C# 单例模式
2021-06-30 19:07
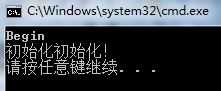
标签:etc 创建 解决方法 opera app new 初始化 tps int 一、多线程不安全方式实现 sealed表示SingleInstance不能被继承。其实构造函数私有化已经达到了这个效果,私有的构造函数不能被继承。为了可读性,可以加个sealed。 不安全的单例指的是在多线程环境下可能有多个线程同时进入if语句,创建了多次单例对象。 二、安全的单例模式 加锁保护,在多线程下可以确保实例值被创建一次。缺点是每次获取单例,都要进行判断,涉及到的锁和解锁比较耗资源。 三、只读属性式 借助readonly属性,instance只被初始化一次,同样达到了单例的效果。在Main函数执行第一句话之前,instance其实已经被赋值了,并不是预期的 只有到访问Instance变量时才创建对象。 如下代码: 输出: 在执行第一句代码之前,实例已经被初始化。 解决方法是在SingleInstance中加上静态构造函数。 在运行输出: 四、使用Lazy Lazy默认是线程安全的。MSDN描述如下: Will the lazily initialized object be accessed from more than one thread? If so, the Lazy 五、泛型单例 https://www.cnblogs.com/lh218/p/4713599.html C# 单例模式 标签:etc 创建 解决方法 opera app new 初始化 tps int 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/asdyzh/p/9968858.html
public sealed class SingleInstance
{
private static SingleInstance instance;
private SingleInstance() { }
public static SingleInstance Instance
{
get
{
if (null == instance)
{
instance = new SingleInstance();
}
return instance;
}
}
}
public sealed class SingleInstance
{
private static volatile SingleInstance instance;
private static readonly object obj = new object();
private SingleInstance() { }
public static SingleInstance Instance
{
get
{
if (null == instance)
{
lock (obj)
{
if (null == instance)
{
instance = new SingleInstance();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
}
public sealed class SingleInstance
{
private static readonly SingleInstance instance = new SingleInstance();
private SingleInstance() { }
public static SingleInstance Instance
{
get
{
return instance;
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin");
var temp = SingleInstance.instance; ;
}
}
public sealed class SingleInstance
{
public static readonly SingleInstance instance = new SingleInstance();
private SingleInstance()
{
Console.WriteLine("初始化初始化!");
}
public static SingleInstance Instance
{
get { return instance; }
}
}
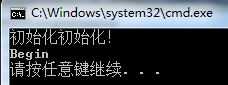
public sealed class SingleInstance
{
public static readonly SingleInstance instance = new SingleInstance();
static SingleInstance() { }
private SingleInstance()
{
Console.WriteLine("初始化初始化!");
}
public static SingleInstance Instance
{
get { return instance; }
}
}
public sealed class SingleInstance
{
private static readonly Lazynew Lazynew SingleInstance());
private SingleInstance(){}
public static SingleInstance Instance
{
get
{
return instance.Value;
}
}
}
class Program
{ static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin");
mySingle.Instance.age = 500;
Console.WriteLine(mySingle.Instance.age);
}
}public abstract class SingleInstance
{ private static readonly Lazynew Lazy
{
var ctors = typeof(T).GetConstructors(BindingFlags.Instance| BindingFlags.NonPublic| BindingFlags.Public);
if (ctors.Count() != 1)
throw new InvalidOperationException(String.Format("Type {0} must have exactly one constructor.", typeof(T)));
var ctor = ctors.SingleOrDefault(c => c.GetParameters().Count() == 0 && c.IsPrivate);
if (ctor == null)
throw new InvalidOperationException(String.Format("The constructor for {0} must be private and take no parameters.", typeof(T)));
return (T)ctor.Invoke(null);
});
public static T Instance
{
get{ return _instance.Value;}
}
}public class mySingle : SingleInstance
{ private mySingle() { }
public int age;
}