【C++】C++string类总结
2021-05-20 06:30
标签:oca return 总结 html 符号 gre cat 特定 相同 首先,为了在程序中使用string类型,必须包含头文件 注意这里不是string.h,string.h是C字符串头文件。 string类是一个模板类,位于名字空间std中,通常为方便使用还需要增加: 声明一个字符串变量很简单: 测试代码: 程序执行结果为: Hello world world wor abcde abc AAAAA Hello 你可以用 ==、>、=、
程序执行结果为: Please input your name: Zhang↙ you are not Wang! Zhang, Welcome! Zhang, Welcome! 上例中,“ coutcout 三、string特性描述 可用下列函数来获得string的一些特性: 测试代码: 程序执行结果为: str is NULL. str is abcdefg str‘s size is 7 str‘s capacity is 15 str‘s max size is 4294967294 str‘s length is 7 str is abcdefgccc str is abcde 由于查找是使用最为频繁的功能之一,string提供了非常丰富的查找函数:(注:string::npos) 注意:查找字符串a是否包含子串b,不是用 strA.find(strB) > 0 而是 strA.find(strB) != string:npos 这是为什么呢?(初学者比较容易犯的一个错误)本部分参考自web100与luhao1993 先看下面的代码 上述代码中,idx的类型被定义为int,这是错误的,即使定义为 unsigned int 也是错的,它必须定义为 string::size_type。npos 是这样定义的: static const size_type npos = -1; 因为 string::size_type (由字符串配置器 allocator 定义) 描述的是 size,故需为无符号整数型别。因为缺省配置器以型别 size_t 作为 size_type,于是 -1 被转换为无符号整数型别,npos 也就成了该型别的最大无符号值。不过实际数值还是取决于型别 size_type 的实际定义。不幸的是这些最大值都不相同。事实上,(unsigned long)-1 和 (unsigned short)-1 不同(前提是两者型别大小不同)。因此,比较式 idx == string::npos 中,如果 idx 的值为-1,由于 idx 和字符串string::npos 型别不同,比较结果可能得到 false。因此要想判断 find()等查找函数的结果是否为npos,最好的办法是直接比较。 测试代码: 运行结果: 五、其他常用函数 测试代码: 程序执行结果为: abc123defg abcdefg 123abcdefg 123abcdefg123 123abcdefg123A helloabcdefg123A abcdefg swap! swap! #include
using namespace std;
string str;
#include #include using namespace std;
int main ( )
{ string str; //定义了一个空字符串str
str = "Hello world"; // 给str赋值为"Hello world"
char cstr[] = "abcde"; //定义了一个C字符串
string s1(str); //调用复制构造函数生成s1,s1为str的复制品
cout
string s2(str,6); //将str内,开始于位置6的部分当作s2的初值
cout
string s3(str,6,3); //将str内,开始于6且长度顶多为3的部分作为s3的初值
cout
string s4(cstr); //将C字符串作为s4的初值
cout
string s5(cstr,3); //将C字符串前3个字符作为字符串s5的初值。
cout
string s6(5,‘A‘); //生成一个字符串,包含5个‘A‘字符
cout
string s7(str.begin(),str.begin()+5); //区间str.begin()和str.begin()+5内的字符作为初值
cout
return 0;
}二、string的比较等操作
#include #include using namespace std;
int main()
{ string str;
cout
"Please input your name:" cin >> str;
if( str == "Li" ) // 字符串相等比较
cout
"you are Li!" else if( str != "Wang" ) // 字符串不等比较
cout
"you are not Wang!" else if( str
"Li") // 字符串小于比较,>、>=、 cout
"your name should be ahead of Li" else
cout
"your name should be after of Li" str += ", Welcome!"; // 字符串+=
cout
for(int i = 0 ; i
cout
// 类似数组,通过[]获取特定的字符 return 0;
}int capacity()const; //返回当前容量(即string中不必增加内存即可存放的元素个数)
int max_size()const; //返回string对象中可存放的最大字符串的长度
int size()const; //返回当前字符串的大小
int length()const; //返回当前字符串的长度
bool empty()const; //当前字符串是否为空
void resize(int len,char c); //把字符串当前大小置为len,多去少补,多出的字符c填充不足的部分
#include #include using namespace std;
int main()
{ string str;
if (str.empty())
cout
"str is NULL." else
cout
"str is not NULL." str = str + "abcdefg";
cout
"str is " cout
"str‘s size is " cout"str‘s capacity is " cout
"str‘s max size is " cout
"str‘s length is " str.resize(20,‘c‘);
cout
"str is " str.resize(5);
cout
"str is " return 0;
}四、string的查找
size_type find( const basic_string &str, size_type index ); //返回str在字符串中第一次出现的位置(从index开始查找),如果没找到则返回string::npos
size_type find( const char *str, size_type index ); // 同上
size_type find( const char *str, size_type index, size_type length ); //返回str在字符串中第一次出现的位置(从index开始查找,长度为length),如果没找到就返回string::npos
size_type find( char ch, size_type index ); // 返回字符ch在字符串中第一次出现的位置(从index开始查找),如果没找到就返回string::npos
int idx = str.find("abc");
if (idx == string::npos);
#include#includeusing namespace std;
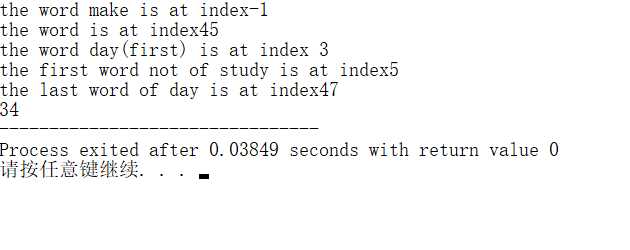
int main(){
int loc;
string s="study hard and make progress everyday! every day!!";
loc=s.rfind("make",10);
cout
"the word make is at index"//-1表示没找到 loc=s.rfind("make");//缺省状态下,从最后一个往前找
cout
"the word make is at index" loc=s.find_first_of("day");
cout
"the word day(first) is at index " loc=s.find_first_not_of("study");
cout
"the first word not of study is at index" loc=s.find_last_of("day");
cout
"the last word of day is at index" loc=s.find("day");//缺陷状态下从第一个往后找
cout
return 0;
}
string &insert(int p,const string &s); //在p位置插入字符串s
string &replace(int p, int n,const char *s); //删除从p开始的n个字符,然后在p处插入串s
string &erase(int p, int n); //删除p开始的n个字符,返回修改后的字符串
string substr(int pos = 0,int n = npos) const; //返回pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串
void swap(string &s2); //交换当前字符串与s2的值
string &append(const char *s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
void push_back(char c) //当前字符串尾部加一个字符c
const char *data()const; //返回一个非null终止的c字符数组,data():与c_str()类似,用于string转const char*其中它返回的数组是不以空字符终止,
const char *c_str()const; //返回一个以null终止的c字符串,即c_str()函数返回一个指向正规C字符串的指针, 内容与本string串相同,用于string转const char*
#include #include using namespace std;
int main()
{ string str1 = "abc123defg";
string str2 = "swap!";
cout
cout
//从索引3开始的3个字符,即删除掉了"123" cout
"123")//在头部插入 cout
"123")//append()方法可以添加字符串 str1.push_back(‘A‘); //push_back()方法只能添加一个字符
cout
cout
"hello")//即将索引0开始的3个字符替换成"hello" cout
//从索引5开始7个字节 str1.swap(str2);
cout
const char* p = str.c_str();
printf("%s\n",p);
return 0;
}