Effective Java 3
2020-12-13 04:41
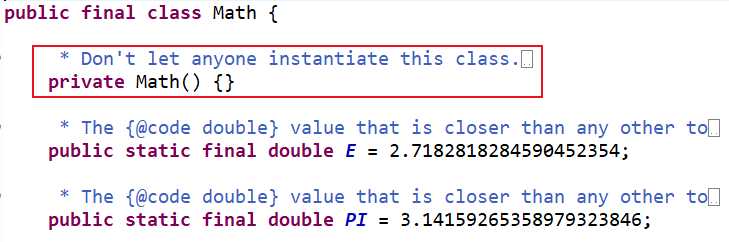
标签:如何 fat 管理 连接 next nta leo singleton 方法调用 《Effective Java》作者是美国的Joshua Bloch,连Gosling都说需要看的书,讨论的是更深层次的Java开发技术,适合于有一定Java基础的人看。 这是一本分享经验于指引您少走弯路的经典著作,针对如何编写高效、设计优良的程序提出了最实用的方针。 Item1 考虑用静态工厂方法代替构造器 1、优点 可读性强。 不会每次调用就通过构造器创建一个新的实例。 可以返回原始类型的任何子类型。 2、缺点 只有私有构造器无法被子类化。 Item 2 遇到多个构造器参数考虑用构建器Builder 1、传统的重叠构造器模式 如果读者想了解那些值是什么意思,必须很费劲的仔仔细细的数着这些参数来探究。如果客户端不小心颠倒了这些参数的顺序,编译器也不会报错,但是程序在运行时会出现错误行为。 JavaBeans模式 这样实例创建很容易,客户端代码读起来很清晰明朗,但是,程序员需要付出额外的努力来确保它的线程安全 Builder模式 builder设置方法返回this,形成了链式调用,这个一个流式的API,客户端代码很容易编写,更为重要的是易于阅读。 2、使用构建器的好处。 在多参数时写法优雅,参数具有可读性,保证线程安全,适合类的继承。 3、使用构建器的坏处。 花费会更高,因此在参数有许多的时候建议使用,特别是有很多可选参数时。 Item 3 Singleton的最佳实现方式是枚举类型 1、什么是枚举类 2、优点 提供序列化机制,甚至在反射机制下也能确保只有单例。 3、缺点 无法继承自除了Enum之外的超类以及其他子类进行继承。 Item 4 通过私有构造器强化不可实例化的能力 1、优点 在需要创建类似工具类等不需要实例化的类时,将构造器私有化,以保证该类在任何情况下都不会被实例化。 2、缺点 无法被继承 Item 5 使用依赖注入去连接资源 1、依赖注入 2、优点 对于一个行为由其他资源所参数化所决定的类来说,使用静态工具类或者单例是不适合的。而是应该当创建一个实例是将资源传入构造器。 Item 6 避免创建不必要的对象 1、优点 对于一些不会发生改变的变量或是常量,使用static块进行初始化,使某些类不会被重复创建,减少开销。例如 new String就是一个不好的习惯。 在构造器中使用静态工厂就是个不错的方法。重点是对静态的使用static(final)。自动装箱也很可能引起巨大的开销。 Item 7消除过期的对象引用 1、优点 例如对于Stack类中的数组当执行pop()操作后,被弹出的元素并不会自动被gc所回收。因此需要手动进行释放。 当一个类自己进行内存的管理时,这种状况就尤其要注意。 进行缓存时也需要注意这个问题。 对于监听器以及回调操作,也需要注意。 Item 8 尽量避免使用Finalizers 1、优点 由于Finalizers的优先级很低,不能保证Finalizers何时会被调用,会导致内存开销的增加,并且会大幅降低程序的性能。 永远不要Finalizers来更新持久状态。 对含有Finalizers方法的类进行子类化会有严重的安全隐患。 使用try-with-resources作为某些资源的结束方法。并且对于其状态是否被关闭需要在私有域中进行记录。这样其他方法调用时可以对状态进行检测。 Finalizers有两种合理的用法: 1、在忘记调用close方法时作为一张安全网,但这也只是一个不得以的备用措施,仍然会造成很大开销,并且不知何时会进行。 2、native peer (?) Item 9 更偏向使用 try-with-resources 块 1、try-with-resources 在try()中进行一个或多个的资源链接或读取。并且这些资源是必须被关闭的的,使用这个语法将会被自动关闭无需显示调用close方法。 在{}进行实际操作。 同样可以使用catch语句 2、优点 可以同时打开多个资源,并保证被关闭,而无需显式调用close方法。 exception不会被覆盖,可以查看每个exception. 参考:《Effective Java》第3版 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/WutingjiaWill/p/9139520.html Effective Java 3 标签:如何 fat 管理 连接 next nta leo singleton 方法调用 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/1906859953Lucas/p/11117694.html
public class NutritionFacts {
private final int servingSize; // (mL) required
private final int servings; // (per container) required
private final int calories; // (per serving) optional
private final int fat; // (g/serving) optional
private final int sodium; // (mg/serving) optional
private final int carbohydrate; // (g/serving) optional
public NutritionFacts(int servingSize, int servings) {
this(servingSize, servings, 0);
}
public NutritionFacts(int servingSize, int servings,
int calories) {
this(servingSize, servings, calories, 0);
}
public NutritionFacts(int servingSize, int servings,
int calories, int fat) {
this(servingSize, servings, calories, fat, 0);
}
public NutritionFacts(int servingSize, int servings,
int calories, int fat, int sodium) {
this(servingSize, servings, calories, fat, sodium, 0);
}
public NutritionFacts(int servingSize, int servings,
int calories, int fat, int sodium, int carbohydrate) {
this.servingSize = servingSize;
this.servings = servings;
this.calories = calories;
this.fat = fat;
this.sodium = sodium;
this.carbohydrate = carbohydrate;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NutritionFacts cocaCola =
new NutritionFacts(240, 8, 100, 0, 35, 27);
}
}
public class NutritionFacts {
// Parameters initialized to default values (if any)
private int servingSize = -1; // Required; no default value
private int servings = -1; // Required; no default value
private int calories = 0;
private int fat = 0;
private int sodium = 0;
private int carbohydrate = 0;
public NutritionFacts() { }
// Setters
public void setServingSize(int val) { servingSize = val; }
public void setServings(int val) { servings = val; }
public void setCalories(int val) { calories = val; }
public void setFat(int val) { fat = val; }
public void setSodium(int val) { sodium = val; }
public void setCarbohydrate(int val) { carbohydrate = val; }
public static void main(String[] args) {
NutritionFacts cocaCola = new NutritionFacts();
cocaCola.setServingSize(240);
cocaCola.setServings(8);
cocaCola.setCalories(100);
cocaCola.setSodium(35);
cocaCola.setCarbohydrate(27);
}
}
public class NutritionFacts {
private final int servingSize;
private final int servings;
private final int calories;
private final int fat;
private final int sodium;
private final int carbohydrate;
public static class Builder {
// Required parameters
private final int servingSize;
private final int servings;
// Optional parameters - initialized to default values
private int calories = 0;
private int fat = 0;
private int sodium = 0;
private int carbohydrate = 0;
public Builder(int servingSize, int servings) {
this.servingSize = servingSize;
this.servings = servings;
}
public Builder calories(int val)
{ calories = val; return this; }
public Builder fat(int val)
{ fat = val; return this; }
public Builder sodium(int val)
{ sodium = val; return this; }
public Builder carbohydrate(int val)
{ carbohydrate = val; return this; }
public NutritionFacts build() {
return new NutritionFacts(this);
}
}
private NutritionFacts(Builder builder) {
servingSize = builder.servingSize;
servings = builder.servings;
calories = builder.calories;
fat = builder.fat;
sodium = builder.sodium;
carbohydrate = builder.carbohydrate;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NutritionFacts cocaCola = new NutritionFacts.Builder(240, 8)
.calories(100).sodium(35).carbohydrate(27).build();
}
}
public class EnumTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("put:");
String input=in.next().toUpperCase();
Size size=Enum.valueOf(Size.class,input);
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(size.getAbbreviation());
System.out.println(Size.SMALL.getAbbreviation());
}
}
enum Size{
SMALL("S"),MEDIUM("M"),LARGE("L");
private String abbreviation;
private Size(String abbreviation){this.abbreviation=abbreviation;}
public String getAbbreviation(){return abbreviation;}
}
public class dependency {
private final String str;
public dependency(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
}
public Object pop() {
if (size == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
Object result = elements[--size];
elements[size] = null; // Eliminate obsolete reference
return result;
}
static void copy(String src, String dst) throws IOException {
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dst)) {
byte[] buf = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
int n;
while ((n = in.read(buf)) >= 0)
out.write(buf, 0, n);
}
}