简单看看jdk7源码之java.lang包01
2020-12-13 04:01
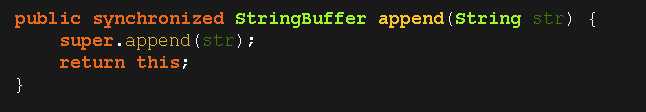
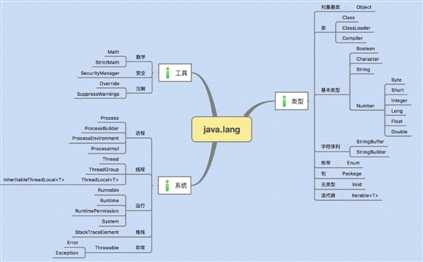
标签:default get 字节码 else 遇到 minimum nat timeout native 从今天开始简单开始读一遍jdk的源码,估计这个时间会很长,慢慢啃吧。。。。(首先说一句抱歉,因为很多图都是直接百度扣的,图太多了不能为每一个图附上原版链接,不好意思!) 在网上看了很多的教程,读源码有一定的顺序,按照包的顺序:java.lang包,java.util包,java.util.concurrent包,java.util.concurrent.atomic包,java.lang.reflect包,java.lang.annotation包,java.util.concurrent.locks包,java.io包,java.nio包,java.sql包,java.net包; 大概数了一下,有11个包,暂时就把这11个包读完应该就差不多了,应该可以对jdk源码会理解很多,而且中间可能会涉及到一些其他的知识,我也是新手,也顺便学一下; 当然也不可能把所有的方法都慢慢的去分析、去读,重点看一些比较重要的方法看看,很多的重载方法和不常用的方法可以选择性的省略。。。适合自己的才是最好的!比如一个方法基本上都用不到的,我们就简单瞄两眼就可以了,用的频繁的方法可以去看看实现原理。 1.概述 对于java.lang包我们可以说是用得很多了,但是一直没有系统的整理一下,比如一个很熟悉的类Object,如果让你说说这个类中有哪些方法啊?(亲身遇到的一个面试题。。。) 先看看这个包下常用都有些什么类吧,借来的一个图,1优先级最高,4优先级最低 下面这个更全面,描述了java.lang包下的类主要是负责哪些方面的; 2.Object类 对于这个类很熟悉吧,所有的类默认都是继承这个类; 3.String类 关于这个类用得很多,初学的时候最多的就是比较String,StringBuffer,StringBulider。。。我就把常用的那些方法给说一下,很少用的方法选择性的删除 4.StringBuilder类 有关于这个类其实很容易,就两层结构,final class StringBuilder extends AbstractStringBuilder,我们重点就在这个父类上,子类其实没做什么事,只是简单的调用了父类实现的那些方法而已。。。 AbstractStringBuilder类: 再看子类StringBuilder那就简单了: 有没有发现,StringBuilder类和String类一样是被final修饰了的,是属于不可变的,关于final关键字修饰的知识,大概提一下,不可能指的是引用不可变,内容可以变,例如下面代码: 随意提一下StringBuffer类,我们看看这个类:final class StringBuffer extends AbstractStringBuilder,居然也是继承了AbstractStringBuilder这个类,那么可以知道内部方法和StringBuilder一模一样,那么有什么区别呢?随便看一个StringBuffer中的简单的方法,如下所示; 很清楚的看到有个synchronized关键字,这个关键字就涉及到多线程的时候,同一时刻只有一个线程能够访问这个方法,想详细了解synchronized关键字用法的可以看看我之前的博客,或者自己看看资料也行。。。 5.总结 自己看看源码还是很有必要的,我总是感觉要行框架中走出来,基础始终都是基础,我们只有把基础搞的扎1) Object 1
2) String 1
3) AbstractStringBuilder 1
4) StringBuffer 1
5) StringBuilder 1
6) Boolean 2
7) Byte 2
8) Double 2
9) Float 2
10) Integer 2
11) Long 2
12) Short 2
13) Thread 2
14) ThreadLocal 2
15) Enum 3
16) Throwable 3
17) Error 3
18) Exception 3
19) Class 4
20) ClassLoader 4
21) Compiler 4
22) System 4
23) Package 4
24) Void 4
//任何类默认都会继承这个类
public class Object {
//这个方法顾名思义,就是将一些native方法注册一下,可以简单理解成每一个native方法都连接着一个C/C++的具体实现
private static native void registerNatives();
//此处的代码块静态会调用上面的这个native方法
//所谓的native方法,就是底层用C/C++实现的,java可以有办法去调用这些其他语言的方法,可以了解一下JNI
static {
registerNatives();
}
//这也是一个native方法,就是获取一个类的字节码文件
public final native Class> getClass();
//获取一个类的hash值,简单说说哈希值,这个在map中用的比较多;其实任意对象----->通过一个hash函数计算------>得到一个很大的数字(这就是hashCode)---
//---->这个hashCode进行取余计算等方式,就得到数组的下标;
public native int hashCode();
//可以看到这里比较的就是两个对象的引用,换句话说就是看看两个对象是不是同一个对象
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
//克隆,想想现实中的克隆人。。。这里就是克隆一个和原来对象一模一样的对象
//注意,克隆分为浅克隆和深度克隆,深度克隆就是克隆出来的对象和原对象无关了,而浅克隆就是和原先对象有点关系,具体的什么关系呢?
//我简单说说浅克隆,原先对象中保存了一个Person实例的引用,而克隆的对象中也保存的是同一个Person的引用,当在克隆对象中对这个引用进行修改,原对象也会牵连。。。
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
//这个方法就是将当前类基本信息以字符串形式打印出来,一般就是类名+@+hashCode变为16进制
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
//多线程中用于随机唤醒一个线程的方法,这两个notify方法都要和wait方法一起用
public final native void notify();
//唤醒所有线程
public final native void notifyAll();
//让一个线程休息一下一定时间,这个方法会释放当前的锁,想了解的可以看看我以前的博客,或者自己看看资料
//注意wait方法和sleep方法的区别
public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;
public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {
if (timeout ) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (nanos 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && timeout == 0)) {
timeout++;
}
wait(timeout);
}
//这个0可不是等待0秒啊,是等待无限长的时间,直到被唤醒
public final void wait() throws InterruptedException {
wait(0);
}
//这个方法看看就好, 最没用的方法;主要用于jvm的垃圾回收,即使调用这个方法但是不保证一定立即进行回收。。。
protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }
}


package java.lang;
import sun.misc.FloatingDecimal;
import java.util.Arrays;
abstract class AbstractStringBuilder implements Appendable, CharSequence {
//看来这个StringBuilder本质上也是一个字节数组,和String不同的是这里没有被final修饰
char[] value;
//字符数组的容量
int count;
AbstractStringBuilder() {
}
//根据传进来的参数确定字符数组的大小
AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) {
value = new char[capacity];
}
//返回字符数组中实际数据的数量
public int length() {
return count;
}
//返回字符数组的最大容量
public int capacity() {
return value.length;
}
//一下三个方法都是确保那个字符数组大小足够而进行的扩容操作;首先判断你要确保新字节数组多大,
//如果新数组容量比原来数组大,那么就进行扩容,扩容的时候还需要进行判断,比较系统自动扩容之后
//的容量和你所确保的容量做个对比,如果系统扩容还达不到你的要求,那么新字节数组的大小就用你确保的那个容量吧
//最后就是将原来数组中的数据复制到新的数组中
public void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
if (minimumCapacity > 0)
ensureCapacityInternal(minimumCapacity);
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0)
expandCapacity(minimumCapacity);
}
void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;
if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity )
newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
if (newCapacity ) {
if (minimumCapacity )
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
}
//去除数组中多余的位置;比如一个数组最大容量为5,但是实际放了3个数据,空出来两个位置,于是
//可以将对于的两个空位置去掉(其实就是将那是那三个数据复制到一个新的数组中,然后改变value引用)
public void trimToSize() {
if (count value.length) {
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, count);
}
}
//设置字节数组的长度,多余的空位置添加‘\0‘,这其实就是代表空字符,可以理解为null
public void setLength(int newLength) {
if (newLength )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(newLength);
ensureCapacityInternal(newLength);
if (count newLength) {
for (; count )
value[count] = ‘\0‘;
} else {
count = newLength;
}
}
//根据传进来的索引获取字节数组对应的数据
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index = count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return value[index];
}
//截取字节数组的连续的某几个字符,放到一个新的字节数组中
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)
{
if (srcBegin )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
if ((srcEnd count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
if (srcBegin > srcEnd)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("srcBegin > srcEnd");
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
//将字符数组某个位置的字符覆盖
public void setCharAt(int index, char ch) {
if ((index = count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
value[index] = ch;
}
//传入一个对象,将这个对象转化为字符串,然后将该字符串(就是一个字符数组)添加到当前字符数组的末尾
//append方法就是在当前字符数组中后面添加所要添加的对象
public AbstractStringBuilder append(Object obj) {
return append(String.valueOf(obj));
}
//首先要确保容量足够,再就是调用String类的getChars方法就是将传进去的str从0到最后,一次复制到value字节数组中
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null) str = "null";
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
//将StringBuffer类型的字符字符数组复制到本类的字符数组中(首先要保证容量足够)
public AbstractStringBuilder append(StringBuffer sb) {
if (sb == null)
return append("null");
int len = sb.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
sb.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
//将一个字符数组的某一段复制到本类的字符数组当中
public AbstractStringBuilder append(char str[], int offset, int len) {
if (len > 0)
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
System.arraycopy(str, offset, value, count, len);
count += len;
return this;
}
//在当前字符数组中添加boolean字符
public AbstractStringBuilder append(boolean b) {
if (b) {
ensureCapacityInternal(count + 4);
value[count++] = ‘t‘;
value[count++] = ‘r‘;
value[count++] = ‘u‘;
value[count++] = ‘e‘;
} else {
ensureCapacityInternal(count + 5);
value[count++] = ‘f‘;
value[count++] = ‘a‘;
value[count++] = ‘l‘;
value[count++] = ‘s‘;
value[count++] = ‘e‘;
}
return this;
}
//在当前字符数组最后中添加一个字符
public AbstractStringBuilder append(char c) {
ensureCapacityInternal(count + 1);
value[count++] = c;
return this;
}
//在当前字符数组后面添加一个int类型(4个字节)的数据,要保证容量足够
//后面还有添加各种数据类型long,double,float等省略
public AbstractStringBuilder append(int i) {
if (i == Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
append("-2147483648");
return this;
}
int appendedLength = (i
: Integer.stringSize(i);
int spaceNeeded = count + appendedLength;
ensureCapacityInternal(spaceNeeded);
Integer.getChars(i, spaceNeeded, value);
count = spaceNeeded;
return this;
}
//对一个字符数组中某一段进行删除,给出了起始位置和终点位置,可以看到就是利用的是数组的复制
//重点System.arraycopy方法,可惜这是一个native方法,看不到源码
public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end) {
if (start )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
end = count;
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException();
int len = end - start;
if (len > 0) {
System.arraycopy(value, start+len, value, start, count-end);
count -= len;
}
return this;
}
//删除字符数组指定位置的字符
public AbstractStringBuilder deleteCharAt(int index) {
if ((index = count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
System.arraycopy(value, index+1, value, index, count-index-1);
count--;
return this;
}
//目的是为了让一个新的字符数组,代替本字符数组的某一段
//其实还是通过数组的复制
public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) {
if (start )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (start > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > length()");
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > end");
if (end > count)
end = count;
int len = str.length();
int newCount = count + len - (end - start);
ensureCapacityInternal(newCount);
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start + len, count - end);
str.getChars(value, start);
count = newCount;
return this;
}
//截取字符数组的某一段,其实就是新建了一个String类型的
public String substring(int start, int end) {
if (start )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end);
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end - start);
return new String(value, start, end - start);
}
//向StringBuilder中插入一个字节数组的某一段,省略好多的重载insert方法
public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int index, char[] str, int offset,
int len)
{
if ((index length()))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
if ((offset str.length - len))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(
"offset " + offset + ", len " + len + ", str.length "
+ str.length);
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
System.arraycopy(value, index, value, index + len, count - index);
System.arraycopy(str, offset, value, index, len);
count += len;
return this;
}
//从前往后查看某个字符串的位置
public int indexOf(String str) {
return indexOf(str, 0);
}
//从前往后其实就是调用String的indexof方法
public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return String.indexOf(value, 0, count,
str.toCharArray(), 0, str.length(), fromIndex);
}
//从后往前找指定字符串的位置
public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return String.lastIndexOf(value, 0, count,
str.toCharArray(), 0, str.length(), fromIndex);
}
//逆序字符数组,实现很简单,不要看hasSurrogate了,反正我是没看懂这个boolean的。。。
public AbstractStringBuilder reverse() {
boolean hasSurrogate = false;
int n = count - 1;
for (int j = (n-1) >> 1; j >= 0; --j) {
char temp = value[j];
char temp2 = value[n - j];
if (!hasSurrogate) {
hasSurrogate = (temp >= Character.MIN_SURROGATE && temp Character.MAX_SURROGATE)
|| (temp2 >= Character.MIN_SURROGATE && temp2 Character.MAX_SURROGATE);
}
value[j] = temp2;
value[n - j] = temp;
}
if (hasSurrogate) {
for (int i = 0; i ) {
char c2 = value[i];
if (Character.isLowSurrogate(c2)) {
char c1 = value[i + 1];
if (Character.isHighSurrogate(c1)) {
value[i++] = c1;
value[i] = c2;
}
}
}
}
return this;
}
//留给子类实现,直接打印字符串
public abstract String toString();
//返回字符数组
final char[] getValue() {
return value;
}
}


package java.lang;
import sun.misc.FloatingDecimal;
import java.util.Arrays;
abstract class AbstractStringBuilder implements Appendable, CharSequence {
//看来这个StringBuilder本质上也是一个字节数组,和String不同的是这里没有被final修饰
char[] value;
//字符数组的容量
int count;
AbstractStringBuilder() {
}
//根据传进来的参数确定字符数组的大小
AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) {
value = new char[capacity];
}
//返回字符数组中实际数据的数量
public int length() {
return count;
}
//返回字符数组的最大容量
public int capacity() {
return value.length;
}
//一下三个方法都是确保那个字符数组大小足够而进行的扩容操作;首先判断你要确保新字节数组多大,
//如果新数组容量比原来数组大,那么就进行扩容,扩容的时候还需要进行判断,比较系统自动扩容之后
//的容量和你所确保的容量做个对比,如果系统扩容还达不到你的要求,那么新字节数组的大小就用你确保的那个容量吧
//最后就是将原来数组中的数据复制到新的数组中
public void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
if (minimumCapacity > 0)
ensureCapacityInternal(minimumCapacity);
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0)
expandCapacity(minimumCapacity);
}
void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;
if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity )
newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
if (newCapacity ) {
if (minimumCapacity )
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
}
//去除数组中多余的位置;比如一个数组最大容量为5,但是实际放了3个数据,空出来两个位置,于是
//可以将对于的两个空位置去掉(其实就是将那是那三个数据复制到一个新的数组中,然后改变value引用)
public void trimToSize() {
if (count value.length) {
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, count);
}
}
//设置字节数组的长度,多余的空位置添加‘\0‘,这其实就是代表空字符,可以理解为null
public void setLength(int newLength) {
if (newLength )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(newLength);
ensureCapacityInternal(newLength);
if (count newLength) {
for (; count )
value[count] = ‘\0‘;
} else {
count = newLength;
}
}
//根据传进来的索引获取字节数组对应的数据
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index = count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return value[index];
}
//截取字节数组的连续的某几个字符,放到一个新的字节数组中
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)
{
if (srcBegin )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
if ((srcEnd count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
if (srcBegin > srcEnd)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("srcBegin > srcEnd");
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
//将字符数组某个位置的字符覆盖
public void setCharAt(int index, char ch) {
if ((index = count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
value[index] = ch;
}
//传入一个对象,将这个对象转化为字符串,然后将该字符串(就是一个字符数组)添加到当前字符数组的末尾
//append方法就是在当前字符数组中后面添加所要添加的对象
public AbstractStringBuilder append(Object obj) {
return append(String.valueOf(obj));
}
//首先要确保容量足够,再就是调用String类的getChars方法就是将传进去的str从0到最后,一次复制到value字节数组中
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null) str = "null";
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
//将StringBuffer类型的字符字符数组复制到本类的字符数组中(首先要保证容量足够)
public AbstractStringBuilder append(StringBuffer sb) {
if (sb == null)
return append("null");
int len = sb.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
sb.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
//将一个字符数组的某一段复制到本类的字符数组当中
public AbstractStringBuilder append(char str[], int offset, int len) {
if (len > 0)
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
System.arraycopy(str, offset, value, count, len);
count += len;
return this;
}
//在当前字符数组中添加boolean字符
public AbstractStringBuilder append(boolean b) {
if (b) {
ensureCapacityInternal(count + 4);
value[count++] = ‘t‘;
value[count++] = ‘r‘;
value[count++] = ‘u‘;
value[count++] = ‘e‘;
} else {
ensureCapacityInternal(count + 5);
value[count++] = ‘f‘;
value[count++] = ‘a‘;
value[count++] = ‘l‘;
value[count++] = ‘s‘;
value[count++] = ‘e‘;
}
return this;
}
//在当前字符数组最后中添加一个字符
public AbstractStringBuilder append(char c) {
ensureCapacityInternal(count + 1);
value[count++] = c;
return this;
}
//在当前字符数组后面添加一个int类型(4个字节)的数据,要保证容量足够
//后面还有添加各种数据类型long,double,float等省略
public AbstractStringBuilder append(int i) {
if (i == Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
append("-2147483648");
return this;
}
int appendedLength = (i
: Integer.stringSize(i);
int spaceNeeded = count + appendedLength;
ensureCapacityInternal(spaceNeeded);
Integer.getChars(i, spaceNeeded, value);
count = spaceNeeded;
return this;
}
//对一个字符数组中某一段进行删除,给出了起始位置和终点位置,可以看到就是利用的是数组的复制
//重点System.arraycopy方法,可惜这是一个native方法,看不到源码
public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end) {
if (start )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
end = count;
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException();
int len = end - start;
if (len > 0) {
System.arraycopy(value, start+len, value, start, count-end);
count -= len;
}
return this;
}
//删除字符数组指定位置的字符
public AbstractStringBuilder deleteCharAt(int index) {
if ((index = count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
System.arraycopy(value, index+1, value, index, count-index-1);
count--;
return this;
}
//目的是为了让一个新的字符数组,代替本字符数组的某一段
//其实还是通过数组的复制
public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) {
if (start )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (start > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > length()");
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > end");
if (end > count)
end = count;
int len = str.length();
int newCount = count + len - (end - start);
ensureCapacityInternal(newCount);
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start + len, count - end);
str.getChars(value, start);
count = newCount;
return this;
}
//截取字符数组的某一段,其实就是新建了一个String类型的
public String substring(int start, int end) {
if (start )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end);
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end - start);
return new String(value, start, end - start);
}
//向StringBuilder中插入一个字节数组的某一段,省略好多的重载insert方法
public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int index, char[] str, int offset,
int len)
{
if ((index length()))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
if ((offset str.length - len))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(
"offset " + offset + ", len " + len + ", str.length "
+ str.length);
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
System.arraycopy(value, index, value, index + len, count - index);
System.arraycopy(str, offset, value, index, len);
count += len;
return this;
}
//从前往后查看某个字符串的位置
public int indexOf(String str) {
return indexOf(str, 0);
}
//从前往后其实就是调用String的indexof方法
public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return String.indexOf(value, 0, count,
str.toCharArray(), 0, str.length(), fromIndex);
}
//从后往前找指定字符串的位置
public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return String.lastIndexOf(value, 0, count,
str.toCharArray(), 0, str.length(), fromIndex);
}
//逆序字符数组,实现很简单,不要看hasSurrogate了,反正我是没看懂这个boolean的。。。
public AbstractStringBuilder reverse() {
boolean hasSurrogate = false;
int n = count - 1;
for (int j = (n-1) >> 1; j >= 0; --j) {
char temp = value[j];
char temp2 = value[n - j];
if (!hasSurrogate) {
hasSurrogate = (temp >= Character.MIN_SURROGATE && temp Character.MAX_SURROGATE)
|| (temp2 >= Character.MIN_SURROGATE && temp2 Character.MAX_SURROGATE);
}
value[j] = temp2;
value[n - j] = temp;
}
if (hasSurrogate) {
for (int i = 0; i ) {
char c2 = value[i];
if (Character.isLowSurrogate(c2)) {
char c1 = value[i + 1];
if (Character.isHighSurrogate(c1)) {
value[i++] = c1;
value[i] = c2;
}
}
}
}
return this;
}
//留给子类实现,直接打印字符串
public abstract String toString();
//返回字符数组
final char[] getValue() {
return value;
}
}


package java.lang;
//我们将这个父类看了一遍这里就简单多了,因为基本的方法父类都已经实现了,这里就是简单调用一下
//我们就简单看看一些重要的方法
public final class StringBuilder extends AbstractStringBuilder
implements java.io.Serializable, CharSequence
{
//初始化字符数组的大小
public StringBuilder() {
super(16);
}
//也可以自定义字符数组的大小
public StringBuilder(int capacity) {
super(capacity);
}
//初始化一个字符串的时候,我们会先创建一个比字符串大16的一个字符数组,然后将字符串添加进去
public StringBuilder(String str) {
super(str.length() + 16);
append(str);
}
//没有做什么事,就是简单的调用的一下父类的方法
public StringBuilder append(Object obj) {
return append(String.valueOf(obj));
}
public StringBuilder append(String str) {
super.append(str);
return this;
}
//扩展一以下,可以在后面添加StringBuilder类型的数据
private StringBuilder append(StringBuilder sb) {
if (sb == null)
return append("null");
int len = sb.length();
int newcount = count + len;
if (newcount > value.length)
expandCapacity(newcount);
sb.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count = newcount;
return this;
}
//下面省略一堆append方法,就是简单的调用父类的append的各种重载方法
//还省略一些知识简单的调用父类方法的这种无聊的方法。。。
//实现父类的toString方法,返回一个字符串
public String toString() {
return new String(value, 0, count);
}
//下面这两个方法挺有意思的,这两个方法是本类独有的,可以传入io流,将数据写入到字节数组中或者从字节数组中读取数据
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
s.defaultWriteObject();
s.writeInt(count);
s.writeObject(value);
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
count = s.readInt();
value = (char[]) s.readObject();
}
}
StringBuilder name = new StringBuilder("java小新人");
final StringBuilder str = name;
name.append("hello");
System.out.println(str); //java小新人hello
str = "world";//这里编译器会报错