多线程(十三、AQS原理-Semaphore信号量)
2020-12-13 02:55
标签:nts har throw 启动 案例 string ext 分析 override Semaphore,限制对共享资源访问的最大线程数量,要访问共享资源,需要先申请许可,申请到许可才能访问。访问结果了,释放许可。 线程的调用顺序如下: 多线程(十三、AQS原理-Semaphore信号量) 标签:nts har throw 启动 案例 string ext 分析 override 原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/janephp/2411705案例:
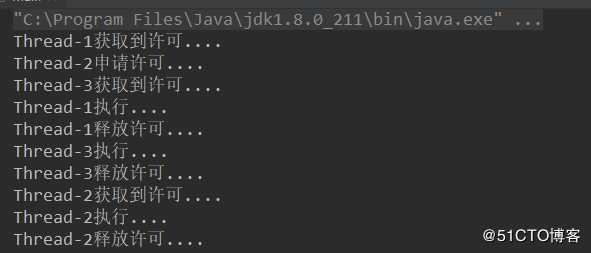
3个线程:Thread-1、Thread-2、Thread-3。一个许可数为2的公平策略的Semaphore。
Thread-1 申请一个许可,等待几秒钟,继续执行
Thread-2 申请2个许可,许可不足,阻塞
Thread-3 申请一个许可,等待几秒钟,继续执行
Thread-1,Thread-3,释放许可之后,Thread-2可以申请许可,成功执行。代码:
Thread-1/3
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
public class Task1 implements Runnable{
private Semaphore semaphore;
public Task1(Semaphore semaphore) {
this.semaphore = semaphore;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到许可....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行....");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "释放许可....");
semaphore.release();
}
}
}
Thread-2
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
public class Task2 implements Runnable{
private Semaphore semaphore;
public Task2(Semaphore semaphore) {
this.semaphore = semaphore;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "申请许可....");
semaphore.acquire(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到许可....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行....");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "释放许可....");
semaphore.release(2);
}
}
}
启动文件
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException, InterruptedException {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(2, true);
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Task1(semaphore),"Thread-1");
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Task2(semaphore),"Thread-2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Task1(semaphore),"Thread-3");
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
结果:
源码分析
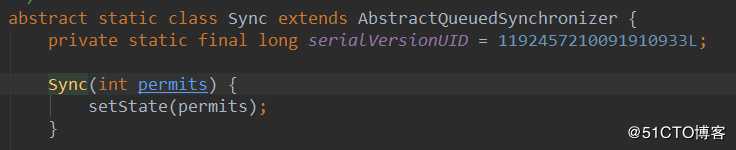
创建公平的Semaphore,就是直接修改AQS的同步状态state
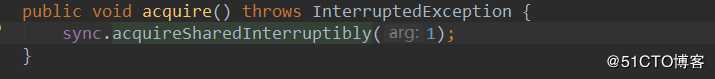
Thread-1,申请许可,执行AQS的acquireSharedInterruptibly
Semaphore是如何实现tryAcquireShared方法的
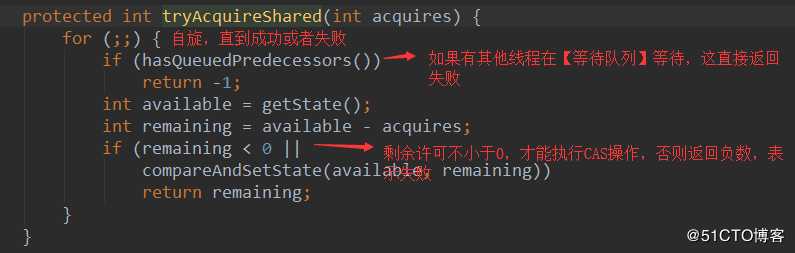
此时,Thread-1申请一个,是足够的,返回成功,然后持有许可,此时state=1。Thread-2申请2个许可,但是state=1,不够的。
Thread-2会申请失败,进入doAcquireSharedInterruptibly
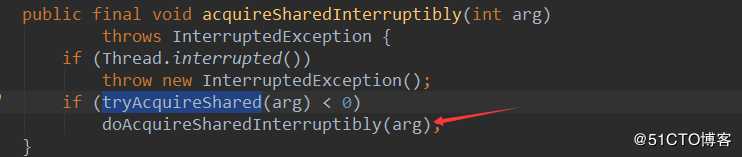
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly方法之前的文章也介绍过了,这里不再详细介绍,最终Thread-2被包装成节点放【等待队列】,同时需要设置【等待队列】头结点为SIGNAL状态,然后Thread-2阻塞了。
Thread-3申请一个许可,是成功的,然后持有许可,此时state=0.
Thread-1,释放了许可,则state=1;
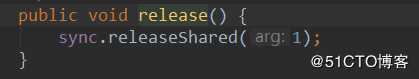
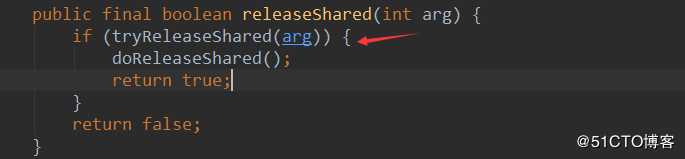
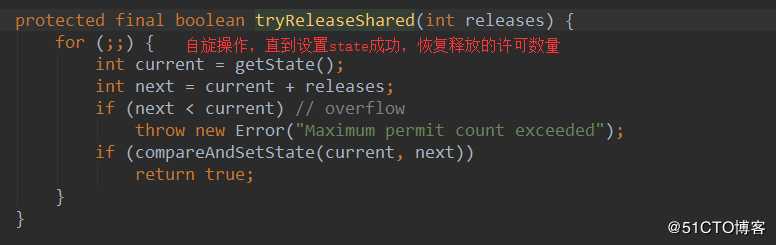
然后执行doReleaseShared,设置头节点状态为0,准备唤醒后继节点,也就是Thread-2.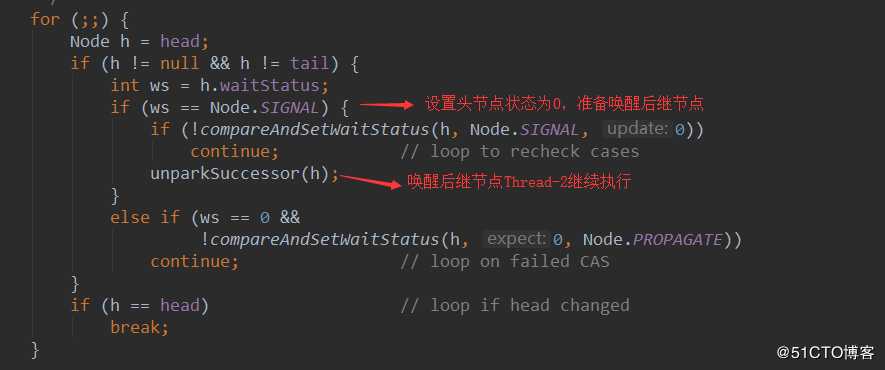
此时,可能Thread-3还没有释放许可,state=1,那么Thread-2又会被阻塞。Thread-3,释放许可,state=2,继续唤醒Thread-2.
Thread-2,获取许可成功,state=0,继续执行。
Thread-2,释放许可,state=2,程序执行完成。