Vgg Net Pytorch实现+论文解读
2021-05-05 02:29
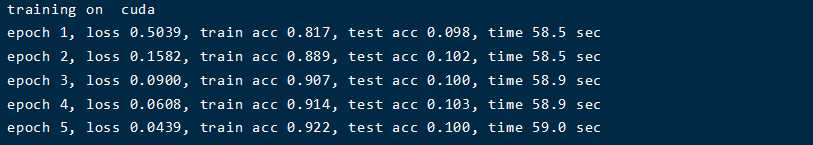
标签:ace 错误 tput ann 样本 app img 思路 ORC 论文为VERY DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORKS FOR LARGE-SCALE IMAGE RECOGNITION,主要讨论了在大规模图片识别中,卷积神经网络的深度对准确率的影响。本篇论文提出的vgg网络在2014年的ImageNet比赛中分别在定位和分类中获得了第一和第二的成绩。 VGGNet对2012年的AlexNet模型主要提出了两种改进思路: 论文中针对网络深度、卷积核尺寸、LRN操作方面做了对比试验,设计了6个VGG结构。如下图所示。 测试主要针对上面的6钟结构,然后加入了多尺寸输入训练以及测试。 本文评估了深度卷积网络(到19层)在大规模图片分类中的应用。 程序中使用MNIST数据集,pytorch打印的网络结构为: 训练结果为: 因为使用原文结构参数量太大,造成显存爆满,于是将结构中的通道数变为1/8。训练结果中,迭代了5次后,训练集精确度提高,但测试集精度结果不是很理想。 已经将代码上传到GitHub:https://github.com/chnngege/vgg-pytorch Vgg Net Pytorch实现+论文解读 标签:ace 错误 tput ann 样本 app img 思路 ORC 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/chnngege/p/12110189.html改进创新点
卷积神经网络设置
架构
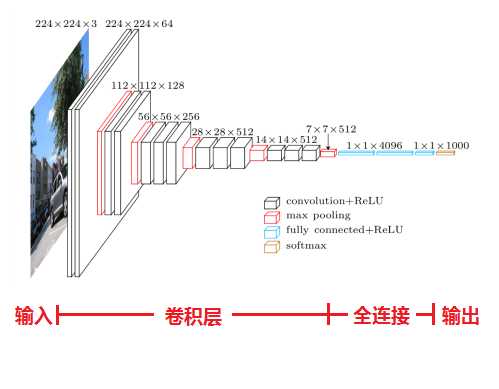
结构特点:
对比试验
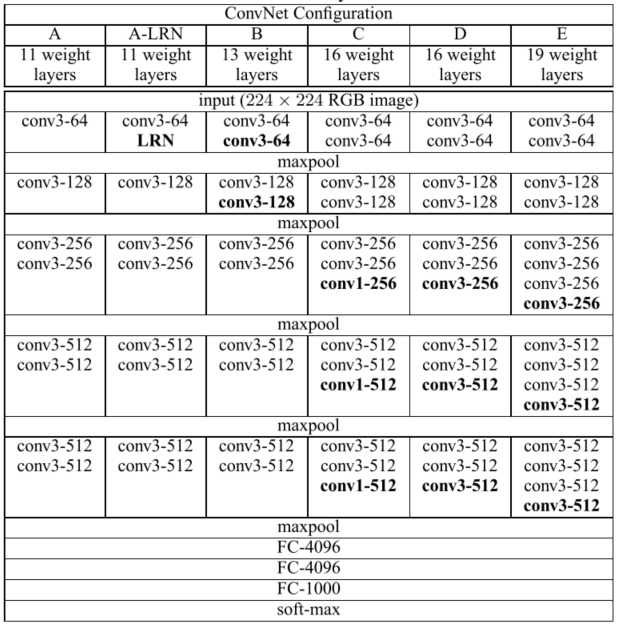
为何使用3x3卷积核
为何使用1x1卷积核
训练
batch size为256,学习率初始化为0.01,用包含动量的小批量梯度下降。
权重随机初始化,从0均值和0.01方差的正态分布中取值。偏差初始化为0。
网络输入的图片尺寸为224x224,因此必须调整图片的尺寸。选取训练图像最小边为S,若S=224,则不需要裁剪;若S>>224,裁剪图像就会取图像的一小部分。这样选择的图片可以选取S>224的图片,作为多尺寸输入,只需要裁剪成224x224规格的图片即可。下面的测试将会分别固定尺寸测试和多尺寸测试。测试
测试的结果:
结论
结果表明,深度有益于提高分类的正确率,通过在传统的卷积网络框架中使用更深的层能够在ImageNet数据集上取得优异的结果。NOTE:
Pytorch实现VGGNet
import torch
import time
from torch import nn, optim
import torchvision
import sys
#定义VGG各种不同的结构和最后的全连接层结构
cfg = {
'VGG11': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256,'M', 512, 'M', 512,'M'],
'VGG13': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'VGG16': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'VGG19': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'FC': [512*7*7, 4096, 10]
}
#将数据展开成二维数据,用在全连接层之前和卷积层之后
class FlattenLayer(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(FlattenLayer, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x): # x shape: (batch, *, *, ...)
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
class VGG(nn.Module):
# nn.Module是一个特殊的nn模块,加载nn.Module,这是为了继承父类
def __init__(self, vgg_name):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
# super 加载父类中的__init__()函数
self.VGG_layer = self.vgg_block(cfg[vgg_name])
self.FC_layer = self.fc_block(cfg['FC'])
#前向传播算法
def forward(self, x):
out_vgg = self.VGG_layer(x)
out = out_vgg.view(out_vgg.size(0), -1)
# 这一步将out拉成out.size(0)的一维向量
out = self.FC_layer(out_vgg)
return out
#VGG模块
def vgg_block(self, cfg_vgg):
layers = []
in_channels = 1
for out_channels in cfg_vgg:
if out_channels == 'M':
layers.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
else:
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3,padding=1, bias=False))
layers.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels))
layers.append(nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
in_channels = out_channels
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
#全连接模块
def fc_block(self, cfg_fc):
fc_net = nn.Sequential()
fc_features, fc_hidden_units, fc_output_units = cfg_fc[0:]
fc_net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(
FlattenLayer(),
nn.Linear(fc_features, fc_hidden_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(fc_hidden_units, fc_hidden_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(fc_hidden_units, fc_output_units)
))
return fc_net
#加载MNIST数据,返回训练数据集和测试数据集
def load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=None, root='~/chnn/Datasets/FashionMNIST'):
"""Download the fashion mnist dataset and then load into memory."""
trans = []
if resize:
trans.append(torchvision.transforms.Resize(size=resize))
trans.append(torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose(trans)
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=root, train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=root, train=False, download=True, transform=transform)
if sys.platform.startswith('win'):
num_workers = 0 # 0表示不用额外的进程来加速读取数据
else:
num_workers = 4
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=num_workers)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=num_workers)
return train_iter, test_iter
#测试准确率
def evaluate_accuracy(data_iter, net, device=None):
if device is None and isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
# 如果没指定device就使用net的device
device = list(net.parameters())[0].device
acc_sum, n = 0.0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in data_iter:
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.eval() # 评估模式, 这会关闭dropout
acc_sum += (net(X.to(device)).argmax(dim=1) == y.to(device)).float().sum().cpu().item()
net.train() # 改回训练模式
else: # 自定义的模型, 3.13节之后不会用到, 不考虑GPU
if('is_training' in net.__code__.co_varnames): # 如果有is_training这个参数
# 将is_training设置成False
acc_sum += (net(X, is_training=False).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
else:
acc_sum += (net(X).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
n += y.shape[0]
return acc_sum / n
#模型训练,定义损失函数、优化函数
def train_ch5(net, train_iter, test_iter, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs):
net = net.to(device)
print("training on ", device)
loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
batch_count = 0
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_l_sum, train_acc_sum, n, start = 0.0, 0.0, 0, time.time()
for X, y in train_iter:
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_l_sum += l.cpu().item()
train_acc_sum += (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().cpu().item()
n += y.shape[0]
batch_count += 1
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(test_iter, net)
print('epoch %d, loss %.4f, train acc %.3f, test acc %.3f, time %.1f sec'
% (epoch + 1, train_l_sum / batch_count, train_acc_sum / n, test_acc, time.time() - start))
def main():
net = VGG('VGG16')
print(net)
#一个batch_size为64张图片,进行梯度下降更新参数
batch_size = 64
#使用cuda来训练
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
#加载MNIST数据集,返回训练集和测试集
train_iter, test_iter = load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224)
lr, num_epochs = 0.001, 5
#使用Adam优化算法替代传统的SGD,能够自适应学习率
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
#训练--迭代更新参数
train_ch5(net, train_iter, test_iter, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs)
main()NOTE:
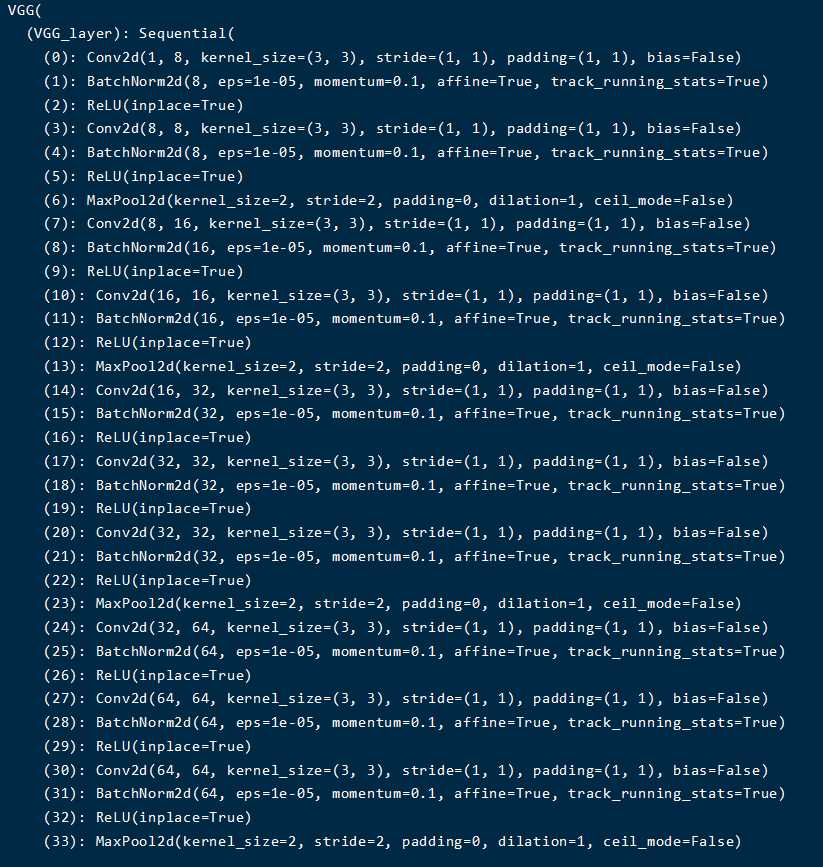
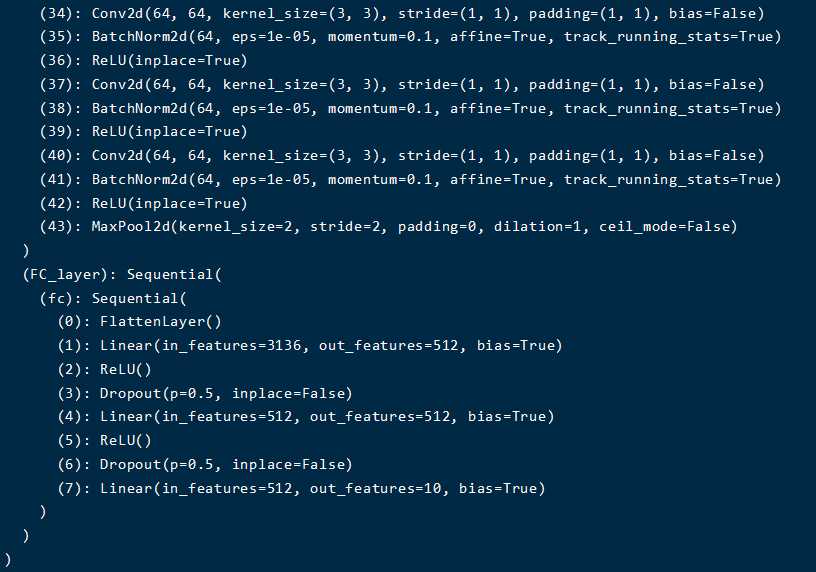
下一篇:jquery 云标签
文章标题:Vgg Net Pytorch实现+论文解读
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/82539.html