
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("bean.xml");
// 2.获取容器
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
// 3.获取对象
IAccountService accountService = beanFactory.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
}
}
2.5bean对象的三种创建方式
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
>
bean id="accountService" class="main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl">bean>
bean id="staticFactory" class="main.java.factory.BeanFactory" factory-method="getBean1">bean>
bean id="instanceFactory" class="main.java.factory.BeanFactory">bean>
bean id="instanceFactoryBean" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getBean2">bean>
beans>
public class CreatBeanTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 1.默认构造函数创建对象,获取方法
IAccountService accountService = context.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
System.out.println(accountService);//main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl@17f7cd29
// 2.静态工厂创建对象,获取方法
IAccountService accountService1 = context.getBean("staticFactory", IAccountService.class);
System.out.println(accountService1);//main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl@7d8704ef
// 3.实例工厂创建对象,获取方法
IAccountService accountService2 = context.getBean("instanceFactoryBean", IAccountService.class);
System.out.println(accountService2);//main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl@17f7cd29
}
}
2.6bean对象的作用范围:
bean id="accountService" class="main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl" scope="prototype">bean>
2.7bean对象的生命周期:
bean id="singleton_accountService" class="main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl" scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory">bean>
bean id="prototype_accountService" class="main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl" scope="prototype" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory">bean>
public class IAccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
IAccountDao iAccountDao=new IAccountDaoImpl();
public IAccountServiceImpl(){
System.out.println("对象创建了!!!");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("对象初始化了");
}
public void destory(){
System.out.println("对象销毁了了");
}
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
iAccountDao.save();
}
}
public class _05LifecycleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.获取容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean_lifecycle.xml");
// 2.获取对象
IAccountService accountService1 = context.getBean("singleton_accountService", IAccountService.class);
System.out.println(accountService1);
IAccountService accountService2 = context.getBean("prototype_accountService", IAccountService.class);
System.out.println(accountService2);
// 3.销毁容器
context.close();
}
}
3.DI依赖注入
3.1介绍两种注入类型
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
bean id="accountService" class="main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl" >
constructor-arg name="name" value="李沁">constructor-arg>
constructor-arg name="age" value="18">constructor-arg>
constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="birthday">constructor-arg>
bean>
bean id="birthday" class="java.util.Date">bean>
bean id="accountService2" class="main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl" >
property name="name" value="李沁2">property>
property name="age" value="17">property>
property name="birthday" ref="birthday">property>
bean>
beans>
public class IAccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public IAccountServiceImpl(String name, int age, Date birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public IAccountServiceImpl(){
System.out.println("对象创建了!!!");
}
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(name+age+birthday);
}
}
public class _06DI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.获取容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean_DI.xml");
// 2.获取对象
IAccountService accountService1 = context.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
accountService1.saveAccount();
IAccountService accountService2 = context.getBean("accountService2", IAccountService.class);
accountService2.saveAccount();
// 3.销毁容器
context.close();
}
}
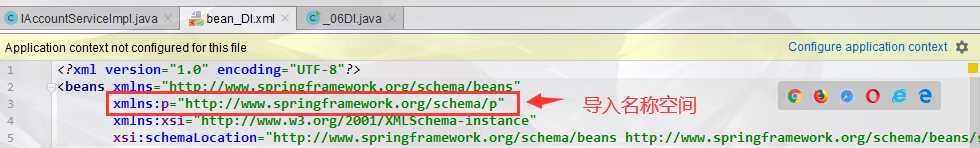
3.2 P名称空间注入:
bean id="accountService3" class="main.java.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl" p:name="李沁3">
bean>
3.3特殊类型属性注入
public class CollectionsDI {
private String [] strings;
private List
bean id="CollectionsDI" class="main.java.service.CollectionsDI" >
property name="strings">
array>
value>argsvalue>
value>argsvalue>
value>argsvalue>
array>
property>
property name="myList">
list>
value>LISTvalue>
value>LISTvalue>
value>LISTvalue>
list>
property>
property name="mySet">
set>
value>SETvalue>
value>SETvalue>
value>SETvalue>
set>
property>
property name="myMap">
map>
entry key="001" value="map">entry>
entry key="002">
value>map注入方式2value>
entry>
map>
property>
property name="myProps">
props>
prop key="url">http:www.baidu.comprop>
props>
property>
bean>
public class _06DI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.获取容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean_DI.xml");
// 2.获取对象
CollectionsDI collectionsdi = context.getBean("CollectionsDI", CollectionsDI.class);
collectionsdi.print();
/**
[args, args, args]
[LIST, LIST, LIST]
{001=map, 002=map注入方式2}
[SET1, SET2, SET3]
{url=http:www.baidu.com}
*/
// 3.销毁容器
context.close();
}
}
property name="strings">
list>
value>LISTvalue>
value>LISTvalue>
value>LISTvalue>
list>
property>
property name="myList">
array>
value>argsvalue>
value>argsvalue>
value>argsvalue>
array>
property>
3.4注入时特殊符号处理
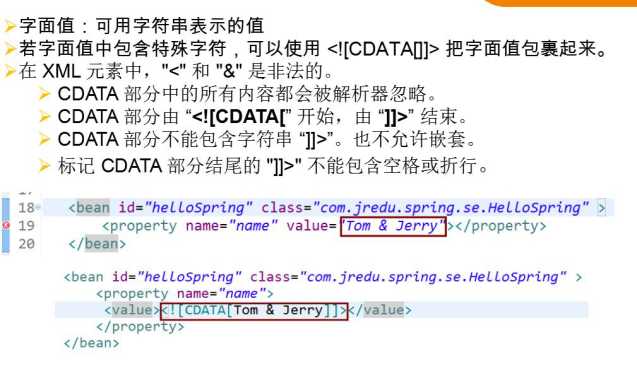
3.5
文章标题:Spring系统学习--1、IOC和DI
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/80636.html