Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:2. 分类数据可视化
2021-06-17 07:06
标签:join hit -- ext ati mat img 一个 折线图 stripplot() / swarmplot() boxplot() / violinplot() / lvplot() barplot() / countplot() / pointplot() Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:2. 分类数据可视化 标签:join hit -- ext ati mat img 一个 折线图 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/shengyang17/p/9704708.html1. 分类数据可视化 - 分类散点图
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
% matplotlib inline
sns.set_style("whitegrid")
sns.set_context("paper")
# 设置风格、尺度
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(‘ignore‘)
# 不发出警告
# 1、stripplot()
# 按照不同类别对样本数据进行分布散点图绘制
tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
print(tips.head())
# 加载数据
sns.stripplot(x="day", # x → 设置分组统计字段
y="total_bill", # y → 数据分布统计字段
# 这里xy数据对调,将会使得散点图横向分布
data=tips, # data → 对应数据
jitter = True, # jitter → 当点数据重合较多时,用该参数做一些调整,也可以设置间距如:jitter = 0.1
size = 5, edgecolor = ‘w‘,linewidth=1,marker = ‘o‘ # 设置点的大小、描边颜色或宽度、点样式
)
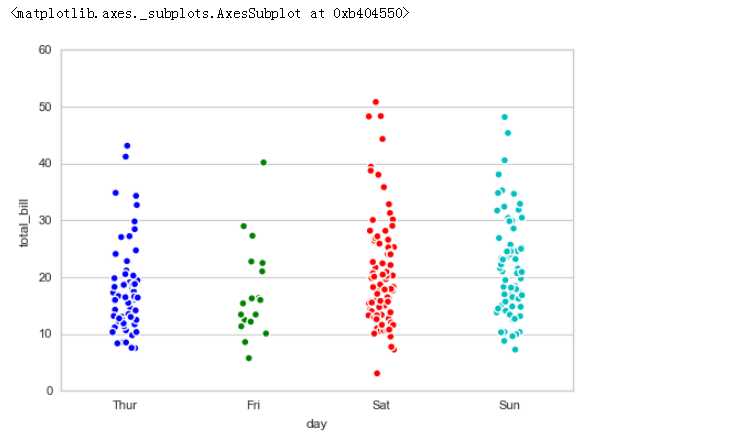
1.1 stripplot()
# 1、stripplot()
# 通过hue参数再分类
sns.stripplot(x="sex", y="total_bill", hue="day",
data=tips, jitter=True)
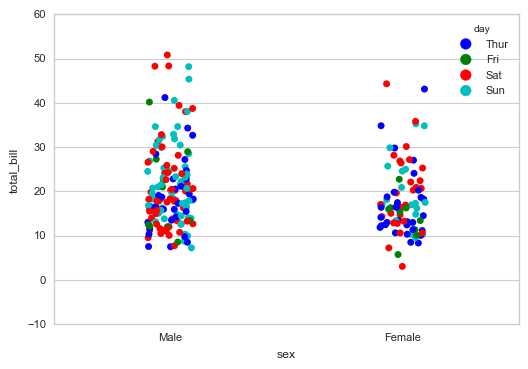
# 1、stripplot()
# 设置调色盘
sns.stripplot(x="sex", y="total_bill", hue="day",
data=tips, jitter=True,
palette="Set2", # 设置调色盘
dodge=True, # 是否拆分
)
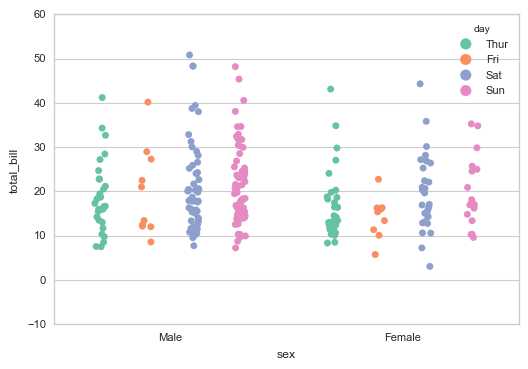
# 1、stripplot()
# 筛选分类类别
print(tips[‘day‘].value_counts())
# 查看day字段的唯一值
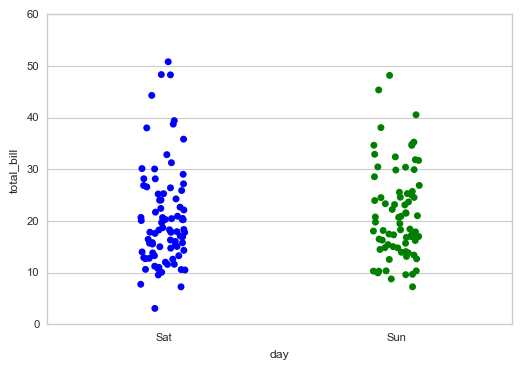
sns.stripplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips,jitter = True,
order = [‘Sat‘,‘Sun‘])
# order → 筛选类别

1.2 swarmplot()
# 2、swarmplot()
# 分簇散点图
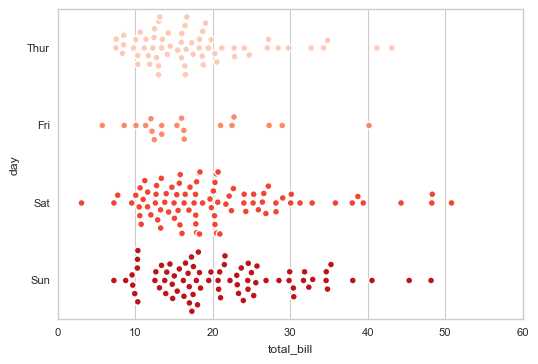
sns.swarmplot(x="total_bill", y="day", data=tips,
size = 5, edgecolor = ‘w‘,linewidth=1,marker = ‘o‘,
palette = ‘Reds‘)
# 用法和stripplot类似
2. 分类数据可视化 - 分布图
2.1 boxplot()箱型图
# 1、boxplot()
# 箱型图
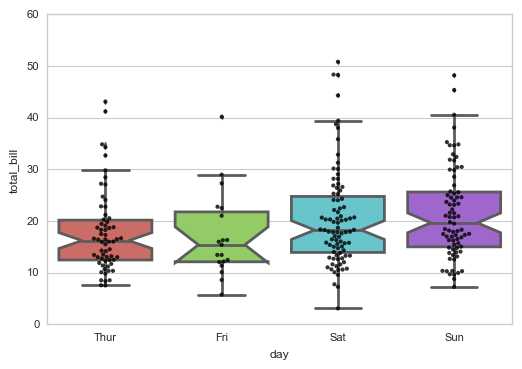
sns.boxplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips,
linewidth = 2, # 线宽
width = 0.8, # 箱之间的间隔比例
fliersize = 3, # 异常点大小
palette = ‘hls‘, # 设置调色板
whis = 1.5, # 设置IQR
notch = True, # 设置是否以中值做凹槽
order = [‘Thur‘,‘Fri‘,‘Sat‘,‘Sun‘], # 筛选类别
)
# 绘制箱型图
sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips,color =‘k‘,size = 3,alpha = 0.8)
# 可以添加散点图
# 1、boxplot()
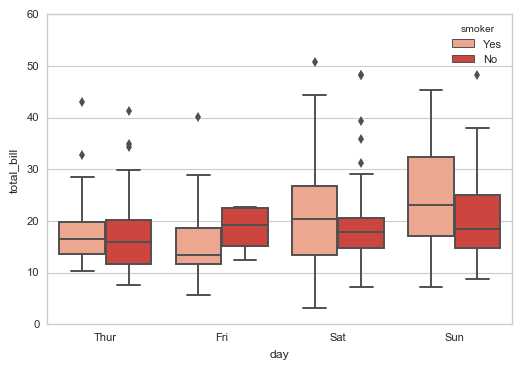
# 通过hue参数再分类
sns.boxplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips,
hue = ‘smoker‘, palette = ‘Reds‘)
# 绘制箱型图
#sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips,color =‘k‘,size = 3,alpha = 0.8)
# 可以添加散点图
2.2 violinplot()小提琴图
# 2、violinplot()
# 小提琴图
sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips,
linewidth = 2, # 线宽
width = 0.8, # 箱之间的间隔比例
palette = ‘hls‘, # 设置调色板
order = [‘Thur‘,‘Fri‘,‘Sat‘,‘Sun‘], # 筛选类别
scale = ‘area‘, # 测度小提琴图的宽度:area-面积相同,count-按照样本数量决定宽度,width-宽度一样
gridsize = 50, # 设置小提琴图边线的平滑度,越高越平滑
inner = ‘box‘, # 设置内部显示类型 → “box”, “quartile”, “point”, “stick”, None
#bw = 0.8 # 控制拟合程度,一般可以不设置
)
# 用法和boxplot类似
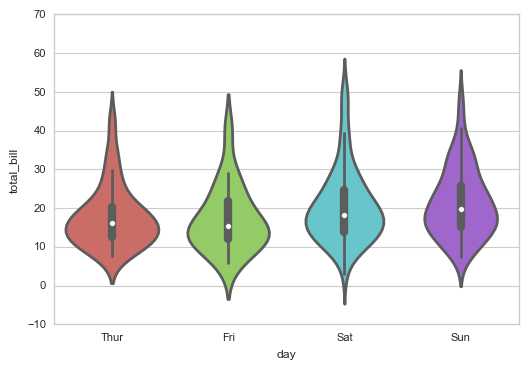
# 2、violinplot()
# 通过hue参数再分类
sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips,
hue = ‘smoker‘, palette="muted",
split=True, # 设置是否拆分小提琴图
inner="quartile")
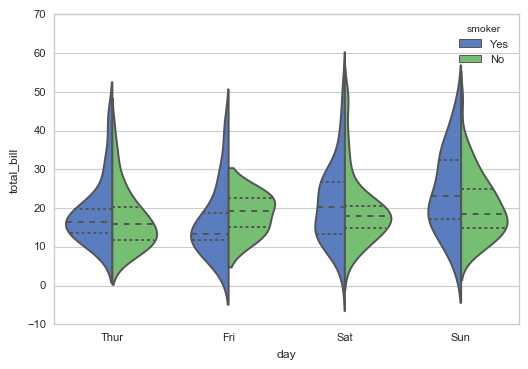
# 2、violinplot()
# 结合散点图
sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, palette = ‘hls‘, inner = None)
sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, color="w", alpha=.5)
# 插入散点图
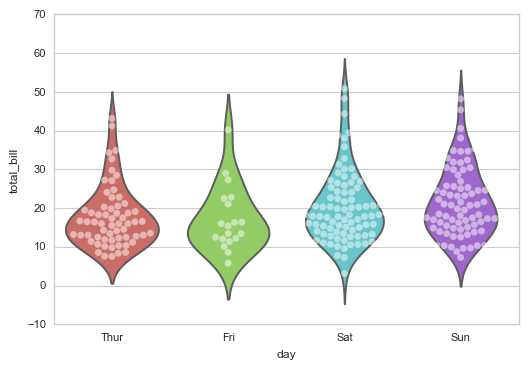
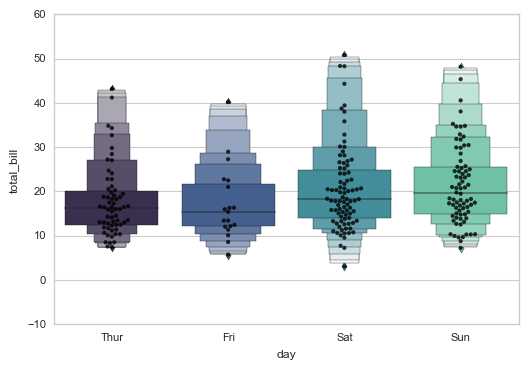
2.3 lvplot() LV图表
# 3、lvplot()
# LV图表
sns.lvplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, palette="mako",
#hue = ‘smoker‘,
width = 0.8, # 箱之间间隔比例
linewidth = 12,
scale = ‘area‘, # 设置框的大小 → “linear”、“exonential”、“area”
k_depth = ‘proportion‘, # 设置框的数量 → “proportion”、“tukey”、“trustworthy”
)
# 绘制LV图
sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips,color =‘k‘,size = 3,alpha = 0.8)
# 可以添加散点图
3. 分类数据可视化 - 统计图
3.1 barplot()
# 1、barplot()
# 柱状图 - 置信区间估计
# 置信区间:样本均值 + 抽样误差
titanic = sns.load_dataset("titanic")
print(titanic.head())
print(‘-----‘)
# 加载数据
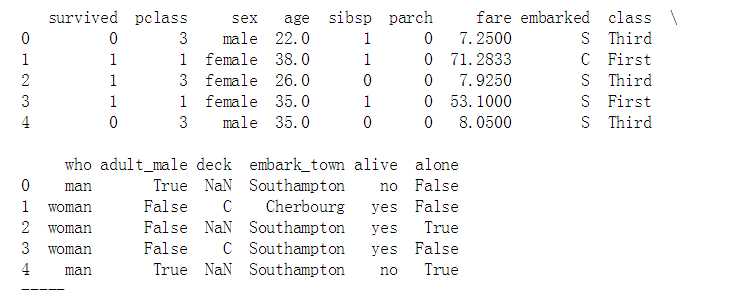
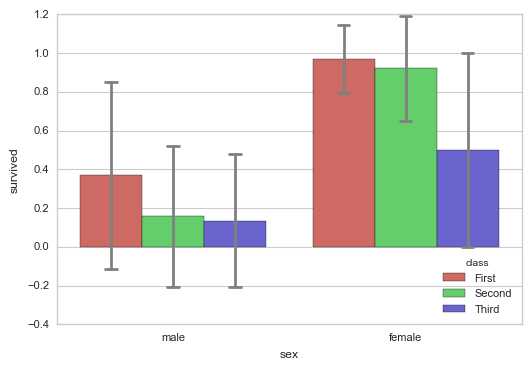
sns.barplot(x="sex", y="survived", hue="class", data=titanic,
palette = ‘hls‘,
order = [‘male‘,‘female‘], # 筛选类别
capsize = 0.05, # 误差线横向延伸宽度
saturation=.8, # 颜色饱和度
errcolor = ‘gray‘,errwidth = 2, # 误差线颜色,宽度
ci = ‘sd‘ # 置信区间误差 → 0-100内值、‘sd‘、None
)
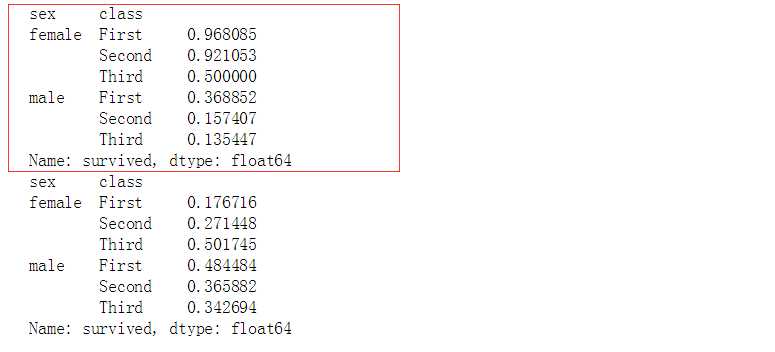
print(titanic.groupby([‘sex‘,‘class‘]).mean()[‘survived‘])
print(titanic.groupby([‘sex‘,‘class‘]).std()[‘survived‘])
# 计算数据
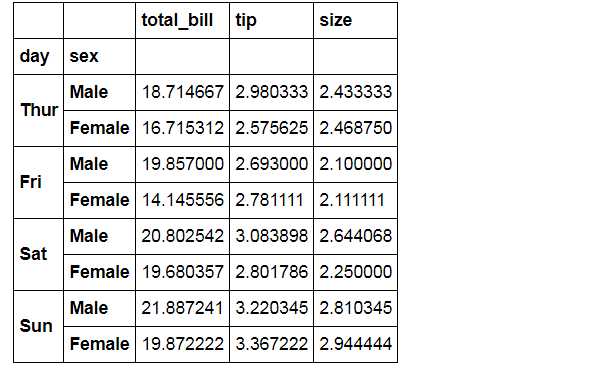
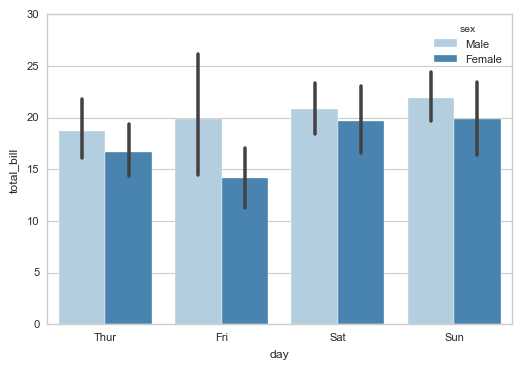
# 1、barplot()
# 柱状图 - 置信区间估计
sns.barplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="sex", data=tips,
palette = ‘Blues‘,edgecolor = ‘w‘)
tips.groupby([‘day‘,‘sex‘]).mean()
# 计算数据
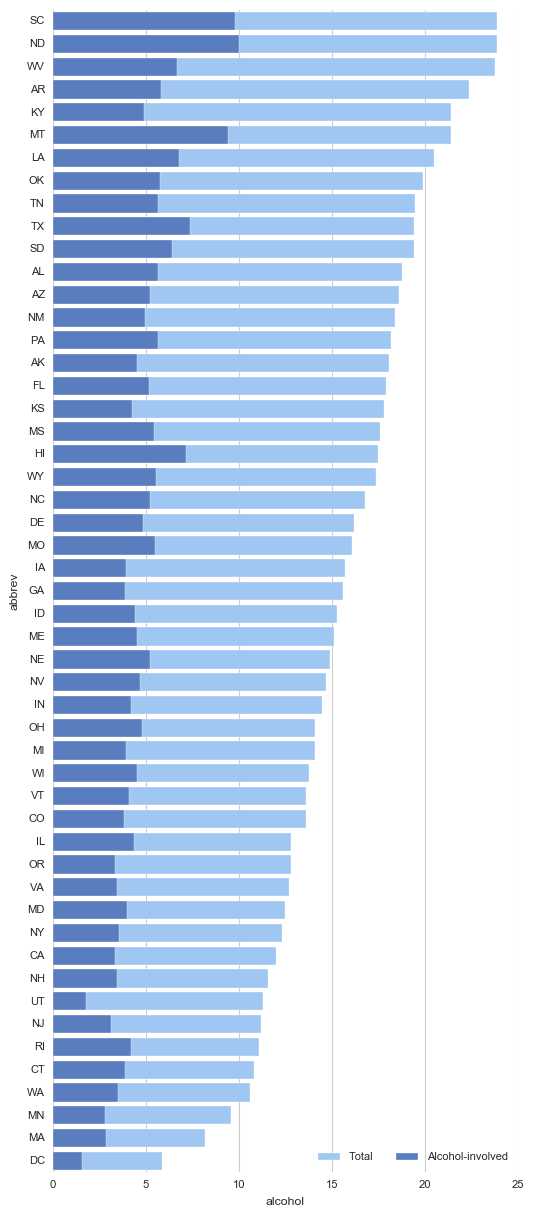
# 1、barplot()
# 柱状图 - 置信区间估计
crashes = sns.load_dataset("car_crashes").sort_values("total", ascending=False)
print(crashes.head())
# 加载数据
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 15))
# 创建图表
sns.set_color_codes("pastel")
sns.barplot(x="total", y="abbrev", data=crashes,
label="Total", color="b",edgecolor = ‘w‘)
# 设置第一个柱状图
sns.set_color_codes("muted")
sns.barplot(x="alcohol", y="abbrev", data=crashes,
label="Alcohol-involved", color="b",edgecolor = ‘w‘)
# 设置第二个柱状图
ax.legend(ncol=2, loc="lower right")
sns.despine(left=True, bottom=True)
3.2 countplot()
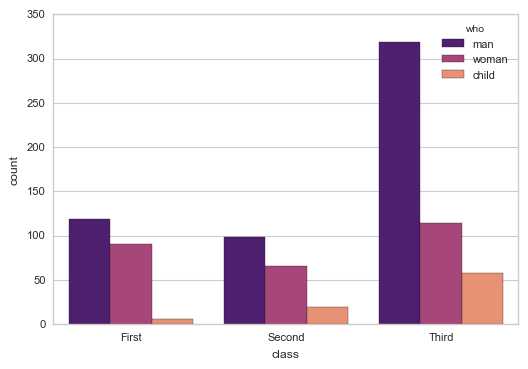
# 2、countplot()
# 计数柱状图
sns.countplot(x="class", hue="who", data=titanic,palette = ‘magma‘)
#sns.countplot(y="class", hue="who", data=titanic,palette = ‘magma‘)
# x/y → 以x或者y轴绘图(横向,竖向)
# 用法和barplot相似
3.3 pointplot()
# 3、pointplot()
# 折线图 - 置信区间估计
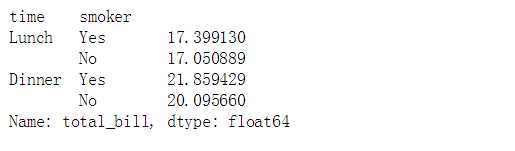
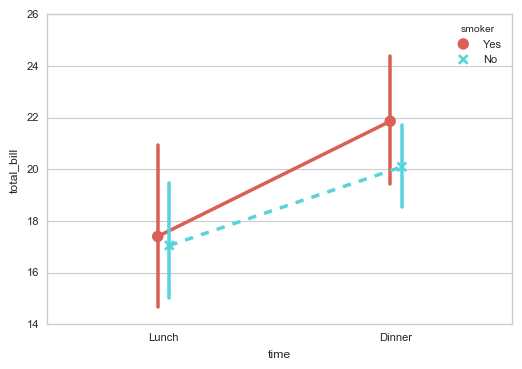
sns.pointplot(x="time", y="total_bill", hue = ‘smoker‘,data=tips,
palette = ‘hls‘,
dodge = True, # 设置点是否分开
join = True, # 是否连线
markers=["o", "x"], linestyles=["-", "--"], # 设置点样式、线型
)
tips.groupby([‘time‘,‘smoker‘]).mean()[‘total_bill‘]
# 计算数据
# # 用法和barplot相似
文章标题:Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:2. 分类数据可视化
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/94938.html