Java IO(三)--输入流和输出流简介
2020-12-13 02:43
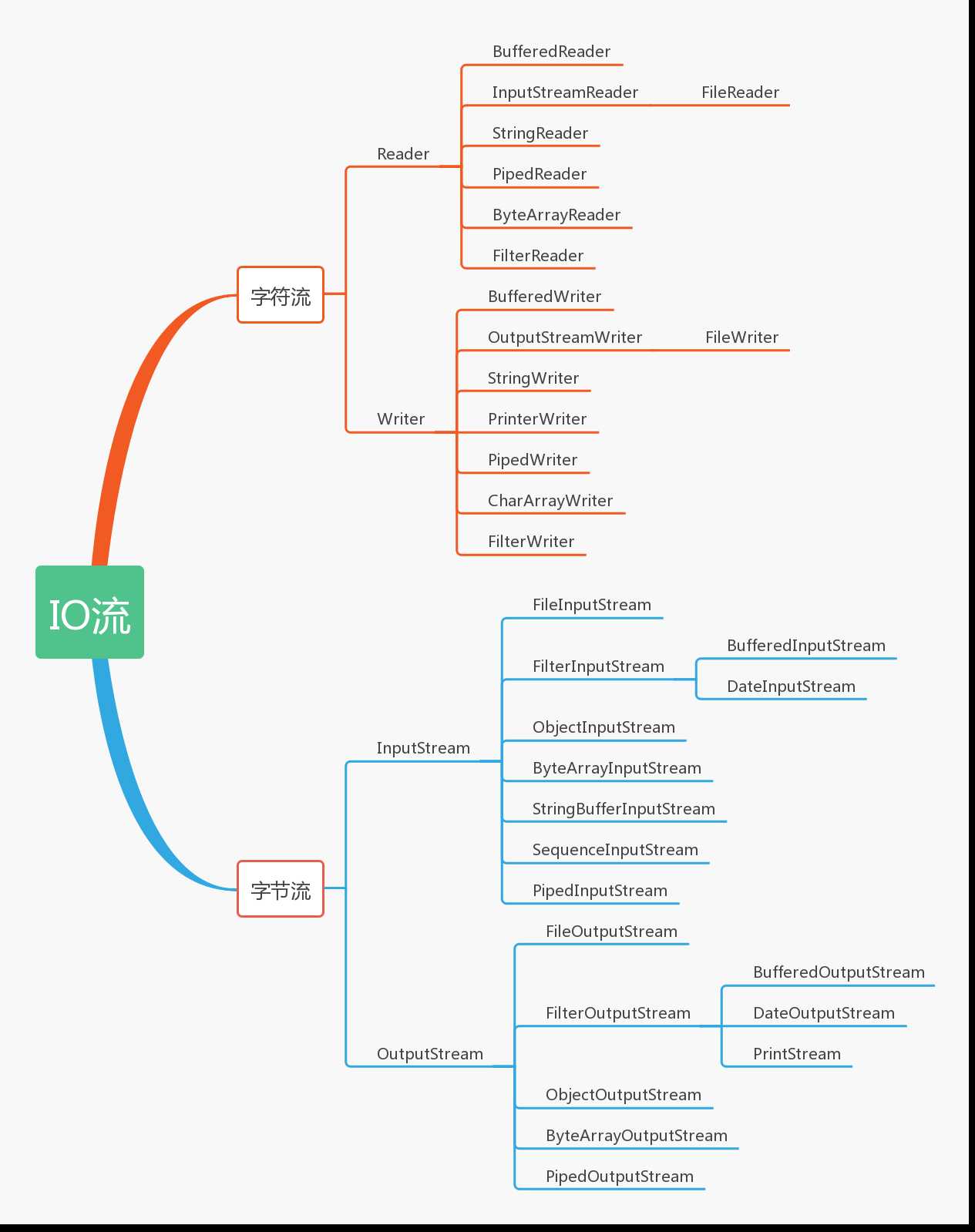
标签:必须 取数 img 读取 path family 读数 private rac InputStream和Read的子类都有read(),用来读取单个字节或字节数组 OutputStream和write的子类都有write(),用来写入单个字节或字节数组 一般都是通过装饰器Decorator模式叠加多个对象提供所期望的功能。创建单一的流,却需要创建多个对象 InputStream为字节输入流,一般都是通过其子类实现功能,是所有字节输入流的基类 OutputStream为字节输出流,一般都是通过其子类实现功能,是所有字节输出流的基类 输出结果: FileOutputStream用来从内存区读数据到文件,如果文件存在,会把内容覆盖,如果不存在,创建文件,然后把数据写入 FileInputStream用来从文件读数据到内存区 ByteArrayOutputStream创建的时候,程序内部创建一个byte[]类型的缓冲区,然后利用ByteArrayOutputStream和ByteArrayInputStream的实例 向数组中写入或读出byte型数据。在网络传输中我们往往要传输很多变量,我们可以利用ByteArrayOutputStream把所有的变量收集到一起,然后一次 性把数据发送出去 在内存中创建一个字节数组缓冲区,从输入流读取的数据保存在该字节数组缓冲区中 输出结果:abc 可以从得到byte[]缓冲区,然后读取数据 Java IO(三)--输入流和输出流简介 标签:必须 取数 img 读取 path family 读数 private rac 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/huigelaile/p/11050319.htmlI/O流分类:
InputStream:
public abstract class InputStream implements Closeable {
private static final int MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE = 2048;
public abstract int read() throws IOException; //读取1byte的数据,返回int类型。若返回值=-1说明没有读取到任何字节
public int read(byte[] var1) throws IOException {} //读取var1.length个字节的数据放到var1数组中,返回值是读取的字节数
public int read(byte[] var1, int off, int len) throws IOException {} //从输入流中最多读取len个字节的数据,存放到偏移量为off的var1数组中。
public long skip(long var1) throws IOException {} //忽略输入流中的n个字节,返回值是实际忽略的字节数, 跳过一些字节来读取
public int available() throws IOException {} //返回输入流中可以读取的字节数。必须是InputStream的子类调用才行,本身调用返回0
public void close() throws IOException {} //每次读取结束,都要关闭输入流并释放与流相关的资源
}
OutputStream:
public abstract class OutputStream implements Closeable, Flushable {
public OutputStream() {}
public abstract void write(int var1) throws IOException; //先将int转换为byte类型,把低字节写入到输出流中
public void write(byte[] var1) throws IOException {} //将数组var1中的字节写到输出流
public void write(byte[] var1, int off, int len) throws IOException {} //将数组var1的字节从偏移量off开始的len个字节写到输出流
public void flush() throws IOException { } //将数据缓冲区中数据全部输出,并清空缓冲区
public void close() throws IOException { } //每次写入结束,都要关闭输出流并释放与流相关的资源
}
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String pathName = "D:" + File.separator + "a.txt";
File file = new File(pathName);
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
outputStream.write("abc1".getBytes());
outputStream.close();
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int length = inputStream.read(bytes);
String s = new String(bytes, 0, length);
System.out.println(s);
inputStream.close();
}
我是好人追加内容
ByteArrayInputStream和ByteArrayOutputStream:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String pathName = "D:" + File.separator + "a.txt";
File file = new File(pathName);
OutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
outputStream.write("abc".getBytes());
byte[] bytes = ((ByteArrayOutputStream) outputStream).toByteArray();
outputStream.close();
InputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes1)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes1, 0, len));
}
}