__proto__ VS. prototype in JavaScript
2020-12-13 05:04
__proto__ is the actual object that is used in the lookup chain to resolve methods, etc. prototype is the object that is used to build __proto__ when you create an object with new:
( new Foo ).__proto__ === Foo.prototype; ( new Foo ).prototype === undefined;
How does __proto__ differ from constructor.prototype?
I‘ve been trying to wrap my head around this recently and finally came up with this "map" that I think sheds full light over the matter
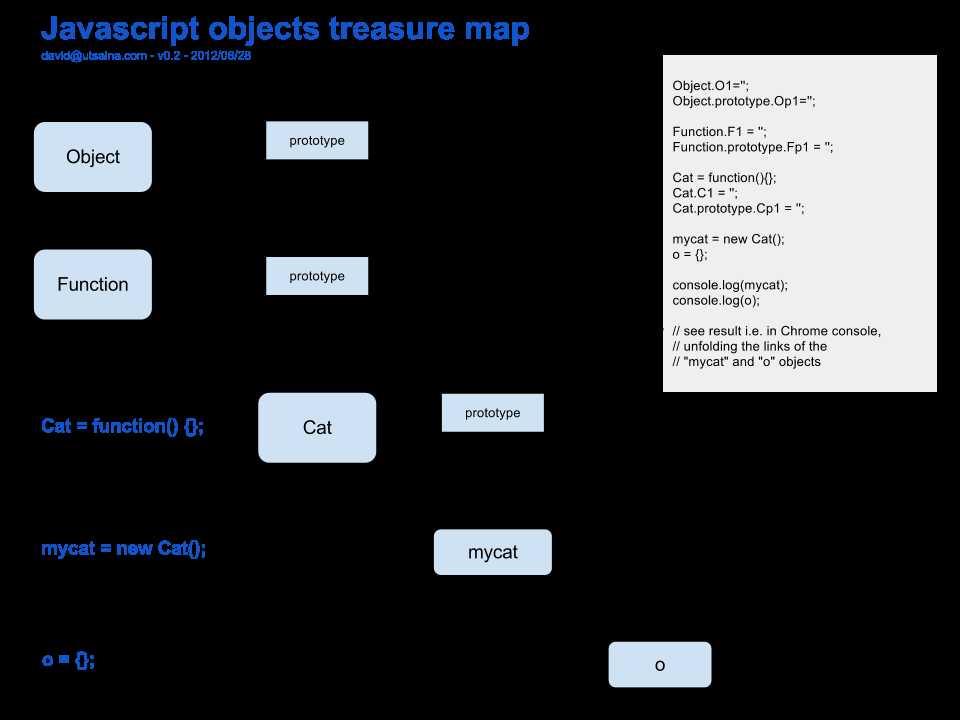
I know I‘m not the first one making this up but it was more interesting figuring it out that finding it :-). Anyway, after that I found e.g. this another diagram that I think says basicly the same:
Javascript object layout
The most surprising thing for me was discovering that Object.__proto__ points to Function.prototype, instead of Object.prototype, but I‘m sure there‘s a good reason for that :-)
I paste the code mentioned in the image here as well for if anyone wants to test it. Note that some properties are added to the objects for making easy to know where we are after some jumps:
Object.O1=‘‘; Object.prototype.Op1=‘‘; Function.F1 = ‘‘; Function.prototype.Fp1 = ‘‘; Cat = function(){}; Cat.C1 = ‘‘; Cat.prototype.Cp1 = ‘‘; mycat = new Cat(); o = {}; // EDITED: using console.dir now instead of console.log console.dir(mycat); console.dir(o);
The reason why Object.__proto__ points to Function.prototype is because Object() by itself is a native function that instantiates an empty object. Therefore, Object() is a function. You‘ll find that all the other major native types‘ __proto__ properties point to Function.prototype. Object, Function, String, Number, and Array all inherit the Function prototype.
文章标题:__proto__ VS. prototype in JavaScript
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/30365.html