python 第二章
2020-12-13 05:23
标签:mic asc inf error number 欧洲 今天 bre img python 第二章 标签:mic asc inf error number 欧洲 今天 bre img 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangshan33/p/11139803.html第二章
while 循环
# while -- 关键字(死循环)
# while 条件 冒号
# 缩进 循环体
# 停止while要点击红色停止,不能只关闭窗口
while True:
print("痒")
print("鸡你太美")
print("卡路里")
print("好运来")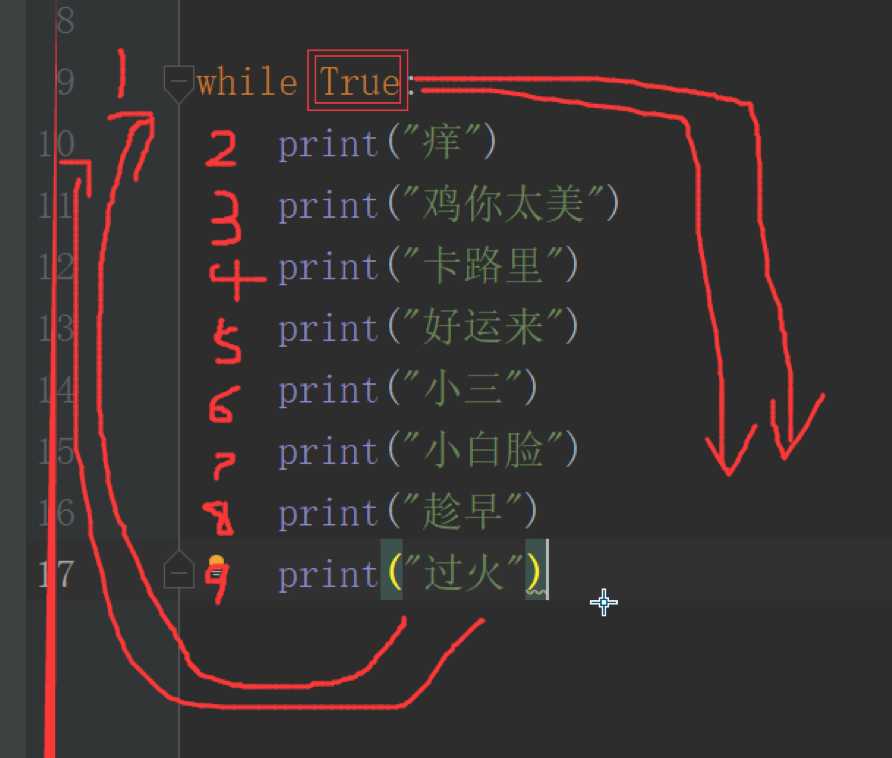
while False:
print("痒")
print("鸡你太美")
print("卡路里")
print("好运来")# 无输出
print(1)
while True:
print("痒")
print("鸡你太美")
print("卡路里")
print("好运来")
print(2)# 循环输出,print(2)不输出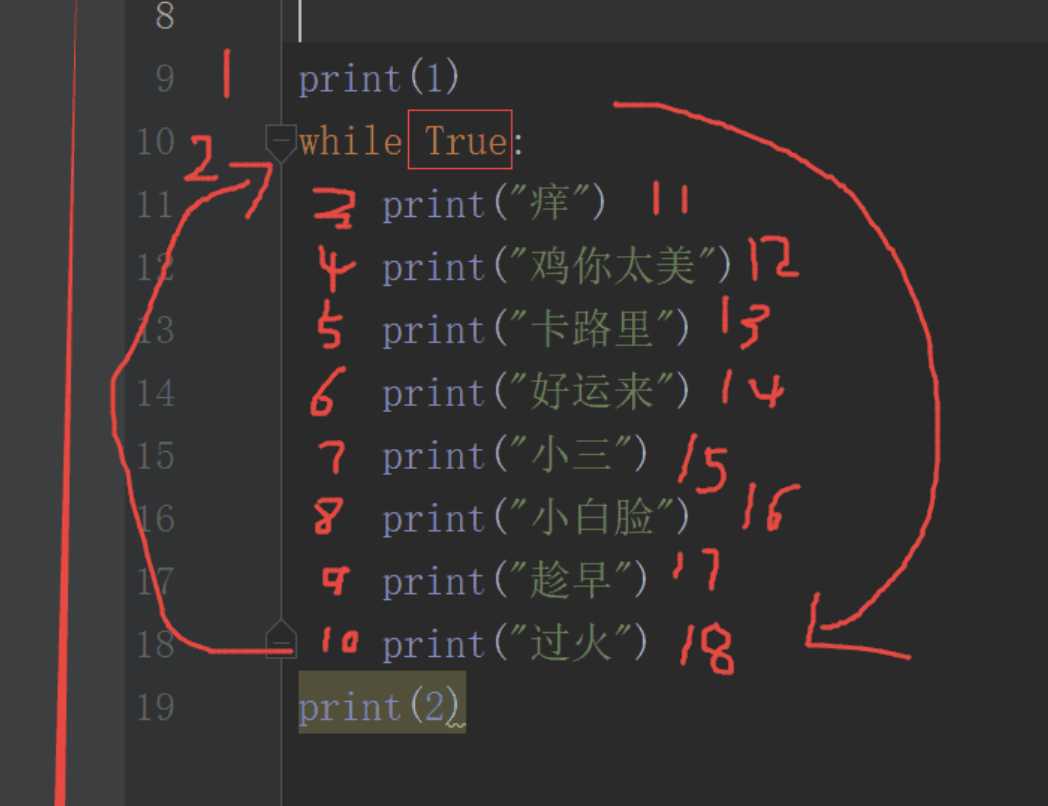
print(1)
while False:
print("痒")
print("鸡你太美")
print("卡路里")
print("好运来")
print(2)# 输出12
falg = True
while falg:
print(1)
print(2)# 循环输出1
# 通过数字转成布尔值
print(bool(1))
# 数字里面非0的都是True
count = 1
while count:
print(count)
count = count + 1# 循环输出,每次+1
# 正序
count = 1
while count 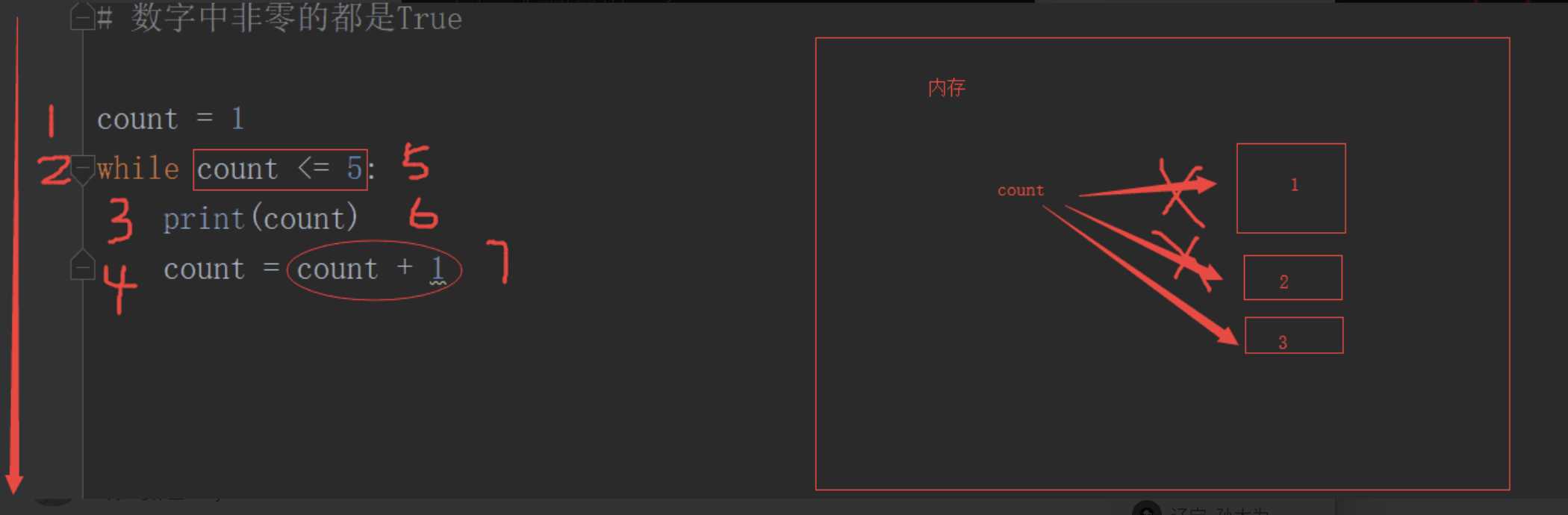
# 倒序
count = 5
while count:
print(count)
count = count - 1# 输出54321
# 正序打印从 25-57
count = 25
while count = 25:
print(count)
count = count - 1# break 终止当前循环,break下方的代码不会进行执行
while True:
print(123)
print(234)
break
print(345)
print(111)# 输出123234111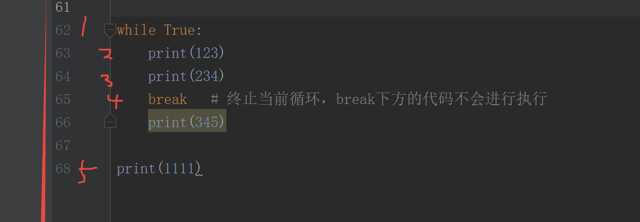
# continue 临时当作循环体中的最后一段代码
# 跳出当前循环,继续下次循环
# 下面的代码不会再执行
while True:
print(123)
print(234)
continue # 伪装成最后一段代码
print(345)
print(111)# 循环输出123234
# else 的用法
# 条件不成立跳出当前while循环
# 当为真的时候
while True:
print(111)
else:
print(222)# 循环输出111
while True:
print(111)
print(222)# 循环输出111
#当为假的时候
while False:
print(111)
else:
print(222)# 输出222
while False:
print(111)
print(222)# 输出222
#为真且有break
while True:
print(111)
break
else:
print(222)# 循环输出111
while True:
print(111)
break
print(222)# 循环输出111222
#为假且有break
while False:
print(111)
break
else:
print(222)# 循环输出222
while False:
print(111)
break
print(222)# 循环输出222# 总结:
# 打断循环的方式:
# 1.通过自己修改条件
# 2.break
# break -- 打破当前循环(终止当前循环)
# continue -- 跳出当前循环,继续下次循环(伪装成最后一段代码continue 什么时候用?)
# break和continue相同之处:以下代码均不执行字符串的格式化
a = "---info---"
b = "name"
c = "age"
d = "job"
e = "---end---"
print(a+b+c+d+e)# 输出
# ---info---nameagejob---end---
a = "---info---"
b = "name"
c = "age"
d = "job"
e = "---end---"
print(a+"\n"+b+"\n"+c+"\n"+d+"\n"+e)# 输出
# ---info---
# name
# age
# job
# ---end---
name = input('请输入姓名:')
age = input('请输入年龄:')
job = input('请输入职业:')
a = "---info---"
b = "name:"
c = "age:"
d = "job:"
e = "---end---"
print(a+'\n'+b+name+'\n'+c+age+'\n'+d+job+'\n'+e)# 输出
# 请输入姓名:张三
# 请输入年龄:25
# 请输入职业:python
# ---info---
# name:张三
# age:25
# job:python
# ---end---# %s 占位符 类型为s 是占的字符串类型的位置
# %d 占位符 类型为数字 是占的数字类型的位置
# s% 按照位置顺序传递,占位和补位一一对应
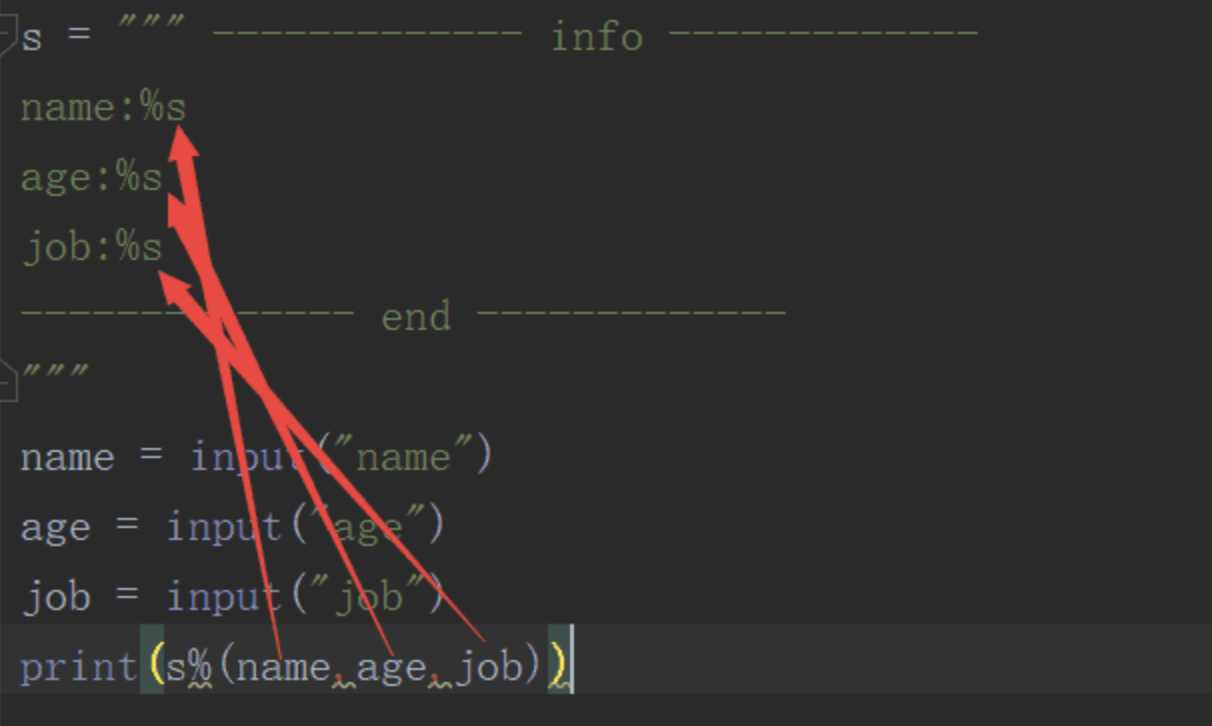
s = """
---info---
name:%s
age:%d
job:%s
---end---
"""
name = input("请输入姓名:")
age = int(input("请输入年龄:"))
job = input("请输入职业:")
print(s%(name,age,job))# 输出
# 请输入姓名:张三
# 请输入年龄:25
# 请输入职业:python
# ---info---
# name:张三
# age:25
# job:python
# ---end---
#多、少位置均不行
s = """
--info--
name:%s
age:%d
job:%s
---end---
"""
name = input("name")
age = int(input("age"))
job = input("job")
print(s%(name,job,))
# 少位置报错:TypeError: %d format: a number is required, not str
# %% 两个百分号为转义
num = input("学习进度:")
B = "学习进度为:%s %%"
print(B%(num))# 输出学习进度为:30 %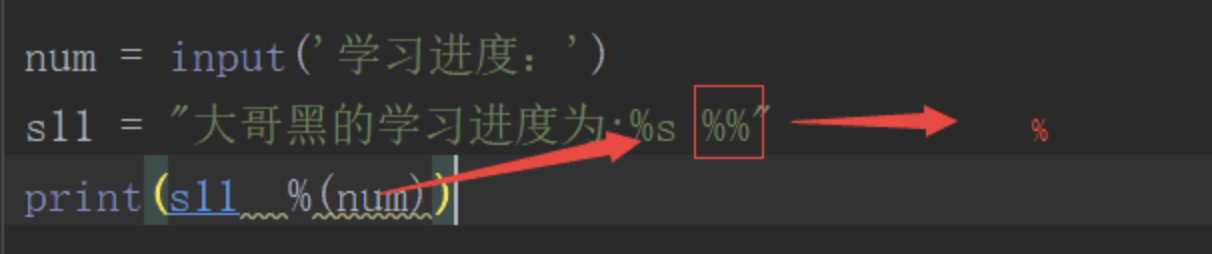
sll = "学习进度为:%s"
print(sll%("不错"))# 输出学习进度为:不错
# f也可以做格式化
s = f"{1}{2}{3}"
print(s)# 输出123
s = f"今天下雨了{input('>>>')}"
print(s)# 输出 今天下雨了+输入的内容运算符
# 算术运算符
# + - * /
# // (整除--地板除)
# python2跟python3的除有区别
# ptyhon2 获取到的是整数
# python3 获取到的是小数 浮点型
print(5//2)# 输出2
# ** 幂 (次方)
print(3**2)# 输出9
# % 模 (取余)
print(5%2)# 输出1
# 比较运算符
# >
# =
# not > and > or
# and 从左向右执行
print(9 and 1 or not False and 8 or 0 and 7 and False)# 输出1
print(9 and 1 or True and 8 or 0 and 7 and False) # not False = True
print(1 or True and 8 or 0 and 7 and False)# 9 and 1 取1
print(1 or 8 or 0 and 7 and False)# True and 8 取8
print(1 or 8 or 0 and False)# 7 and False 取False
print(1 or 8 or 0)# 0 and False 取0
# 1 or 8 or 0 取1
# 成员运算符
# in 存在
# not in 不存在
s = "abc"
if "ab" in s:
print(True)
else:
print(False)# 输出True
s = "abc"
if "ab" not in s:
print(True)
else:
print(False)# 输出False编码初识
# ascii (美国) 不支持中文
# gbk (国标) 英文8位,中文16位
# unicode(万国码) 英文16位 中文32位
# utf-8 (可变长编码) 英文8位 欧洲文16位 亚洲24位
# linux -- utf -8
# mac -- utf -8
# windows -- gbk
# 单位转换:
# 1字节 = 8 位
# 1Bytes = 8bit
# 1024Bytes = 1KB
# 1024KB = 1MB
# 1024MB = 1GB
# 1024GB = 1TB
# 1024TB = 1PB
# 1024PB = 1EB
# 1024EB = 1ZB
# 1024ZB = 1YB
# 1024YB = 1NB
# 1024NB = 1DB今日总结
# 1、while循环 死循环:
# while 条件 冒号
# 缩进 循环体
#
# 打断死循环:
# break:终止当前循环
# 改变条件:自动自定义修改控制执行次数
#
# 关键字:
# break:终止当前循环
# continue:伪装成循环体中最后一行代码(跳出本次循环,继续下次循环)
# while else:while 条件成立,后面代码不执行;条件不成立,继续执行else
#
# while else
# while 条件成立的时候不执行
# 条件成立执行else
#
# 2、字符串格式化:
# % 占位
# %s 占字符串类型的位
# %d 占数字类型的位
# %% 转义成普通的百分号
# 变量名%() 起到连接的作用
# s = "您好%s"
# s%("我好")
# print(s%("我好"))
# f"{变量名}{字符串}{}"3.6以及以上才能使用
#
# 3、运算符:
# 算数运算符: + - * / // ** %
# 比较运算符: > = 优先级:not > and > or
# 成员运算符: in not in
#
# 4、编码:
# 编码集(密码本)
# ascii:不支持中文
# gbk:
# 英文 8位 1字节
# 中文 16位 2字节
# unicode:
# 英文 16位 2字节
# 中文 32位 4字节
# utf-8:
# 英文 8位 1字节
# 欧洲 16位 2字节
# 亚洲 24位 3字节
# # 单位转换:
# # 1字节 = 8位
# # 1Bytes = 8bit ***
# # 1024Bytes = 1KB
# # 1024KB = 1MB
# # 1024MB = 1GB
# # 1024GB = 1TB