html元素height(width)是怎么确定的?
2021-05-30 00:04
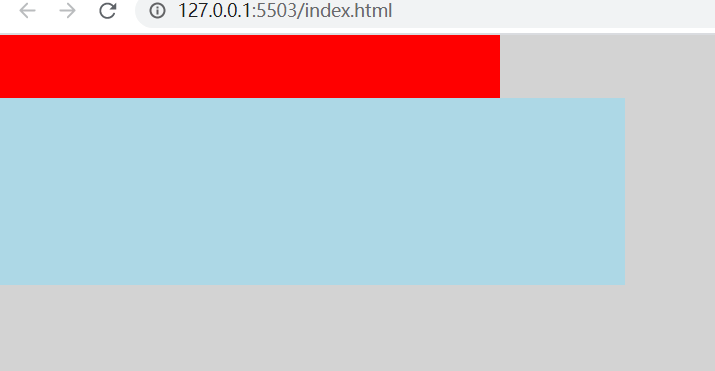
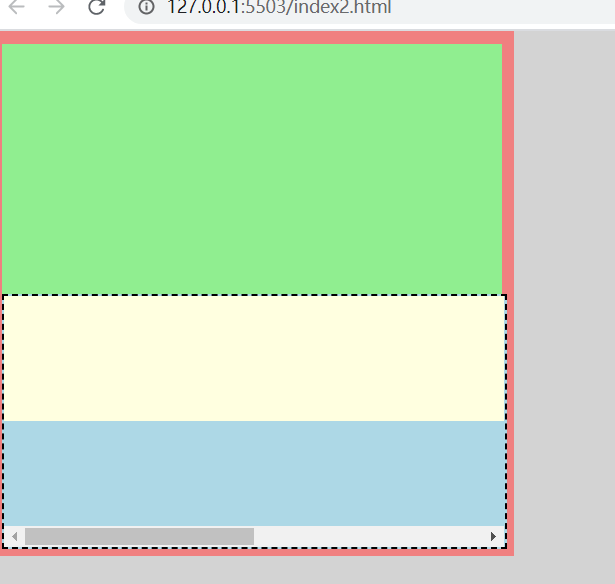
标签:header port log 外部 loading splay png scale 高度 1.若height是确定的(比如height:100px),则height直接可确定(还受min-height,max-height影响,见height,min-height,max-heigth的作用机制问答)。 2.若width是不确定的(比如width: min-content 或 width:100px,min-width:fit-content),此时width受子元素影响 (height:100px,min-height:fit-content时heigth已确定就是100px) 则依次确定每一个子元素的width,如果子元素的width可以由自己确定(比如子元素width写死了或者子元素width为min-content,max-content都能确定)则设置width为子元素width,如果子元素的width不能确定(比如写的width为100%,fit-content等需要确定外部元素高度的属性)则递归计算子元素的width,然后设置父元素width为最大宽度子元素的width,再用这个width去确定子元素中需要使用外部元素宽度来确定本身宽度的宽度。 看几个例子 1.父元素min-height: 100px,子元素height: 100%; 这个情况子元素最终高度为0。 2.父元素width: 0;子元素1 width: 100%;子元素2 width: 100px. 这个情况子元素1最终宽度 100px; 3. 这个例子中,flex-grow: 1; width: 0,这个元素已经确定了width,宽度确定就不会往他的子元素进行了,container元素再确定子元素宽度的时候会认为flex元素的宽度为0。最后的结果就是flex元素的最终宽度就是container的宽度而不会是body元素的宽度。 4. 这个例子body不会出现滚动条,因为container的width需要子元素来确定,body在第一轮计算最大宽度的时候递归到了child里面得出了结果800,就不需要开滚动条了。 要想让body在计算宽度的时候不受child影响,须在递归进入child之前确定body的宽度,办法就是例3里面的使用flex html元素height(width)是怎么确定的? 标签:header port log 外部 loading splay png scale 高度 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/chen8840/p/14699578.htmlDOCTYPE html>
html lang="en">
head>
meta charset="UTF-8">
meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
title>Documenttitle>
style>
html, body {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
background: lightgray;
}
.container {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
min-width: fit-content;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background: red;
}
.body {
width: 500px;
height: 150px;
background: lightblue;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="container">
div class="header">div>
div style="display: flex;height: 100%;">
div style="flex-grow: 1; width: 0">
div class="body">
div>
div>
div>
div>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
html lang="en">
head>
meta charset="UTF-8">
meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
title>Documenttitle>
style>
html, body {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
background: lightgray;
}
.container {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
min-width: fit-content;
padding: 10px;
background: lightcoral;
}
.header {
height: 200px;
background: lightgreen;
}
.body {
height: 200px;
width: 100%;
background: lightblue;
overflow: auto;
}
.child {
width: 800px;
height: 100px;
background: lightyellow;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="container">
div class="header">div>
div class="body">
div class="child">div>
div>
div>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
html lang="en">
head>
meta charset="UTF-8">
meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
title>Documenttitle>
style>
html, body {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
background: lightgray;
}
.container {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
min-width: fit-content;
padding: 10px;
background: lightcoral;
}
.header {
height: 200px;
background: lightgreen;
}
.body {
border: 2px dashed black;
height: 200px;
width: 100%;
background: lightblue;
overflow: auto;
}
.child {
width: 800px;
height: 100px;
background: lightyellow;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="container">
div class="header">div>
div class="flex" style="display: flex;height: 100%;">
div style="flex-grow: 1; width: 0">
div class="body">
div class="child">div>
div>
div>
div>
div>
body>
html>
上一篇:jsp的实现和原理理解
下一篇:动手-文字检测-PSENet
文章标题:html元素height(width)是怎么确定的?
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/89324.html