Spring 事务介绍
2021-06-06 18:05
标签:inf ras 状态 ice hold 没有 jta nat util 接着上篇 数据库事务简介,来聊聊 Spring 事务。 Spring 本身并不实现事务,Spring 事务的本质还是底层数据库对事务的支持,没有数据库事务的支持,Spring 事务就不会生效。 Spring 事务提供了一套抽象的事务管理,并且结合 Spring IOC 和 Spring AOP,简化了应用程序使用数据库事务,并且通过声明式事务,可以做到应用程序无侵入的事务功能。例如使用 JDBC 操作数据库,想要使用事务的步骤为: 而采用了 Spring 事务后,只需要关注第三步的实现即可,其他的步骤都是 Spring 完成。 Spring 事务的本质其实就是 AOP 和 数据库事务,Spring 将数据库的事务操作提取为切面,通过 AOP 的方式增强事务方法。 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:默认,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务;如果当前存在事务,加入到这个事务中。 PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:如果当前没有事务,那么就以非事务的形式执行;如果当前存在事务,加入到这个事务中。 PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:必须在一个事务中执行。如果当前没有事务,则抛出异常;如果当前存在事务,加入到这个事务中。 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务;如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起,新建一个事务。 PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:当前不支持事务。如果当前没有事务,那么就以非事务的形式执行;如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起,以非事务的形式执行。 PROPAGATION_NEVER:不能在事务中执行。如果当前没有事务,那么就以非事务的形式执行;如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。 PROPAGATION_NESTED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务;如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。 我们经常使用的基于 XML 配置或者注解的方式使用的事务方式。 Advice:用于定义拦截行为,祖先接口为 Pointcut:用于定义拦截目标集合,祖先接口为 Advisor:充当 Advice 和 Pointcut 的适配器,一般有 advice 和 pointcut 属性。祖先接口为 Spring 事务把整个事务流程模板化,采用 AOP 的形式增强到需要事务的方法, 因此,调用 Spring 事务方法,就委托给了 TransactionInterceptor 的 invoke 方法。 PlatformTransactionManager 是 Spring 事务结构中的核心接口,Spring 并不直接管理事务,而是提供了多种事务管理器(JDBC、Hibernate、JTA 等),然后将事务管理的职责委托给这些事务管理器。
Spring 事务介绍 标签:inf ras 状态 ice hold 没有 jta nat util 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jmcui/p/14551907.html一、简介
二、Spring 事务传播行为
三、使用 Spring 事务
1. 通过 PlatformTransactionManager使用(不推荐)
@org.junit.Test
public void test1() {
// 默认的事务定义
DefaultTransactionDefinition transactionDefinition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager = SpringUtils.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class);
// 开启事务
TransactionStatus transactionStatus = transactionManager.getTransaction(transactionDefinition);
try {
// do something
} catch (Exception e) {
// 事务回滚
transactionManager.rollback(transactionStatus);
}
// 事务提交
transactionManager.commit(transactionStatus);
}
2. 通过 TransactionTemplate 使用事务
@org.junit.Test
public void test2() {
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager = SpringUtils.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class);
TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate = new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager);
Boolean execute = transactionTemplate.execute(transactionStatus -> {
// do something
return Boolean.TRUE;
});
}
3. 声明式事务
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public OrderDealResultDTO createOrder(OrderCreateParam orderCreateParam) { xxx }
四、实现原理
1. Spring 中的 Advisor,Advice,Point 概述
org.aopalliance.aop.Advice,该接口只是标识接口,应用中可直接实现 BeforeAdvice、ThrowsAdvice、MethodInterceptor、AfterReturningAdvice、IntroductionInterceptor 等子接口。org.springframework.aop.Pointcut。org.springframework.aop.Advisor,应用中可直接使用 org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor。2. BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 就是 Spring 事务的增强方法,其中 Ponintcut 是 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut,Advice 是 TransactionInterceptor。 @Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor());
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx. @Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport‘s invokeWithinTransaction...
// Spring 事务处理逻辑
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
3. PlatformTransactionManager
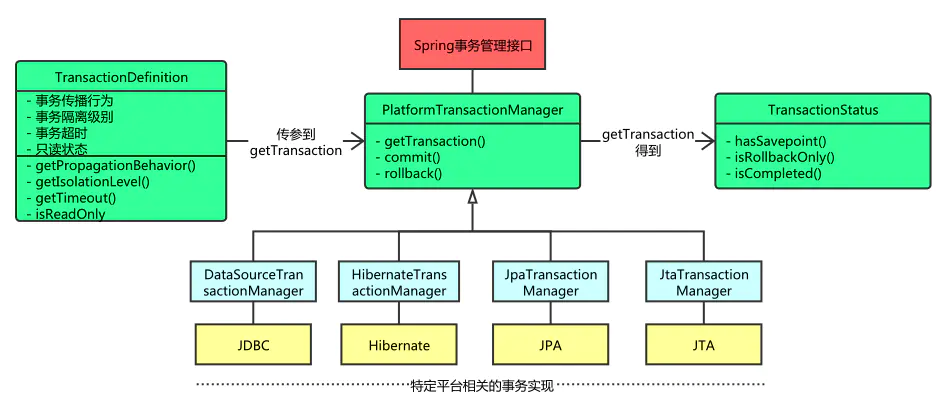
4. org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// 1. 准备事务的基本信息
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 事务定义 TransactionAttribute 是 TransationDefinition 的子类
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 获取事务管理器,根据事务定义指定的事务管理器获取到指定的事务管理器。
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 2. 开启事务
// 如果必要才会开启事务,这里会根据事务的传播能力信息来决定是否开启事务还是加入到一个已经存在的事务,这里会涉及到事务的挂起
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 执行目标方法或者执行 AOP 拦截链中的下一个拦截器
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 3. 事务的回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 清理事务信息
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
// 4. 提交事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
// 省略下文
}
5. 其它
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new TransactionSynchronizationAdapter() {
@Override
public void beforeCommit(boolean readOnly) {
// do something
}
@Override
public void afterCommit() {
// do something
}
});
参考文章: