python 实现 wc.exe
2021-06-28 11:06
标签:led 位置 列表 reporting split() else 学习 end 改进 github项目地址:https://github.com/qq1040673290/untitled/blob/master/wc.py WC 项目要求 wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,给出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。 实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。 基本功能列表: wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数 wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目 wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数 扩展功能列表 -s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件 (未实现) -a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行) 高级功能 PSP2.1 Personal Software Process Stages 预估耗时(分钟) 实际耗时(分钟) Planning 计划 · Estimate · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 Development 开发 · Analysis · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) · Design Spec · 生成设计文档 · Design Review · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) · Coding Standard · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) · Design · 具体设计 · Coding · 具体编码 · Code Review · 代码复审 · Test · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) Reporting 报告 · Test Report · 测试报告 · Size Measurement · 计算工作量 · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 合计 通过main()函数里的输入函数获取操作指令和文件参数,再根据指令对文件进行基本功能和拓展功能操作。 基本功能函数: 统计字符数:使用open()和read()函数读取文本内容,用len()统计字符数。 统计行数:使用readlines()把文本以行为单位读取,再用len()统计行数。 统计单词数:使用正则表达式(使用re模块)和split()函数把文本中的非英文字符删除,再用len()统计单词数。 拓展功能函数( -a ): 统计空行、代码行和注释行:使用strip()删去每行文本两端的空格,字符数少于2的即为空行;用starswith()判断每行开头字符是否为‘#’或" ‘‘‘ "来判断注释行。 基本功能函数: 扩展功能函数 -a : main()函数: 测试对象:一个源文件 (1)基础功能: (2)拓展功能 -a : 这次软工作业用的是我刚学不久的python来写的,完成的时间比我预想的要多的多。大量时间都是花费在查找资料和学习一些函数和模块的使用,在编写代码的过程中也出现很多报错,修改代码和测试也成为花时间的主要项目。本次作业中最大的收获就是学会了python中很多对字符串的处理方法和实用的函数,但是对python中的re模块中“正则表达式”的用法还有很多疑问,还要花更多时间去研究学习。 python 实现 wc.exe 标签:led 位置 列表 reporting split() else 学习 end 改进 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/qq1040673290/p/9649092.html
-x 程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。(未实现)PSP
40
60
40
55
600
750
80
110
40
70
30
30
30
30
100
60
180
200
40
30
60
90
60
40
30
40
20
10
20
20
1370
1595
设计思路
代码说明
def getchar(file_name):
f = open(file_name, "r")
return len(f.read())
def getline(file_name):
f = open(file_name, "r")
read = f.readlines()#以行为单位读取文本并存入列表
return len(read)
def getword(file_name):
f = open(file_name, "r")
read = re.split(r‘[^a-zA-Z]+‘,f.read())
return len(read)
def getexpend(file_name):
f = open(file_name, "r")
_line = 0 #记录多行注释位置
line_ = 0
emptyline = 0 #空行
codeline = 0 #代码行
commentline = 0 #注释行
is_comment = False #多行注释标记
comment_sign = 0
read = f.read(). split(‘\n‘)
for line in read:
_line+=1
line= line.strip()
if not is_comment:
if len(line):
emptyline += 1
elif line.startswith(‘#‘): #检索以‘#‘开头的单行注释
commentline += 1
elif line.startswith("‘‘‘") or line.startswith(‘"""‘):
comment_sign += 1
line_=_line
is_comment =True
if comment_sign%2==0 and comment_sign>0:
commentline = commentline + _line - line_
is_comment = False
line_ = _line
else: codeline += 1
print(‘空行数:‘,emptyline)
print(‘代码行数:‘,codeline)
print(‘注释行数:‘,commentline)
def main():
str, name = input(‘输入命令符和文件路径(以空格分开):\n‘).split()
if str==‘-c‘:
print(‘字符数:‘,getchar(name))
elif str==‘-w‘:
print(‘单词数:‘,getword(name))
elif str==‘-l‘:
print(‘行数:‘,getline(name))
elif str==‘-a‘:
getexpend(name)
测试运行

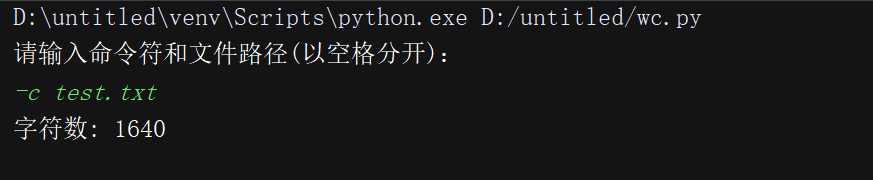
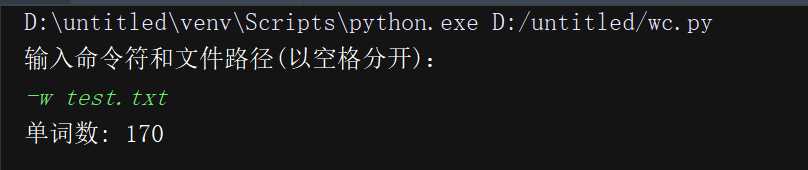
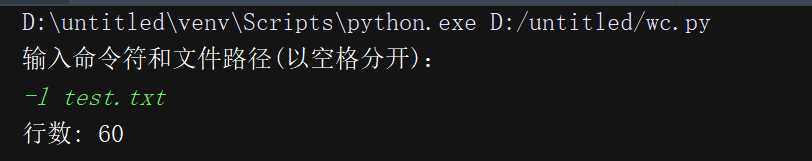
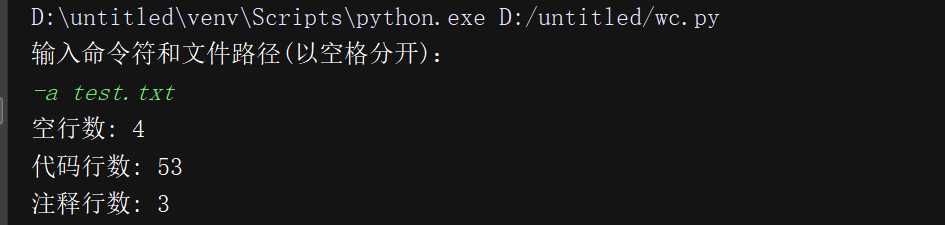
代码覆盖率
项目总结
下一篇:21.Python:指定字符编码