简单排序--冒泡排序
2021-06-10 18:03
标签:arrays ++ 简单 技术 compareto rabl inf mic com 简单排序--冒泡排序 标签:arrays ++ 简单 技术 compareto rabl inf mic com 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/RealQ/p/14253388.html排序原理:
1. 比较相邻的元素。如果前一个元素比后一个元素大,就交换这两个元素的位置。
2. 对每一对相邻元素做同样的工作,从开始第一对元素到结尾的最后一对元素。最终最后位置的元素就是最大值。
排序过程:
例:{4,5,6,3,2,1}
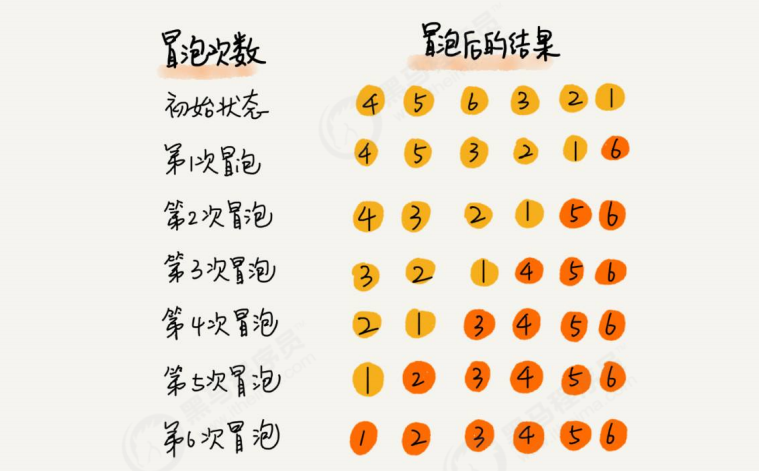
package com.sort;
/*--------------
* Author:Real_Q
* Date:2021-01-06
* Time:10:01
* Description:冒泡排序
* {4,5,6,3,2,1};
---------------*/
public class BubbleSort {
//排序
public static void bubbleSort(Comparable[] comparables) {
//冒泡排序 小------>大
//排序次数 i
for (int i = comparables.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
//比较大小次数及交换次数 i
for (int j = 0; j 0;
}
//交换元素
public static void exchange(Comparable[] comparable, int leftIndex, int rightIndex) {
Comparable temp;
temp = comparable[leftIndex];
comparable[leftIndex] = comparable[rightIndex];
comparable[rightIndex] = temp;
}
}
测试类:
import java.util.Arrays;
import static com.sort.BubbleSort.bubbleSort;
public class TestBubble {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] integers = {4,6,8,7,9,2,10,1};
bubbleSort(integers);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(integers));
}
}
上一篇:c++编译知识