leetcode题解之34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
2021-05-04 13:27
方法 1:线性扫描
想法
对 target 检查每一个下标,一定能得到正确答案。
算法
首先,我们对 nums 数组从左到右做线性遍历,当遇到 target 时中止。如果我们没有中止过,那么 target 不存在,我们可以返回“错误代码” [-1, -1] 。如果我们找到了有效的左端点坐标,我们可以坐第二遍线性扫描,但这次从右往左进行。这一次,第一个遇到的 target 将是最右边的一个(因为最左边的一个存在,所以一定会有一个最右边的 target)。我们接下来只需要返回这两个坐标。
class Solution {
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] targetRange = {-1, -1};
// find the index of the leftmost appearance of `target`.
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == target) {
targetRange[0] = i;
break;
}
}
// if the last loop did not find any index, then there is no valid range
// and we return [-1, -1].
if (targetRange[0] == -1) {
return targetRange;
}
// find the index of the rightmost appearance of `target` (by reverse
// iteration). it is guaranteed to appear.
for (int j = nums.length-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (nums[j] == target) {
targetRange[1] = j;
break;
}
}
return targetRange;
}
}
class Solution:
def searchRange(self, nums, target):
# find the index of the leftmost appearance of target. if it does not
# appear, return [-1, -1] early.
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] == target:
left_idx = i
break
else:
return [-1, -1]
# find the index of the rightmost appearance of `target` (by reverse
# iteration). it is guaranteed to appear.
for j in range(len(nums)-1, -1, -1):
if nums[j] == target:
right_idx = j
break
return [left_idx, right_idx]
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度: 。
这个暴力解法检测了
num数组中每个元素恰好两次,所以总运行时间是线性的。 -
空间复杂度: 。
线性扫描方法使用了固定大小的数组和几个整数,所以它的空间大小为常数级别的。
方法 2:二分查找
想法
因为数组已经排过序了,我们可以使用二分查找的方法去定位左右下标。
算法
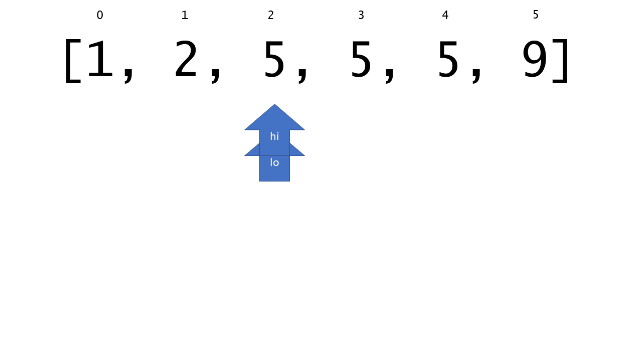
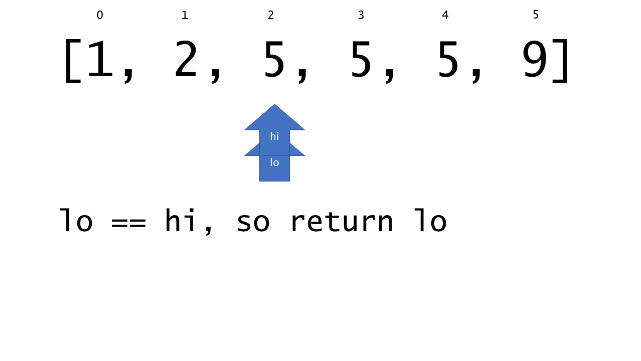
总体算法工作过程与线性扫描方法类似,除了找最左和最右下标的方法。这里我们仅仅做几个微小的调整,用这种修改过的二分查找方法去搜索这个排过序的数组。首先,为了找到最左边(或者最右边)包含 target 的下标(而不是找到的话就返回 true ),所以算法在我们找到一个 target 后不能马上停止。我们需要继续搜索,直到 lo == hi 且它们在某个 target 值处下标相同。
另一个改变是 left 参数的引入,它是一个 boolean 类型的变量,指示我们在遇到 target == nums[mid] 时应该做什么。如果 left 为 true ,那么我们递归查询左区间,否则递归右区间。考虑如果我们在下标为 i 处遇到了 target ,最左边的 target 一定不会出现在下标大于 i 的位置,所以我们永远不需要考虑右子区间。当求最右下标时,道理同样适用。
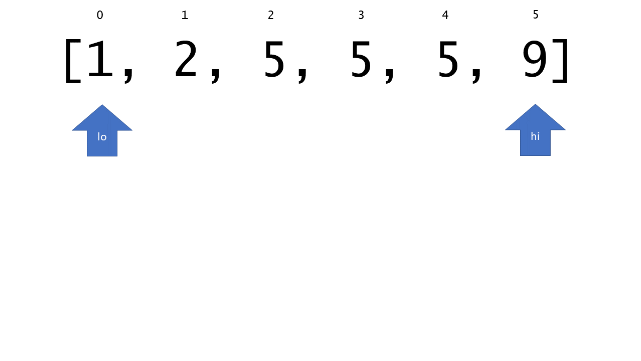
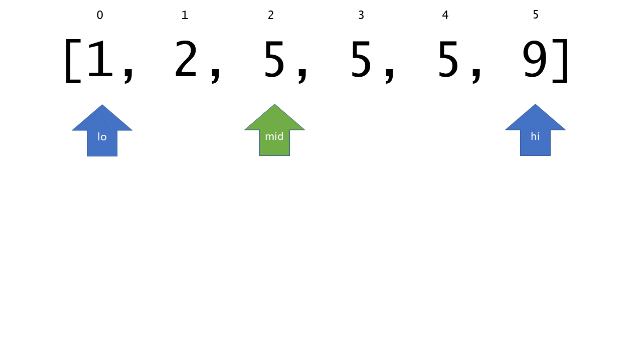
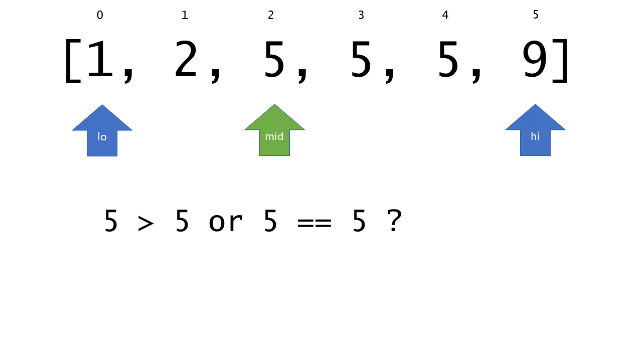
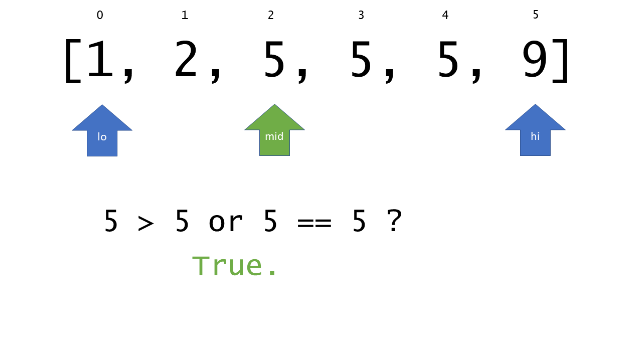
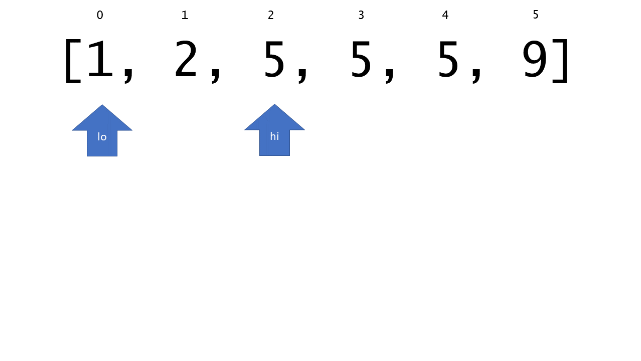
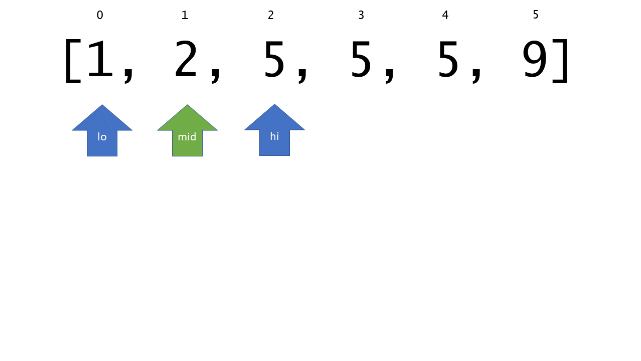
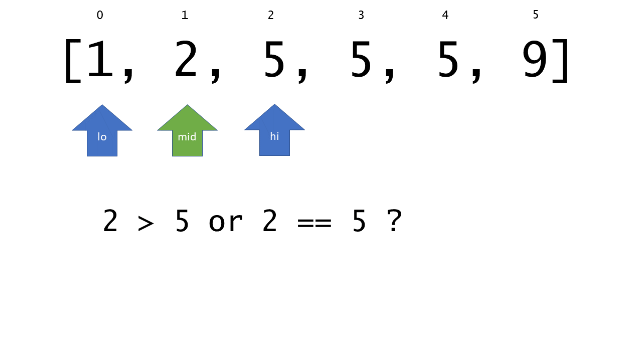

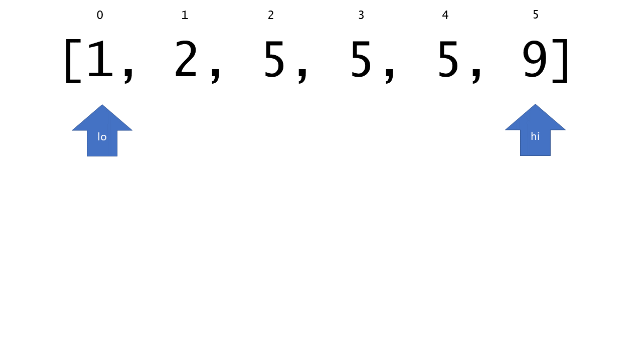
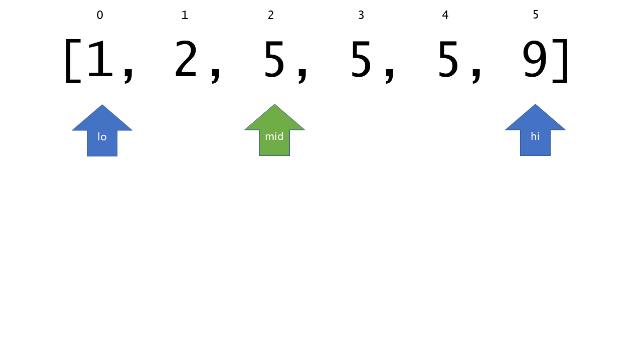
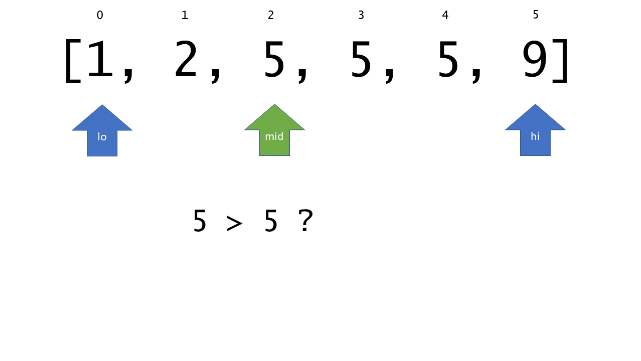
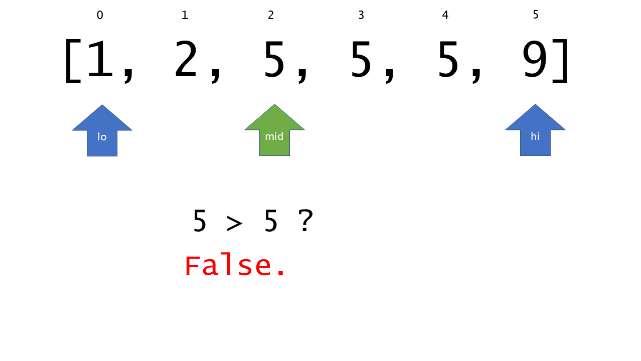
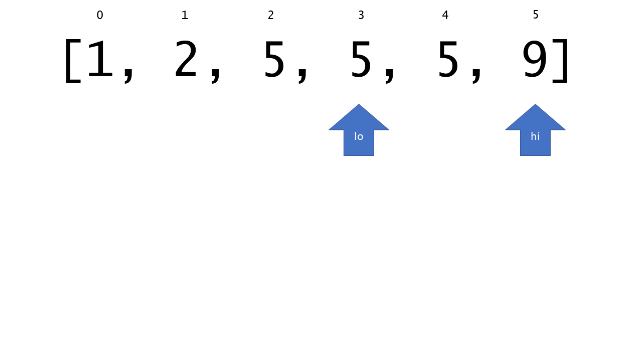
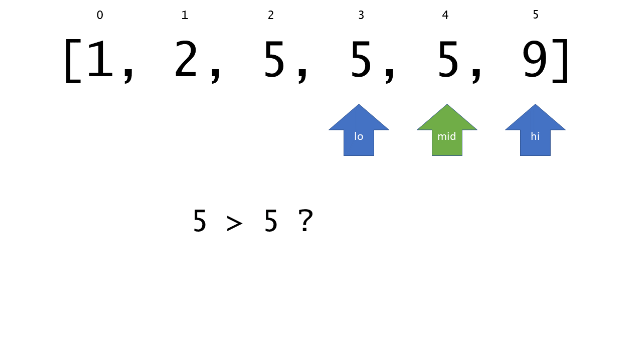
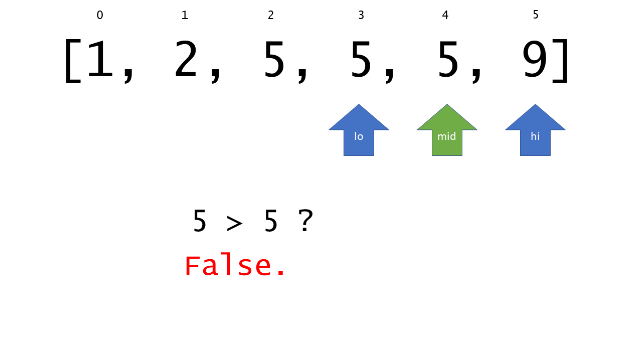
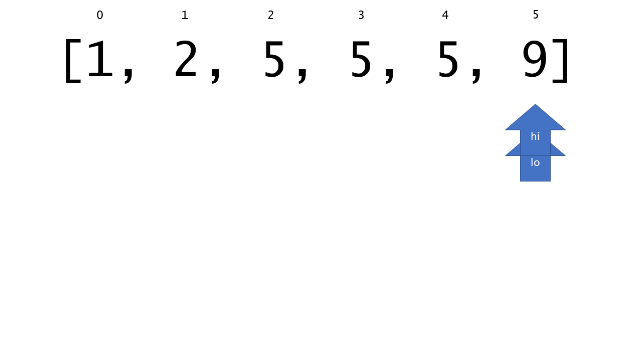

class Solution {
// returns leftmost (or rightmost) index at which `target` should be
// inserted in sorted array `nums` via binary search.
private int extremeInsertionIndex(int[] nums, int target, boolean left) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = nums.length;
while (lo < hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > target || (left && target == nums[mid])) {
hi = mid;
}
else {
lo = mid+1;
}
}
return lo;
}
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] targetRange = {-1, -1};
int leftIdx = extremeInsertionIndex(nums, target, true);
// assert that `leftIdx` is within the array bounds and that `target`
// is actually in `nums`.
if (leftIdx == nums.length || nums[leftIdx] != target) {
return targetRange;
}
targetRange[0] = leftIdx;
targetRange[1] = extremeInsertionIndex(nums, target, false)-1;
return targetRange;
}
}
class Solution:
# returns leftmost (or rightmost) index at which target should be inserted in sorted
# array nums via binary search.
def extreme_insertion_index(self, nums, target, left):
lo = 0
hi = len(nums)
while lo < hi:
mid = (lo + hi) // 2
if nums[mid] > target or (left and target == nums[mid]):
hi = mid
else:
lo = mid+1
return lo
def searchRange(self, nums, target):
left_idx = self.extreme_insertion_index(nums, target, True)
# assert that `left_idx` is within the array bounds and that `target`
# is actually in `nums`.
if left_idx == len(nums) or nums[left_idx] != target:
return [-1, -1]
return [left_idx, self.extreme_insertion_index(nums, target, False)-1]
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度: 。
由于二分查找每次将搜索区间大约划分为两等分,所以至多有 次迭代。二分查找的过程被调用了两次,所以总的时间复杂度是对数级别的。
-
空间复杂度: 。
所有工作都是原地进行的,所以总的内存空间是常数级别的。
文章标题:leetcode题解之34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/82277.html