基数排序及其并行化
2021-06-27 08:04
标签:方式 over UNC ax1 nta 最大值 ensure nes .com 基数排序是比较适合并行化的排序算法之一,因为它不需要他的元素和数组当中的其他元素去进行一一对比来决定放的位置。另外还有比较适合并行化的就是双调排序。 以从小到大,一次排序只考虑一位为例。基数排序一般从数据的最低有效位(LSB)开始进行排序,即考察所有的数据的当前位,其当前位为0的数据放到前面,为1的放到后面,当前位具有相同值的就保持上一步的相对位置。处理好之后,处理更高的一位。如此迭代,直至处理完所有位。所有位一般即意味着当前所有数据的最大值的最高位。 网络上有一些典型的错误的并行化,或者说并不是真正高效的利用基数排序特点的并行化。比如这个,这个实现的总体思路就是把数据分段,每段分别用基数排序排好,然后在每次从所有排好序的段中取最小值来合并结果。虽然这样的处理也确实是并行化,但是这样的处理方式并没有有效利用基数排序的特点,这样的处理方式可以说把任意一种排序算法替代每段排序时用到的基数排序都是适用的。 SOF上较好的一个回答。在这里有一个较好的使用pthread实现的版本,其核心函数,每个线程的处理代码如下: 基数排序及其并行化 标签:方式 over UNC ax1 nta 最大值 ensure nes .com 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/willhua/p/9652899.html基数排序原理
基数排序的并行化
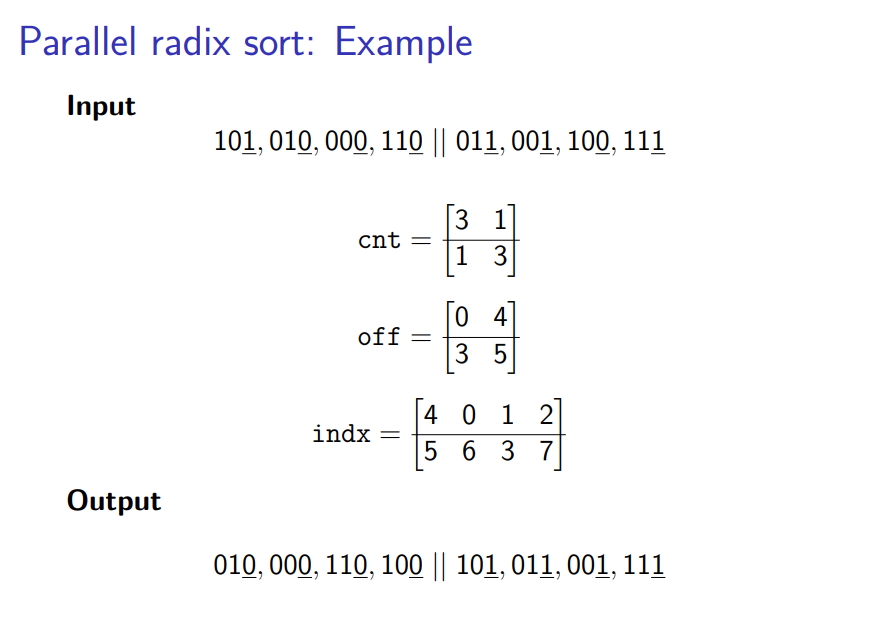
在这个PPT中介绍了基数排序的并行化,其并行化的核心就是计算出每个线程所处理数据中,当前位为0和1的数据,其offset分别为多少,然后基于此计算出本线程中的每个数据在本次迭代中,应该放在整个数据中的哪个位置。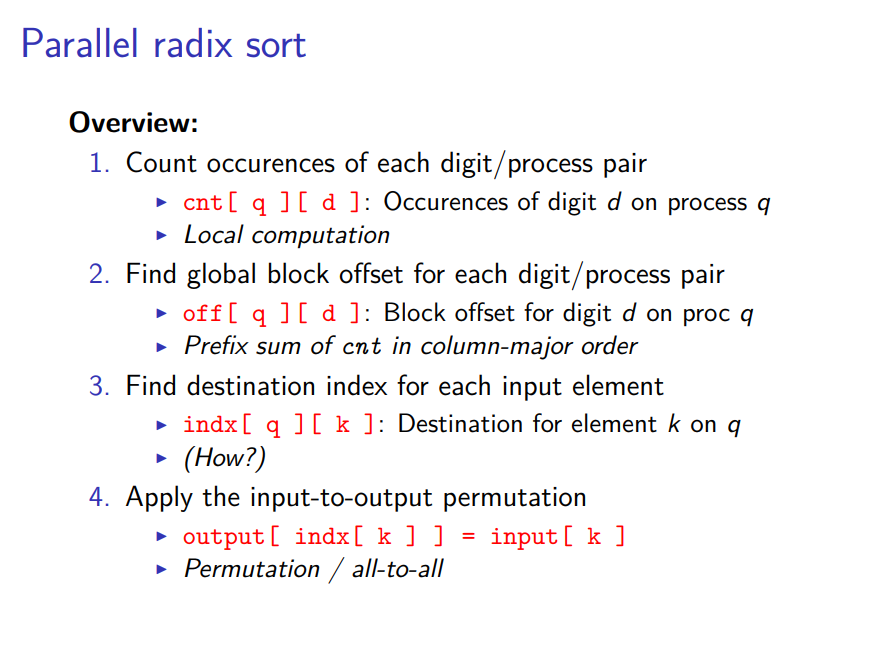
/* Individual thread part of radix sort. */
void radix_sort_thread (unsigned *val, /* Array of values. */
unsigned *tmp, /* Temp array. */
int start, int n, /* Portion of array. */
int *nzeros, int *nones, /* Counters. */
int thread_index, /* My thread index. */
int t) /* Number of theads. */
{
/* THIS ROUTINE WILL REQUIRE SOME SYNCHRONIZATION. */
/* MAYBE A CALL TO barrier() or TWO. */
unsigned *src, *dest;
int bit_pos;
int index0, index1;
int i;
printf("###### Got in main function, thread %d\n", thread_index);
/* Initialize source and destination. */
src = val;
dest = tmp;
/* For each bit... */
for ( bit_pos = 0; bit_pos > bit_pos) & 1) == 0 ) {
nzeros[thread_index]++;
}
}
nones[thread_index] = n - nzeros[thread_index];
/* Ensure all threads have reached this point, and then let continue */
pthread_barrier_wait(&barrier);
/* Get starting indices. */
index0 = 0;
index1 = 0;
for ( i = 0; i > bit_pos) & 1) == 0 ) {
dest[index0++] = src[i];
} else {
dest[index1++] = src[i];
}
}
/* Ensure all threads have reached this point, and then let continue */
pthread_barrier_wait(&barrier);
/* Swap arrays. */
tmp = src;
src = dest;
dest = tmp;
}
printf ("\n====== Printing nzeros array of thread %d\n\n", thread_index);
print_array (nzeros, n);
printf ("\n====== Printing nones array of thread %d\n\n", thread_index);
print_array (nones, n);
// printf ("\n====== Printing val array of thread %d\n\n", thread_index);
// print_array (val, n);
// printf ("\n====== Printing temp array of thread %d\n\n", thread_index);
// print_array (dest, n);
}
上一篇:逻辑回归(分类算法)
下一篇:关于PYTHON课程的小建议