Java设计模式之Iterator
2020-12-13 01:34
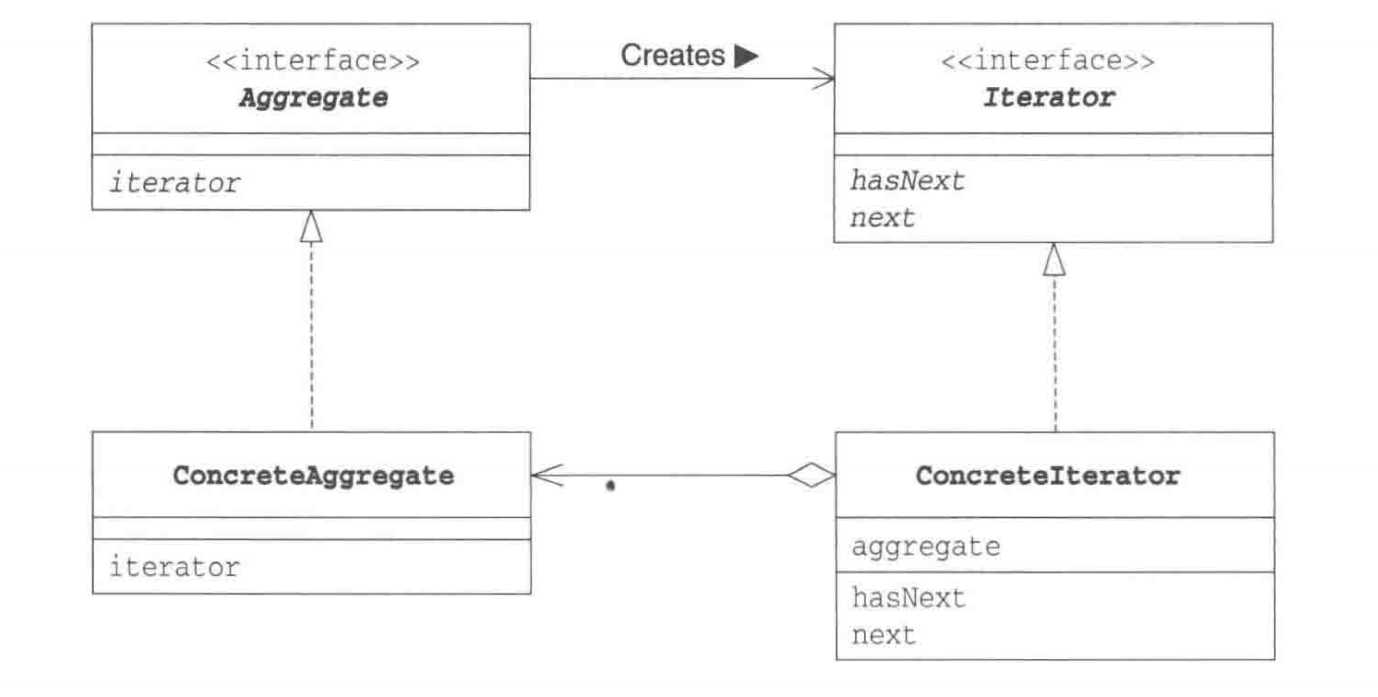
标签:this get 适用于 class 元素 void abs 停止 imp Java设计模式之Iterator 标签:this get 适用于 class 元素 void abs 停止 imp 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/gegelaopiaoke/p/11002244.htmlpublic interface Aggregate {
//调用iterator方法生成实现Iterator接口的类的实例
public abstract Iterator iterator();
}
public interface Iterator {
//判断是否存在下个元素的hasNext方法和获取下一个元素的next方法
//hasNext返回boolean类型,因为存在下一个元素的时候返回true,不存在的时候即遍历至集合末尾,返回false
public abstract boolean hasNext();
//返回类型为Object,表明返回的是集合的一个元素,这方法还隐含着将迭代器移动至下一个元素处理。
//隐含是因为Iterator接口只知道方法名,想知道next到底做了什么处理,还需要看实现了Iterator接口的类才能看懂作用
public abstract Object next();
}
public class Book {
private final String name;
public Book(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//通过getName方法获取书的名字,书的名字是外部调用Book类的构造函数并初始化Book类时作为参数传递给Book类
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
//集合处理该类,实现了Aggregate接口和他的iterator方法
public class BookShelf implements Aggregate{
//定义了books字段,他是Book的数组,数组大小在生成BookShelf的实例的时候被指定
//之所以把books字段设置为private就是为了防止被外部改变
private final Book[] books;
private int last = 0;
public BookShelf(int maxsize) {
this.books = new Book[maxsize];
}
public Book getBookAt(int index) {
return books[index];
}
public void appendBooke(Book book) {
this.books[last] = book;
last++;
}
public int getLength() {
return last;
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new BookShelfIterator(this);
}
}
//因为需要发挥Iterator的作用,所以实现了该接口
public class BookShelfIterator implements Iterator {
//bookShelf字段表示BookShelfIterator所要遍历的暑假,index字段表示迭代器当前所指向书的下标
//构造函数会将接收到的BookShelf实例保存在bookShelf字段中,并将index初始化为0
private final BookShelf bookShelf;
private int index;
public BookShelfIterator(BookShelf bookShelf) {
this.bookShelf = bookShelf;
this.index = 0;
}
@Override
//hasNext方法是Iterator接口中声明的方法,该方法会判断有没有下一本书,悠久返回ture,没有就返回false。
//判断有没有下一本书,只需要比较index和书架中书的总册数(bookShelf.getLength()的返回值)来判断
public boolean hasNext() {
return index bookShelf.getLength();
}
/**
*
* @return
*/
@Override
//next方法会返回迭代器当前所指向的书(Book的实例)。并让迭代器指向下一位本书。先取出book变量做返回值,然后让index指向后面一本书
public Object next() {
Book book = bookShelf.getBookAt(index);
index++;
return book;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//bookShelf.iterator()得到的it适用于遍历书架的Iterator实例,while部分的条件是it.hasNext(),只要书架上有书就不会停止。程序通过it.hasNext()一本本遍历
BookShelf bookShelf = new BookShelf(4);
bookShelf.appendBooke(new Book("Around the World in 80 Days"));
bookShelf.appendBooke(new Book("Bible"));
bookShelf.appendBooke(new Book("Cinderella"));
bookShelf.appendBooke(new Book("Daddy-Long-Legs"));
Iterator it = bookShelf.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Book book = (Book) it.next();
System.out.println(book.getName());
}
}
}