标签:abstract sse this swa erro check parent 成功 efault
集合框架示图
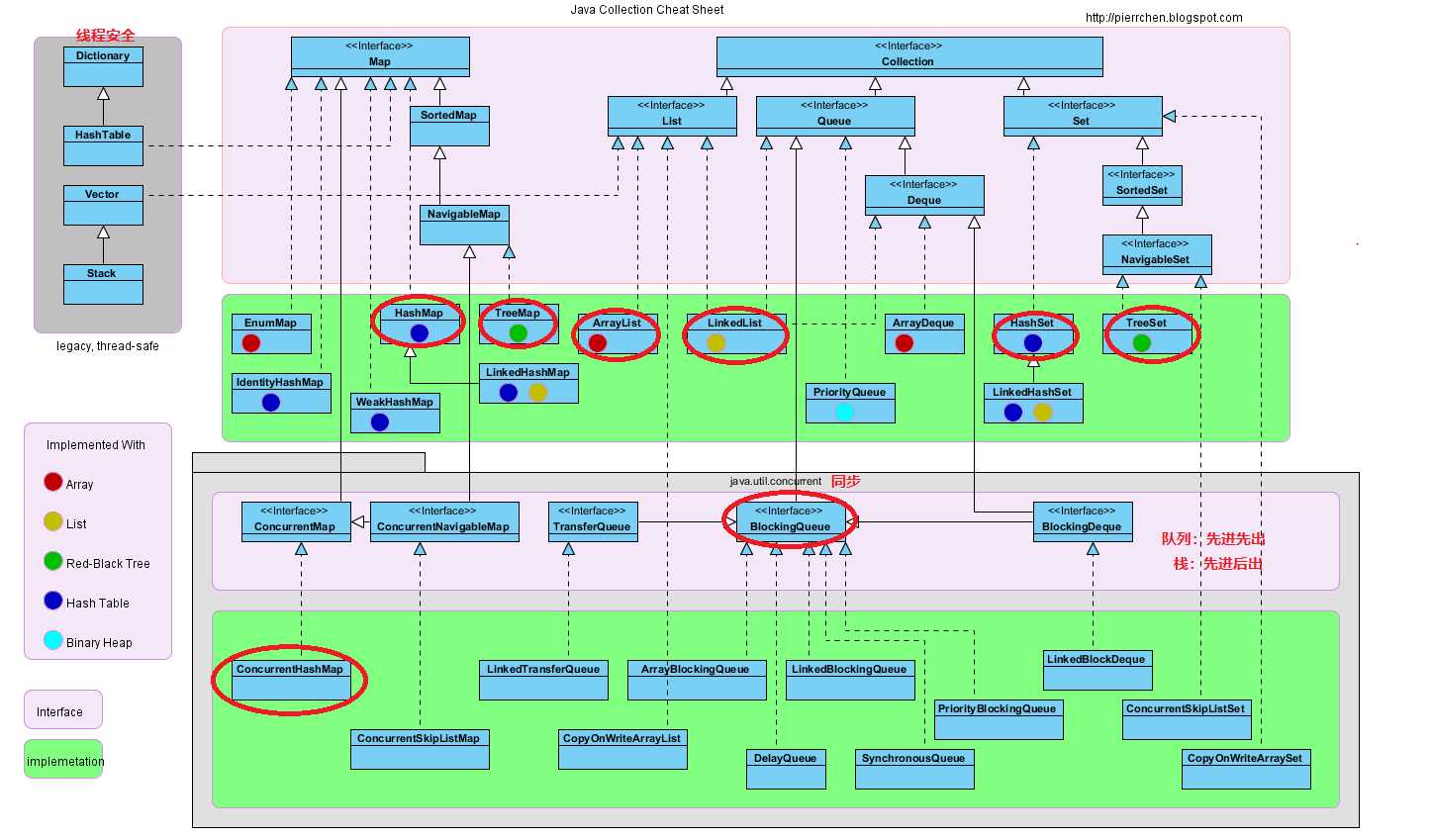
Collection接口和Map接口 方法API介绍
Collection接口:
boolean add(E e) :添加元素到集合中
boolean addAll(Collection extends E> c) : 将指定 collection 中的所有元素都添加到此 collection 中(可选操作)。
void clear() : 移除此 collection 中的所有元素(可选操作)。
boolean contains(Object o) :如果此 collection 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。
boolean containsAll(Collection> c) : 如果此 collection 包含指定 collection 中的所有元素,则返回 true。
boolean equals(Object o) : 比较此 collection 与指定对象是否相等。
int hashCode() :返回此 collection 的哈希码值。
boolean isEmpty() : 如果此 collection 不包含元素,则返回 true。
Iterator
boolean remove(Object o) : 从此 collection 中移除指定元素的单个实例,如果存在的话(可选操作)。
boolean removeAll(Collection> c):移除此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素(可选操作)。
boolean retainAll(Collection> c) :仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素(可选操作)。
int size() :返回此 collection 中的元素数。
Object[] toArray() :返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组。
default Spliterator
default Stream
Map接口:
- void clear() :从此映射中移除所有映射关系(可选操作)。
- boolean containsKey(Object key) :如果此映射包含指定键的映射关系,则返回 true。
- boolean containsValue(Object value) :如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回 true。
- Set> entrySet() :返回此映射中包含的映射关系的 Set 视图。
- boolean equals(Object o) :比较指定的对象与此映射是否相等。
- V get(Object key) :返回指定键所映射的值;如果此映射不包含该键的映射关系,则返回 null。
- int hashCode() :返回此映射的哈希码值。
- boolean isEmpty() :如果此映射未包含键-值映射关系,则返回 true。
- Set
- V put(K key, V value) :将指定的值与此映射中的指定键关联(可选操作)。
- void putAll(Map extends K,? extends V> m) :从指定映射中将所有映射关系复制到此映射中(可选操作)。
- V remove(Object key) :如果存在一个键的映射关系,则将其从此映射中移除(可选操作)。
- int size() :返回此映射中的键-值映射关系数。
常用集合
-
List:ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
-
Map:TreeMap、CurrentHashMap、HashTable
-
Set:HashSet、TreeSet
集合原理详解
List集合
ArrayList
说明:
ArrayList底层基于对象数组来实现,默认的容量是10,超过该容量后会按照原来的1.5倍再加1来去扩容。
特点:查询和更加速度快,删除添加慢,有序排列
构造器:
//对象数组
private transient Object[] elementData;
//默认构造器
public ArrayList() {
this(10); //默认容量为10
}
//指定容量构造器
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity c) {
elementData = c.toArray(); //返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组
size = elementData.length; //得到该数组的长度
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class){
//如果elementData数组不是Object[].class类型,则进行复制操作,返回包含相同元素和长度的Object类型的数组
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
}
add方法:
//元素添加 size:初始化大小是一开始对象数组的长度,记录当前数组长度
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacity(size + 1); //判断是否需要扩容
elementData[size++] = e; //将元素添加到对象数组最后
return true;
}
//将元素添加到指定位置
public void add(int index, E element) {
//如果指定的角标大于或者小于当前对象数组长度,抛出角标越界异常
if (index > size || index oldCapacity) {
Object oldData[] = elementData;
//定义新数组的容量,为原数组容量的1.5倍+1
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;
//如果扩容后还是不够当前对象数组最少应该有的容量值,那么直接用该容量值作为新数组的容量值
if (newCapacity
get方法:
//根据index获取元素
public E get(int index) {
RangeCheck(index); //检查传入的指定下标是否合法
return (E) elementData[index]; //返回数组下标为index的数组元素
}
//判断指定的index是否越界
private void RangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);
}
remove方法:
//移除指定index元素并返回该元素
public E remove(int index) {
RangeCheck(index); //检查index是否越界
modCount++;
E oldValue = (E) elementData[index]; //获取指定index的数组元素
int numMoved = size - index - 1; //要移动的元素个数
if (numMoved > 0)
//参数1:原数组 参数2:原数组初始角标 参数3:目标数组 参数4:目标数组的其实角标 参数5:复制的个数
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); //空出index位置,后面全部元素左移动一位
elementData[--size] = null; //将引用置空,让gc进行回收
return oldValue;
}
//移除指定的元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
//插入的值为null时,移除数组中的null值元素
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index 0)
//空出index位置,后面全部元素左移动一位
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; //将引用置空,让gc进行回收
}
clone方法-浅克隆:
public Object clone() {
try {
ArrayList v = (ArrayList) super.clone(); //调用Object类的clone方法返回一个ArrayList对象
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); //复制目标数组
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn‘t happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError();
}
}
LinkedList
说明:
LinkedList底层基于双向链表实现,可以实现双向链表,双端队列和栈等数据结构
特点:删除添加快,查询和更加速度慢(不支持高效的随机元素访问),有序排列
基本数据结构:
//节点类
//实现双向链表
private static class Node {
E item; //当前节点元素
Node next; //下一个元素
Node prev; //上一个元素
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
//add get remove set方法 均基于该方法
Node node(int index) {
//二分法查找
if (index > 1)) { //左边
Node x = first;
for (int i = 0; i x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
add方法:
transient int size = 0; //当前集合大小
transient Node first; //链头
transient Node last; //链尾
//将元素添加到链头
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
//将元素添加到链尾
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
//将元素添加到链头实现
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node f = first; //获取到链头
//参数1:上一个节点 参数2:当前节点元素 参数3:下一个节点
final Node newNode = new Node(null, e, f);
first = newNode; //将包含当前元素的节点设置为链头
if (f == null)
//如果这是f为null(表示这是集合是第一次添加元素),则当前节点即使链头也是链尾,前后节点都为null
last = newNode;
else
//将新增的节点赋给链头的prev,即代替当前链头成为新的链头
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//将元素添加到链尾实现
private void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last; //获取到链尾
final Node newNode = new Node(l, e, null); //当前节点
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
//如果这是l为null(表示这是集合是第一次添加元素),则当前节点即使链头也是链尾,前后节点都为null
first = newNode;
else
//将新增的节点赋给链尾的next,即代替当前链尾成为新的链尾
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
add方法 - jdk 1.6:
//区别:添加成功返回boolean值
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
get方法:
//根据索引获取 : 二分查找
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
//获取链头
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
//获取链尾
public E getLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
get方法 - jdk 1.6:
区别:如果获取的值为null则返回null不抛异常
public E peekFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
public E peekLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
remove方法:
//移除链头节点并返回链头元素
public E removeFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
//移除链尾节点并返回链尾元素
public E removeLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
//移除链头节点并返回链头元素实现
private E unlinkFirst(Node f) {
final E element = f.item; //获取到链头中的元素对象
final Node next = f.next; //获取到链头的next节点
//置空引入,让gc回收对象
f.item = null;
f.next = null;
//用当前链头的next节点来代替当前链头成为新的链头
first = next;
//next为null表示当前几个只有一个元素,即上下节点都为null
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//移除链尾节点并返回链尾元素实现
private E unlinkLast(Node l) {
final E element = l.item;
final Node prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
remove方法 - jdk 1.6:
区别:不抛异常返回null
public E pollFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E pollLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
LinkedList实现Stack:
//jdk 1.6
public E pollFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
//jdk 1.6
public E pollLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
Vector
说明:
Vector是jdk 1.0的容器,和ArrayList一样基于对象数组,初始容量同样默认为10,但不同的是扩容时会增加为原来的2倍,且每个方法都使用synchronize修饰,是一个同步的线程安全的容器
特点:使用Enumeration遍历元素,有序排列
Map集合
HashMap 基于JDK 1.8
说明:
HashMap底层基于哈希表来实现(在Java中哈希表通过数组+链表来实现,称链表散列或拉链法)也称作关联数组,不记录元素插入顺序,默认的容量是16,扩容按照2的n次幂递增,但不能超过1
数据结构实现图解(JDK 1.8):
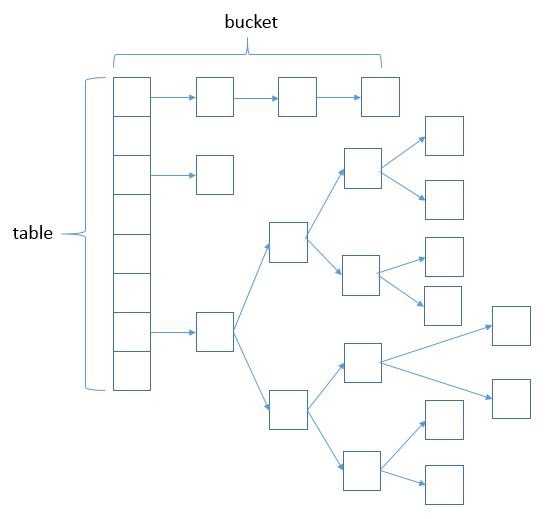
基本数据结构:
//单向链表节点
static class Node implements Map.Entry {
final int hash; //当前节点Hash值
final K key; //当前节点key值
V value; //当前节点value值
Node next; //当前节点的next节点
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry,?> e = (Map.Entry,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
//红黑树节点
static final class TreeNode extends LinkedHashMap.Entry {
TreeNode parent; //父亲节点
TreeNode left; //左子节点
TreeNode right; //右子节点
TreeNode prev; //上一个节点
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
/**
* 返回root节点
*/
final TreeNode root() {
for (TreeNode r = this, p;;) {
if ((p = r.parent) == null) //当一个节点没有父节点时该节点就是root节点
return r;
r = p;
}
}
/**
* Ensures that the given root is the first node of its bin.
*/
static void moveRootToFront(Node[] tab, TreeNode root) {
int n;
if (root != null && tab != null && (n = tab.length) > 0) {
int index = (n - 1) & root.hash;
TreeNode first = (TreeNode)tab[index];
if (root != first) {
Node rn;
tab[index] = root;
TreeNode rp = root.prev;
if ((rn = root.next) != null)
((TreeNode)rn).prev = rp;
if (rp != null)
rp.next = rn;
if (first != null)
first.prev = root;
root.next = first;
root.prev = null;
}
assert checkInvariants(root);
}
}
//重置数组长度
final Node[] resize() {
//旧数组
Node[] oldTab = table;
//获取就数组的长度
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
//获取初始化阈值
int oldThr = threshold;
//初始化新容量和新阈值 往后给新数组用
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
//就数组长度大于最大值限制时
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap [] newTab = (Node[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
//将旧数组元素复制到新数组中
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
几个重要的属性:
//默认容量值
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 数组
transient Node[] table;
//Map.Entry的Set集合
transient Set> entrySet;
//元素个数
transient int size;
//由链表转换成树的阈值(又叫临界值,是指一个效应能够产生的最低值或最高值)
//当桶中bin的数量【超过】TREEIFY_THRESHOLD时使用树来代替链表。默认值是8
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
//由树转换成链表的阈值
//当执行resize操作时,当桶中bin的数量【少于】UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD时使用链表来代替树。默认值是6
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
//当桶中的bin被树化时最小的hash表容量
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
构造器:
//默认构造器
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
//指定容量构造器
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
//指定初始化容量和加载因子构造器
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
//初始化容量值少于0,抛异常
if (initialCapacity MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
//初始化加载因子小于或者等于0时,又或者不是一个数字时,抛异常
if (loadFactor m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
put方法:
//存入键值对
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
Node[] tab;
Node p;
int n, i;
/** 当Node[] table为空时
> 当前节点数组 tab = table
> 当前节点数组的长度 n = tab.length
*/
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
/** 存储key-value的时候是以 (n - 1) & hash 作为节点数组的角标来存储的
> hash:当前插入key值的hashCode
> (n - 1):当前节点数组的最大角标
*/
//如果添加的这个key在table对应的位置没有值,直接创建一个新节点添加到Node[] table中
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
/**
在当前Node[] table中有对应 (n - 1) & hash 作为节点数组的角标值时(值是节点)
*/
else {
Node e;
K k;
//如果已经存在一样的key,那么就覆盖该key
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //如果是节点数
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) //当桶中bin的数量【超过】TREEIFY_THRESHOLD时使用树来代替链表
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
get方法:
//获取对应key的value
public V get(Object key) {
Node e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node[] tab;
Node first, e;
int n;
K k;
//容器必须有元素才能操作,否则返回null
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//如果first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]就是要获取的节点,直接返回
if (first.hash == hash && ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
//如果当前节点有下一个节点的信息
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
//如果当前节点是节点树形式存储的节点,调用节点数节点获取方法获取
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null); //链表遍历获取
}
}
return null;
}
get方法:
//移除指定key的value
public V remove(Object key) {
Node e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
final Node removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node[] tab;
Node p;
int n, index;
//容器必须有元素才能操作,否则返回null
//当前数组长度:n = tab.length
//该key的节点位于数组的位置的角标: index = (n - 1) & hash
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node node = null, e;
K k;
V v;
//如果p = tab[(n - 1) & hash]就是要获取的节点,直接复制给node变量
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
//如果p = tab[(n - 1) & hash]不是要找的节点,那么循环查找
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
//如果该节点是节点树的节点,那么调用节点树查找方法获取node节点
if (p instanceof TreeNode) node = ((TreeNode)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
//如果遍历到了该key的节点
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e; //记录主 key对应节点的上一个节点
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//node != null表示经过上面的代码后找到了该key的节点
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
//如果该节点是节点树的节点,那么调用节点树移除方法移除节点
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
//p是node节点的上一个节点
p.next = node.next; //将要删除的节点的next赋值给上一个节点的next
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
clear方法:
public void clear() {
Node[] tab;
modCount++;
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
size = 0;
//循环将引用置空,让gc回收
for (int i = 0; i
entrySet方法:
//依Set>形式返回Node[] table数组
public Set> entrySet() {
Set> es;
return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es;
}
final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); }
//返回迭代器
public final Iterator> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}
public final boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry,?> e = (Map.Entry,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Node candidate = getNode(hash(key), key);
return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
}
//移除节点
public final boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry,?> e = (Map.Entry,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Object value = e.getValue();
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
}
return false;
}
public final Spliterator> spliterator() {
return new EntrySpliterator(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer super Map.Entry> action) {
Node[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e);
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
TreeMap
说明:
TreeMap底层基红黑树来实现,查看“键”或“键值对”时,它们会被排序(次序由Comparable或Comparator决定)。TreeMap的特点在于,所得到的结果是经过排序的。
TreeMap是唯一的带有subMap()方法的Map,它可以返回一个子树
特点:key不能为null,value可以,自然排序或比较器排序
红黑树基本介绍:
示意图:
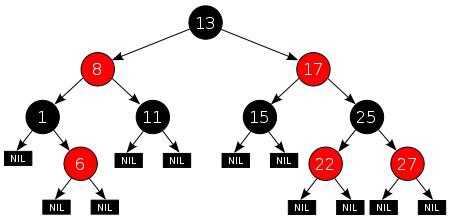
红黑树需要满足的条件:
每个节点不是红色就是黑色的;
根节点总是黑色的;
如果节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的(反之不一定);
-
从根节点到叶节点或空子节点的每条路径,必须包含相同数目的黑色节点(即相同的黑色高度);
在红-黑树中插入的节点都是红色的,这不是偶然的,因为插入一个红色节点比插入一个黑色节点违背红-黑规则的可能性更小。
原因是:插入黑色节点总会改变黑色高度(违背规则4),但是插入红色节点只有一半的机会会违背规则3。
另外违背规则3比违背规则4要更容易修正
以上红黑树数据结构理解来自:http://blog.csdn.net/eson_15/article/details/51144079
基本数据结构:
static final class Entry implements Map.Entry {
K key; //key值
V value; //value值
Entry left; //左子节点
Entry right; //右子节点
Entry parent; //父节点
boolean color = BLACK; //黑色,注意:红黑树很节点必须为黑色
Entry(K key, V value, Entry parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public V setValue(V value) {
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry,?> e = (Map.Entry,?>)o;
return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue());
}
public int hashCode() {
int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode());
int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
return keyHash ^ valueHash;
}
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
//左旋
private void rotateLeft(Entry p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry r = p.right;
p.right = r.left;
if (r.left != null)
r.left.parent = p;
r.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = r;
else if (p.parent.left == p)
p.parent.left = r;
else
p.parent.right = r;
r.left = p;
p.parent = r;
}
}
//右旋
private void rotateRight(Entry p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry l = p.left;
p.left = l.right;
if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p;
l.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = l;
else if (p.parent.right == p)
p.parent.right = l;
else p.parent.left = l;
l.right = p;
p.parent = l;
}
}
//插入变色
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry x) {
x.color = RED;
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
Entry y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
} else {
Entry y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
root.color = BLACK;
}
//删除变色
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry x) {
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
Entry sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateRight(sib);
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
} else { // symmetric
Entry sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateLeft(sib);
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK);
}
几个重要的属性:
//比较器,排序使用
private final Comparator super K> comparator;
//根节点
private transient Entry root;
//节点数
private transient int size = 0;
//修改标记
private transient int modCount = 0;
构造器:
//默认构造器
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
//带有比较器的构造器
public TreeMap(Comparator super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
//使用一个map集合创建一个TreeMap 构造器
public TreeMap(Map extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null; //无比较器
putAll(m);
}
//使用一个SortedMap集合创建一个TreeMap 构造器
public TreeMap(SortedMap m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
put方法:
//比较排序
final int compare(Object k1, Object k2) {
return comparator==null ? ((Comparable super K>)k1).compareTo((K)k2) : comparator.compare((K)k1, (K)k2);
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry t = root; //获取根节点
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
//如果root为空,将第一个put如的key-value节点作为根节点
root = new Entry(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry parent;
//获取比较器
Comparator super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
//循环找位置将节点设入去
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp 0) //放右边
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value); //替换
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable super K> k = (Comparable super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry e = new Entry(key, value, parent);
if (cmp
get方法:
//获取到指定key的节点
public V get(Object key) {
Entry p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
//获取到指定key的节点实现
final Entry getEntry(Object key) {
//有比较器的时候
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
//key为null的时候抛异常
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable super K> k = (Comparable super K>) key; //向上转型
Entry p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp 0)
p = p.right; //k等于p.key,即找到该节点
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
final Entry getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
Entry p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
if (cmp 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p; //k等于p.key,即找到该节点
}
}
return null;
}
remove方法:
//移除指定的节点对象
public boolean remove(Object o) {
//当o不是Map.Entry的实例就返回false
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
//将o转为强转成Map.Entry对象
Map.Entry,?> entry = (Map.Entry,?>) o;
//获取该对象的值
Object value = entry.getValue();
//根据该对象的key值从红黑树中获取到对应的红黑树节点
Entry p = getEntry(entry.getKey());
/*
对比传进来的这个对象的value,和利用该对象的key在红黑树中获得的节点的value进行对比
如果相同,证明确实有这个节点,那么就记性删除,否者但会false
*/
if (p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value)) {
deleteEntry(p);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//移除指定key的节点对象,并返回移除了的节点的value值
public V remove(Object key) {
//根据key在红黑树总查找到对应的节点
Entry p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p); //删除节点
return oldValue;
}
//获取红黑树节点中指定key的节点
final Entry getEntry(Object key) {
//当有自定义比较器的时候
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//将key强转成Comparable实例,这就是为什么TreeMap要么传入比较器,要么实现Comparable的原因
Comparable super K> k = (Comparable super K>) key;
//获取红黑树的根节点
Entry p = root;
//遍历红黑树来获取当前key的节点
while (p != null) {
//从根节点开始查找
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
//删除指定节点实现,注意:是要删除的节点
private void deleteEntry(Entry p) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
}
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
Entry replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
//如果当前是左节点,利用父节点来移除自己
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
//如果当前是右节点,利用父节点来移除自己
p.parent.right = null;
//移除父节点
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
HashTable
说明:
基于散列(数组+链表)实现,操作方法都被synchronize修饰,所以是线程安全的容器
特点:key不能为null,value不能为null,使用Enumeration遍历
和HashMap的基本对比:
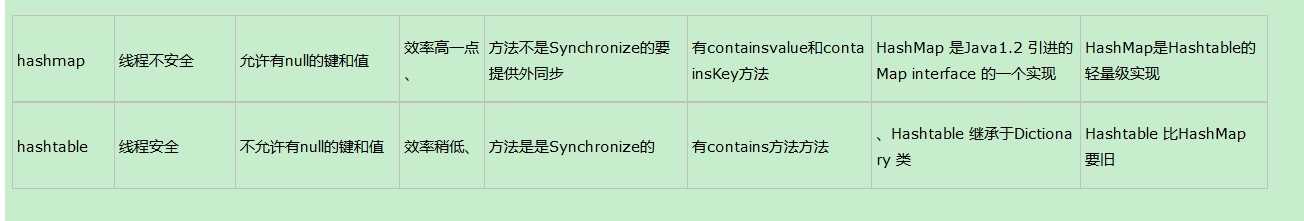
ConcurrentHashTable
说明:
可以高效地支持并发操作,开源框架Spring的底层数据结构就是使用ConcurrentHashMap实现的;
与同是线程安全的老大哥HashTable相比,它已经更胜一筹,因此它的锁更加细化,而不是像HashTable一样为几乎每个方法都添加了synchronized锁,这样的锁无疑会影响到性能;
JDK8的版本,与JDK6的版本有很大的差异。实现线程安全的思想也已经完全变了,它摒弃了Segment(锁段)的概念,
而是启用了一种全新的方式实现,利用CAS算法,它沿用了与它同时期的HashMap版本的思想,底层依然由“数组”+链表+红黑树的方式思想,
但是为了做到并发,又增加了很多辅助的类,例如TreeBin,Traverser等对象内部类。
注意:ConcurrentHashMap不允许key或value为null值
Set集合
HashSet
说明:
基于HashMap实现(散列),所以可以得出结论,值不能为重复,但可以为null,重复会被覆盖
TreeSet
说明:
基于TreeMap实现,元素的顺序取决于元素自身的自然顺序或者在构造时提供的比较器
注意:TreeMap的key不能为null,所以TreeSet的元素不能为null
Java集合框架浅析
标签:abstract sse this swa erro check parent 成功 efault
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/tandi19960505/p/9642322.html



