算法(递归)---写的很乱
2020-12-13 03:20
标签:无法 长度 元素 move 时间复杂度 依次 noi code number 前言 特点 所有的循环都可以改成递归 讲A柱子上n-1个盘子暂时移到B柱子上 A柱子只剩下最大的盘子,把他移到目标柱子C上 最后再将B柱子上的n-1个盘子移到目标C上 左边找(递归) 中间比 右边找(递归) 每一个元素都像一个黑盒子 不需要准备的知道每个元素究竟是什么 只需要能够两两比较他们的大小 类似合并排序--相同点-- 分治策略 先找到一个基准点(一般指数组的中部),然后数组被该基准点分为两部分,依次与该基准点数据比较,如果比它小,放左边;反之,放右边。 非比较型排序 一般用于范围小于100的排序 时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为数组的数字范围 太变态了,无法理解!!!! 每一个元素对应位置上数字的大小进行排序:个位与个位,十位与十位... 看得我头皮发麻,算了,来点轻松的东西 "Attribute" 是在html中定义的,而"property" 是在DOM上定义的 算法(递归)---写的很乱 标签:无法 长度 元素 move 时间复杂度 依次 noi code number 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/fangdongdemao/p/11073556.html
本周花了大量的时间再研究算法,这个东西不是一下子就能搞懂的,可能花了大量的时间的看不到见效,也就是得不到一些有效的反馈,这也是我现在比较苦恼的问题,是继续先研究数据结构和算法,还是直接刷leetcode呢?我也不清晰,两眼摸黑,能怎么办呢?学呗,没准一年后就入门了,每天啃一点,没准哪天突然领悟了,后面就会轻松一些
查找一定区域的范围值
const f2=(a,b)=>{
if(a>b) return;
console.log(a);
return f2(a + 1, b);
};
对数组求和
const f1=(a,b=0)=>{
if(a.length-1==b) return a[b];
return a[b]+f1(a,b+1);
};
console.log(f1([1, 2, 3]));
字符串倒序
const s1=(a,b=0)=>{
if(b == 0 ) return a.charAt(0);
return a.charAt(b) + s1(a, b - 1);
};
console.log(s1('123456789',2));
const reverse(str)=>{
if(str.length{
if(str.length) return true;
if(str.length==2) return str[0] == str[1];
if(str[0]==str.slice(-1)){
return isPalindrome(str.slice(1))
}
};
console.log(isPalindrome('aka'));
数组扁平化
const flatten = arr => arr.reduce((acc, val) => {
return acc.concat(Array.isArray(val) ? flatten(val) : val);
}, []);
接受一个对象,这个对象的值是偶数,让其想加
let obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: {d: 3},
e: {f: {g: 6}},
t: {f: {g: {f:10}}},
};
const objSum = obj => {
let sum = 0;
for (let key in obj) {
if (typeof obj[key] == 'object') {
sum += objSum(obj[key])
} else if (typeof obj[key] == 'number' && obj[key] % 2 == 0) {
sum += obj[key];
}
}
return sum
};
console.log(objSum(obj));
const reduceSum=obj=>
Object.values(obj).
reduce((acc,val)=>
typeof val=='object'?
acc+reduceSum(val):
acc+val,0);
汉诺塔
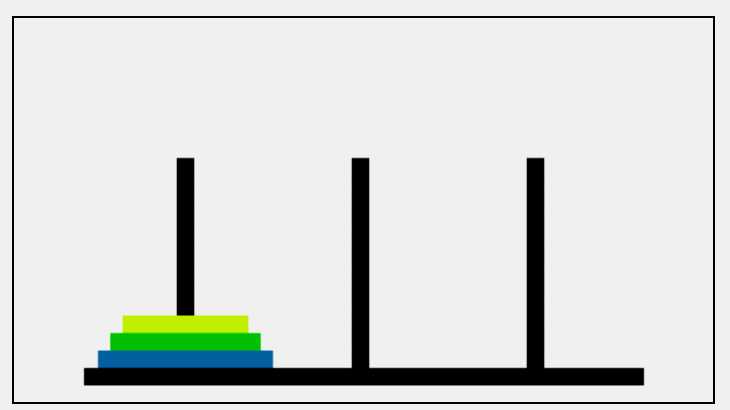
参数
最大编号 初始柱子 辅助的柱子 目标的柱子
const hanoi = (n, a, b, c) => {
if (n == 1) {
//a到c
// move(a, c);
console.log('Move' + n + ' ' + a + ' ' + c);
} else {
// a绕过c放到b
hanoi(n - 1, a, c, b);
// move(a, c);
console.log('Move' + n + ' ' + a + ' ' + c);
//b绕过a放到c
hanoi(n - 1, b, a, c);
}
};
console.log(hanoi(3, 'a', 'b', 'c'));二分查找递归
//在一定范围内L R 求最大值
const getMax=(arr,L,R)=>{
if(L==R) return arr[L];
let mid=Math.floor((L+R)/2);
let maxLeft = getMax(arr, L, mid);
let maxRight = getMax(arr, mid + 1, R);
return Math.max(maxLeft, maxRight);
};
let arr = [1, 3, 44, 5, 6, 7, 8];
console.log(getMax(arr, 0, arr.length-1));希尔排序
归并排序
举例说明
[9, 3, 6, 4]
[9, 3] | [6, 4]
[9] | [3] [6] | [4]
[3, 9] | [4, 6]
[3, 4, 6, 9]
我们把数组拆分成多个最小的块,可以利用slice方法来实现
// 排序合并
const merge=(left,right)=>{
let result=[];
while (left.length > 0 && right.length > 0) {
if (left[0] {
if(array.length基于比较的排序
插入 比较 冒泡 合并 快速 分块[1,2,3].sort((a,b)=>a-b)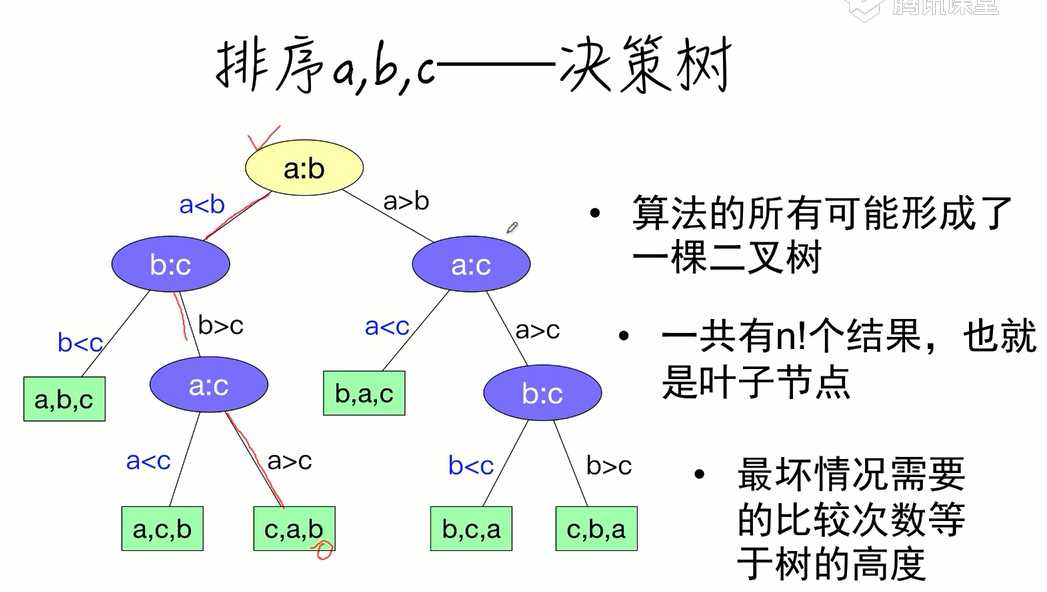
快速排序
const quickSort=arr=>{
if(arr.length计数排序
基数排序
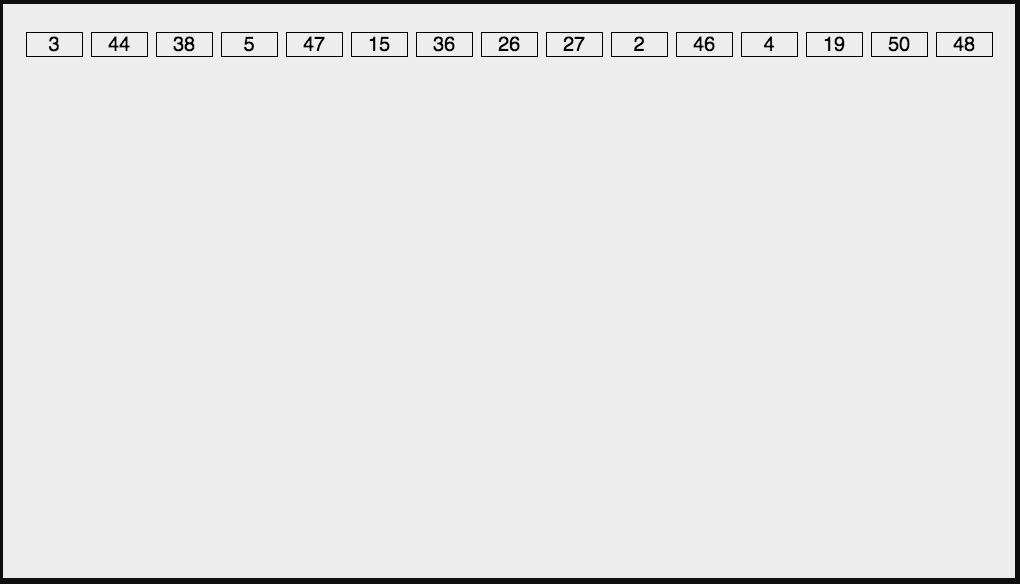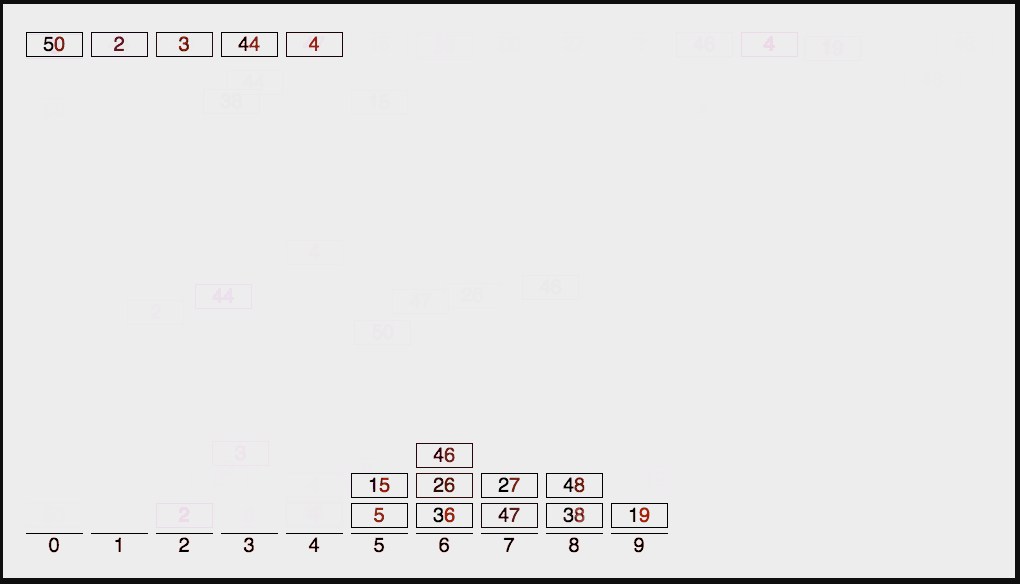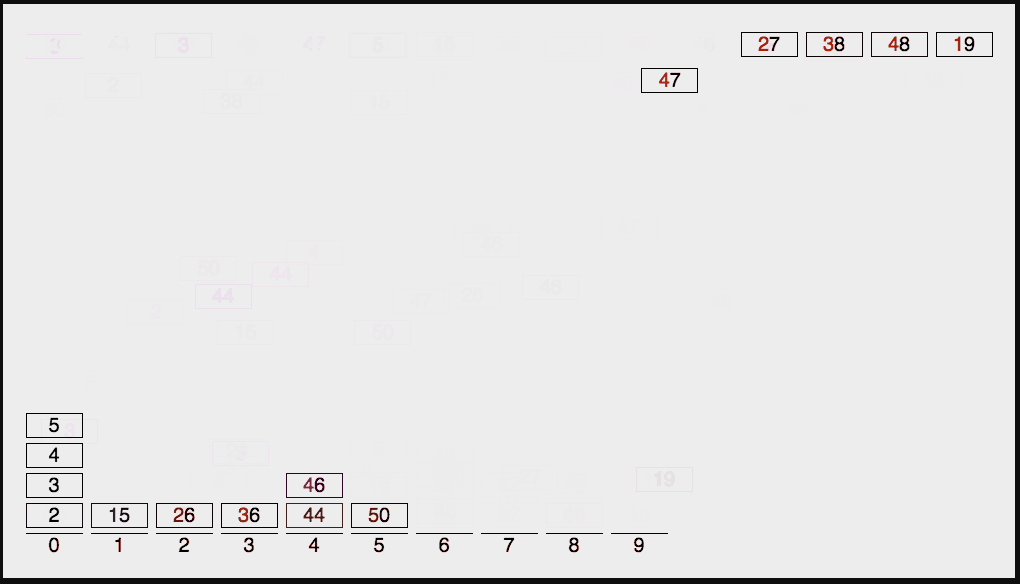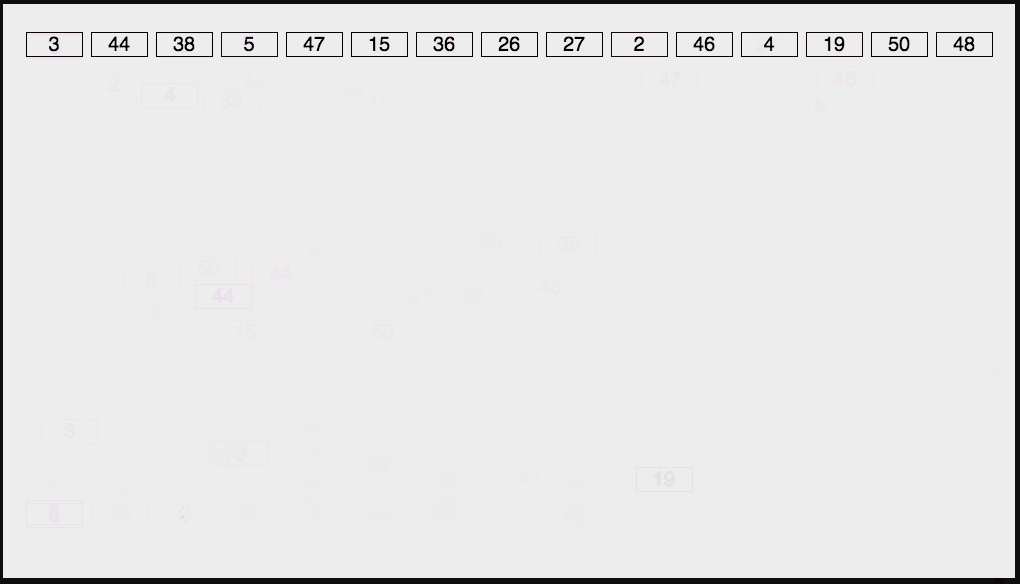
||的妙用
去重(直接保留刚开始的第0项)
const uniq=array=>array.sort((a, b) => a - b)
.filter((item,index,array)=>!index||item!==array[index-1])Attribute 和 Property 的区别
说明区别
const input = document.querySelector('input');
console.log(input.getAttribute('value')); // Hello
console.log(input.value); // Hello
console.log(input.getAttribute('value')); // Hello
console.log(input.value); // Hello World!