Spring容器初始化
2020-12-13 04:27
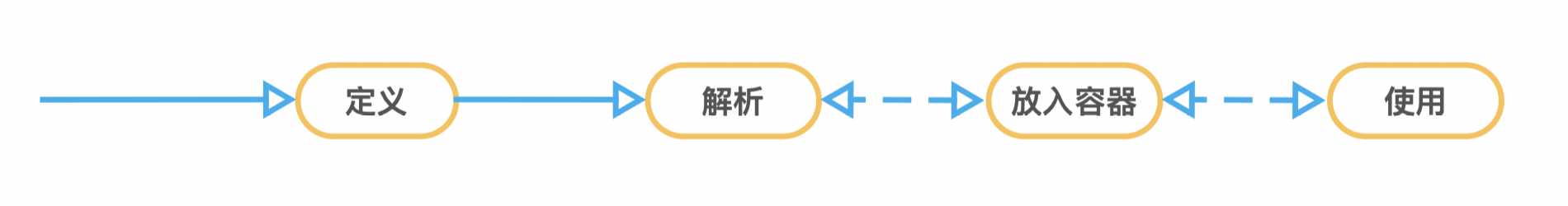
标签:onclick sde 包括 moni record ref 面向接口编程 名称 encoding 问:Spring容器、SpringIOC是什么? 那么Spring容器到底是什么东西呢,长什么样子呢?为什么感觉像是哆啦A梦的百宝箱,什么东西都能拿出来? 所以本文针对以上问题对一个简单的说明, 1、首先我们整个过程中要保持一个概念,容器中的Bean要经历以下步骤带着这个思想去看就会好理解一些: 2、来个简单的例子 ??:XML方式定义Bean 上面 xml 描述了一个日期Date对象的定义 ??:简单使用 上述代码做了三件事:1.初始化容器,将Bean定义等信息加载进去;2.从容器中获取刚刚定义的Bean;3.验证Bean是否已经真的可以正常使用 主要说一下 前两件事情,对于Spring来说都做了那些事情 3、So,开始撸代码 ??:根据上面介绍说到的总体思想,我们bean的定义这一步已经做好了,现在就是等待告诉Spring 咱bean定义文件叫什么名,在哪里。代码中的第一行既是此操作。 Spring知道咱的定义位置之后该做什么呢?那肯定是要获取并加载这个资源了。Spring中资源文件的加载获取会实现接口 ResourceLoader,这个接口一共两方法。获取资源And获取ClassLoader 题外话:查看该接口的实现,可以很清楚的看到我们常用的一些Context的资源加载方式, 接着上面说Spring是在何时去使用这个资源加载的呢?Spring在 AbstractApplicationContext 这个抽象类中定义了容器初始化的模版方法 这个模版方法里其实根据方法名都已经能够很清楚的知道在做些什么事情。首先一上来就开始做容器初始化的准备工作,然后接下来是真正的创建容器。也就是在这个时候将资源文件加载并且解析成为Spring中自己定义的Bean的数据结构 上述代码中关键点1创建的实际上是一个 DefaultListableBeanFactory 实例,该实例包含了Spring IOC最基础的功能。 所以至此我们就可以回答第一个问题了,Spring容器长什么样?以下代码是 DefaultListableBeanFactory 中的部分属性定义。基于此我们可以大概明白日常使用中根据bean name或者bean type来获取bean是怎么一回事了。其实说白了就是从一个事先准备好的Map里面找到对应key的value值返回(当然实际上还有更多的操作,比如缓存、lazy等等), 对于 loadBeanDefinitions 这个方法,其作用是加载 beanDefinition。BeanDefinitions接口实际上是描述了bean定义过程中的操作。实际上Bean定义时定义了那些东西。这个可以在其实现类中找到,其部分属性如下(有兴趣可以针对每个属性做详细理解): 至此,定义、解析容器创建已完成 接下来是不是该将定义的BeanDefinitions转化为真正可用的Bean了呢?是的,回到一开始的模版方法refresh(),找到 finishBeanFactoryInitialization 方法。然后一探究竟: 同样的抽象类 AbstractApplicationContext 已经给实现了bean。(所以说面向接口编程很重要呢) 上面的代码官方对于两个for循环,已经做出了很具体的说明,像我这种英语渣渣都能看懂,相信你也能看懂。我们主要说明第一个for循环中做的事情。至于初始化完成之后的回调操作这里就不做解析了。 接下来,主要看下getBean方法,由于此函数内容较多,就不直接展示了。getBean方法一上来就会先到cache中去寻找该Bean,找到直接返回。找不到会先在父容器中寻找,找到返回,找不到才会执行实例化逻辑。 先说明以下在初始化Bean之前,当前这个Bean如果需要注入其他属性,Spring是怎么实现的: 首先遍历依赖的bean名称,进行依赖注册。接着真正加载依赖Bean。这样就构成了一个递归循环,出口自然是被依赖的bean没有任何依赖。 接下来是Bean的真正实例化。由于Bean的Scope不尽相同,这里只做单例的说明: getSingleton方法会去执行实例化操作,并且将实例注册进容器,也就是Map; 真正实例化的操作方法 createBean,其中包括整个Bean的属性注入以及方法校验。后续如果有机会再撸下这块的具体注入过程。 最后一步,使用Bean。看完前面的内容,其实这一步说与不说是一样的,因为 总结: Spring容器简单来说就是一个个Map。维护着各种关系,比如,名称跟Bean定义、名称、别名、类型等之间的相互关系。在容器启动时候,初始化完成各种事件的注册以及部分bean的实例化。使用到cache(实际上也是Map)、父子容器这种逻辑关系,使得容器更加可用。当然本文只说明了的加载配置文件方式Bean初始化的过程。实际上其他Bean定义方式也是一样的,只不过是BeanDefinitions的来源不一样。 感概: 作为一个开发者来说,数据结构跟设计模式真的特别重要。两者恰到好处的结合才能写出优雅的代码。不为了使用而使用,强搬设计模式或者数据结构,这样的代码反而使可读性下降、程序性能也随之降低。比如说单例模式,很多人可能对这个都熟到不能再熟。许多人都写到最安全最方便的该是使用枚举来实现单例模式。既解决了线程安全问题,也解决了反射带来的多实例问题。事实上在Spring中也有使用到单例模式,但是其代码却是使用 双重判断 的单例。所以适合自己的才是最好的。 Spring容器初始化 标签:onclick sde 包括 moni record ref 面向接口编程 名称 encoding 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/funmans/p/11107136.html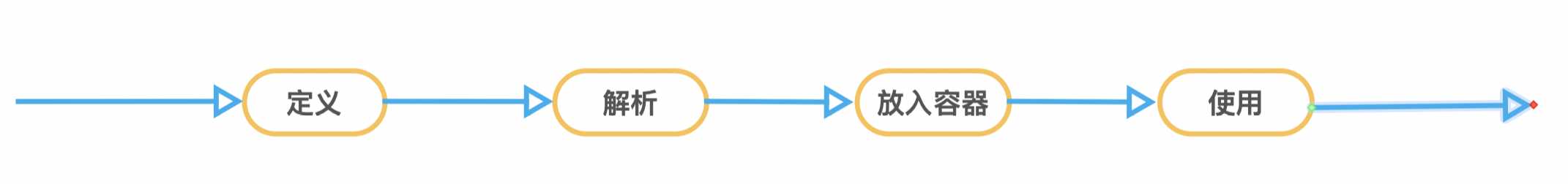
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
bean id="date" class="java.util.Date"/>
beans>
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Date date = context.getBean("date", Date.class);
System.out.println(Objects.requireNonNull(date).getTime());
}
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
//设置文件位置
this.setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
this.refresh();
}
}public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
/**Return a Resource handle for the specified resource location. */
Resource getResource(String location);
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
this.prepareRefresh();//准备工作
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();//创建容器
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
上述模版方法中包含整个容器初始化所做的很多工作,篇幅有限,只对创建容器以及Bean的初始化做说明,其他bean前、bean后处理、事件广播等等有兴趣自己可以看下源码。protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
//如果存在进行销毁
if (this.hasBeanFactory()) {
this.destroyBeans();
this.closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.createBeanFactory();//创建bean工程
beanFactory.setSerializationId(this.getId());
this.customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);//加载Bean的定义
synchronized(this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
} catch (IOException var5) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + this.getDisplayName(), var5);
}
}
/** Optional OrderComparator for dependency Lists and arrays */
private Comparator
private volatile Object beanClass;
private String scope = SCOPE_DEFAULT;
private boolean abstractFlag = false;
private boolean lazyInit = false;
private int autowireMode = AUTOWIRE_NO;
private int dependencyCheck = DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE;
private String[] dependsOn;
private boolean autowireCandidate = true;
private boolean primary = false;
private final Map
从上面的属性可以看到Bean定义过程中包含:bean是否懒加载、是否抽象、自动注入模式、依赖关系、是否Primary Bean、初始化方法、销毁方法等等。
loadBeanDefinitions 的作用就是将咱的XML转化为BeanDefinitions然后放入上述DefaultListableBeanFactory实例的 beanDefinitionMap 中。
具体过程:protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = this.getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = this.getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
Resource进行包装编码,使用前文提到的ResourceLoader中的getResource方法拿到资源转为输入流
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
Set
接下来关键的地方来了,doLoadBeanDefinitions 方法
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//这里我就不解释了,总体意思就是将利用将DOM元素转化为BeanDefinitions ,有兴趣的化可以看下XML文档在整个过程中的校验、解析等操作,以及在register过程(DefaultBeanDefinitionsDocumentReader类)中使用到的代理技术。
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (beanFactory.containsBean("conversionService") && beanFactory.isTypeMatch("conversionService", ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService((ConversionService)beanFactory.getBean("conversionService", ConversionService.class));
}
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver() {
public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) {
return AbstractApplicationContext.this.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal);
}
});
}
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
String[] var3 = weaverAwareNames;
int var4 = weaverAwareNames.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 var5) {
String weaverAwareName = var3[var5];
this.getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader((ClassLoader)null);
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
/**
* 首先这个方法来自上文已经提到过的 DefaultListableBeanFactory ,所以 beanDefinitionNames 当然是在初始化容器的时候放进去的啦。*/public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List
//说明一点:Spring 中是有父子容器的,所以在查看源码时候,你会看到很多有关parent的东西
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
//不是抽象的 是单例 不是懒加载的
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {//实际上就是判断这个bean名字是不是以指定前缀开始的,默认“&”
final FactoryBean> factory = (FactoryBean>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction

protected
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between ‘" + beanName + "‘ and ‘" + dep + "‘");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"‘" + beanName + "‘ depends on missing bean ‘" + dep + "‘", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory
//真正实例化要执行的操作,会被getSingleton调用
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It‘s a prototype -> create a new instance.
.....
}
else {
.......
}public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory> singletonFactory) {
.....try {
//实例化,并改变标记为true
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
//注册进容器
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}
}Date date = context.getBean("date", Date.class);
这句话实际上调用就是上文中的getBean方法。getBean方法一上来就会先到cache中去寻找该Bean,找到直接返回。找不到会先在父容器中寻找,找到返回,找不到才会自己执行上述逻辑。