C# 7.0 新特性:本地方法
2021-05-07 21:29
标签:mod number strong sync ogr 程序集 oca color eof VS 2017 的 C# 7.0 中引入了本地方法,本地方法是一种语法糖,允许我们在方法内定义本地方法。更加类似于函数式语言,但是,本质上还是基于面向对象实现的。 先看一个示例: 在此示例中,在 Main 方法内,嵌套定义了两个方法:Add 和 Multiply。这个方法可以在 Main 方法内被使用。这种方法被称为本地方法。英文称为:Local function. 使用 ILDasm 工具,可以看到编译之后的结果。 这两个本地方法被翻译成了两个静态的私有方法,它只能在定义的方法内被调用。 本地方法的语法定义为: 方法的修饰符只有两种:async 和 unsafe,所有的本地方法都是私有的 本地方法也可以带有返回类型。如果类型用错的话,Visual Studio 可以给出提示。 本地方法不需要维护调用堆栈,而递归方法需要维护调用堆栈,本地方法效率更高。下面的示例演示了两种方法的区别。 注意:该示例使用了类型 BigInteger ,需要添加对程序集 System.Numeric.dll 的引用。 代码如下。 在我的机器上,结果如下: Using local function: 181770 可以看到两者之间的性能差异。 此时,为了传递 result ,在生成的代码中,编译器会自动做一些额外的工作。 当创建 Lambda 的时候,将会创建一个委托,这需要内存分配,因为委托是一个对象。而本地方法则不需要,它是一个真正的方法。 另外,本地方法可以更为有效地使用本地变量,Lambda 将变量放到类中,而本地方法可以使用结构,而不使用内存分配。 这意味着调用本地方法更为节约且可能内联。 Lambda 也可以实现递归,但是代码丑陋,您需要先赋予 lambda 为 null。本地方法可以更为自然地递归。 Lambda 不能使用泛型。这是因为需要赋予一个实例类型的变量。 Lambda 不能使用 yield return (以及 yield break)关键字,以实现 IEnumerable C# 7.0 新特性2: 本地方法 Thoughts on C# 7 Local Functions C# 7.0 新特性:本地方法 标签:mod number strong sync ogr 程序集 oca color eof 原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/haogj/p/7636915.htmlC# 7.0:本地方法
1. 本地方法
1 using static System.Console;
2
3 namespace UseLocalFunctions
4 {
5 class Program
6 {
7 static void Main(string[] args)
8 {
9 void Add(int x, int y)
10 {
11 WriteLine($"Sum of {x} and {y}: is {x + y}");
12 }
13
14 void Multiply(int x, int y)
15 {
16 WriteLine($"Multiply of {x} and {y} is: {x * y}");
17 Add(30, 10);
18 }
19
20 Add(10, 30);
21 Multiply(40, 30);
22
23 ReadLine();
24 }
25 }
26 }

2. 带有返回类型的本地方法
1 class Program
2 {
3 static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5 PrintStudentMarks(101,
6 new Subject
7 {
8 SubjectName = "Math",
9 Marks = 96
10 }, new Subject
11 {
12 SubjectName = "physics",
13 Marks = 88
14 }, new Subject
15 {
16 SubjectName = "Chem",
17 Marks = 91
18 });
19
20 ReadLine();
21 }
22
23 public static void PrintStudentMarks(int studentId, params Subject[] subjects)
24 {
25 WriteLine($"Student Id{studentId} Total Marks: {CalculateMarks()}");
26 WriteLine($"Student wise marks");
27 foreach(var subject in subjects)
28 {
29 WriteLine($"Subject Name: {subject.SubjectName}\t Marks: {subject.Marks}");
30 }
31
32 decimal CalculateMarks()
33 {
34 decimal totalMarks = 0;
35 foreach(var subject in subjects)
36 {
37 totalMarks += subject.Marks;
38 }
39
40 return totalMarks;
41 }
42 }
43
44 public class Subject
45 {
46 public string SubjectName
47 {
48 get; set;
49 }
50
51 public decimal Marks
52 {
53 get; set;
54 }
55 }
56 }
3. 使用本地方法实现递归
1 class Program
2 {
3 static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5 Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
6 watch.Start();
7 BigInteger f1 = GetFactorialUsingLocal(9000);
8 watch.Stop();
9 WriteLine($"Using local function: {watch.ElapsedTicks}");
10
11 watch.Reset();
12 watch.Start();
13 BigInteger f2 = GetFactorial(9000);
14 watch.Stop();
15 WriteLine($"Using recursive function: {watch.ElapsedTicks}");
16 }
17
18 private static BigInteger GetFactorialUsingLocal(int number)
19 {
20 if (number 0)
21 throw new ArgumentException("negative number", nameof(number));
22 else if (number == 0)
23 return 1;
24 BigInteger result = number;
25 while (number > 1)
26 {
27 Multiply(number - 1);
28 number--;
29 }
30
31 void Multiply(int x) => result *= x;
32 return result;
33 }
34
35 private static BigInteger GetFactorial(int number)
36 {
37 if (number 0)
38 throw new ArgumentException("nagative number", nameof(number));
39 return number == 0 ? 1 : number * GetFactorial(number - 1);
40 }
41 }
Using recursive function: 456602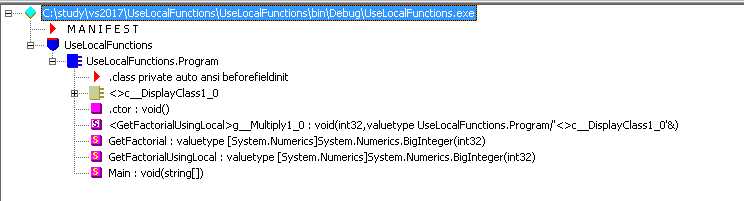
4. 本地方法与 Lambda 的比较
1. 性能
2. 本地方法可以递归
3. 本地方法可以使用泛型
4. 本地方法可以实现迭代器
5. 本地方法更为易读
5. 其它资源:
上一篇:API -- 图书