MonkeyDevcie API 实践全记录
2020-12-13 13:37
1. 背景
使用SDK自带的NotePad应用作为实践目标应用,目的是对MonkeyDevice拥有的成员方法做一个初步的了解。
下面是官方列出的方法的Overview。
|
Return Type |
Methods |
Comment |
|
void |
broadcastIntent (string uri, string action, string data, string mimetype, iterable categories dictionary extras, component component, iterable flags) Broadcasts an Intent to this device, as if the Intent were coming from an application. |
|
|
void |
drag (tuple start, tuple end, float duration, integer steps) Simulates a drag gesture (touch, hold, and move) on this device‘s screen. |
|
|
object |
getProperty (string key) Given the name of a system environment variable, returns its value for this device. The available variable names are listed in the detailed description of this method. |
|
|
object |
getSystemProperty (string key) . The API equivalent of adb shell getprop use by platform developers. |
|
|
void |
installPackage (string path) Installs the Android application or test package contained in packageFile onto this device. If the application or test package is already installed, it is replaced. |
Obsolete,返回值是Boolean |
|
dictionary |
instrument (string className, dictionary args) Runs the specified component under Android instrumentation, and returns the results in a dictionary whose exact format is dictated by the component being run. The component must already be present on this device. |
|
|
void |
press (string name, dictionary type) Sends the key event specified by type to the key specified by keycode. |
|
|
void |
reboot (string into) Reboots this device into the bootloader specified by bootloadType. |
|
|
void |
removePackage (string package) Deletes the specified package from this device, including its data and cache. |
Obsolete,返回值是Boolean |
|
object |
shell (string cmd) Executes an adb shell command and returns the result, if any. |
|
|
void |
startActivity (string uri, string action, string data, string mimetype, iterable categories dictionary extras, component component, flags) Starts an Activity on this device by sending an Intent constructed from the supplied arguments. |
|
|
MonkeyImage |
takeSnapshot() Captures the entire screen buffer of this device, yielding a MonkeyImage object containing a screen capture of the current display. |
|
|
void |
touch (integer x, integer y, integer type) Sends a touch event specified by type to the screen location specified by x and y. |
|
|
void |
type (string message) Sends the characters contained in message to this device, as if they had been typed on the device‘s keyboard. This is equivalent to callingpress() for each keycode in message using the key event type DOWN_AND_UP. |
|
|
void |
wake () Wakes the screen of this device. |
|
事实上官方这个表是没有及时更新的,我如今手头上用到的MonkeyRunner是当前最新的,里面就拥有好几个官网没有列出来的API,我怀疑是不是自从UIAutomator在03年出来后,google就不打算再继续维护MonkeyRunner了?假设有朋友知道事实的话,还麻烦告知。
下面是我整理出来的源代码多出来的可用公共API列表
|
Return Type |
Methods |
Comment |
|
HierarchyViewer |
getHierarchyViewer(PyObject args[], String kws[]) 获取一个HierarchyViewer对象 |
请查看《MonkenRunner通过HierarchyViewer定位控件的方法和建议》 |
|
PyList |
getPropertyList(PyObject args[], String kws[]) |
取得全部的property属性键值 |
|
PyList |
getViewIdList(PyObject args[], String kws[]) |
Failed |
|
MonkeyView |
getViewById(PyObject args[], String kws[]) |
Failed |
|
MonkeyView |
getViewByAccessibilityIds(PyObject args[], String kws[]) |
Failed |
|
MonkeyView |
getRootView(PyObject args[], String kws[]) |
Failed |
|
PyList |
getViewsByText(PyObject args[], String kws[]) |
Failed |
但可惜的是在本人尝试以上多出来的API的时候,发现除了最上面两个可用之外,其它的都不可用并抛出错误。且网上资料少的可怜,别人碰到相同的问题也找不到解决的方法。所以本人怀疑这些“隐藏”API是不是并没有完好,或者说google不准备完好,所以才没有列出到官网上面去。本人用的SDK tools和Platform tools已经是当前最新的23.0.2和20.
一个台湾网友碰到的问题描写叙述:http://imsardine.simplbug.com/note/monkeyrunner/api/hierarchy-viewer.html
2. Void broadcastIntent
(string uri, string action,string data, string mimetype, iterable categories dictionary extras, componentcomponent, iterable flags)
2.1 分析
本人理解的此方法的本意是想广播一个Intent给我们的AndroidDevice,目标应用接收到该Intent做对应的处理,比方打开一个Activity等。但在我的多次尝试下并没有成功!
targetDevice.broadcastIntent(action='android.intent.action.INSERT',
mimetype='vnd.android.cursor.dir/contact',
extras = {'name':'user1501488', 'phone':'123-15489'}
假设使用相同的參数,使用以下的startActivity是没有问题的。
targetDevice.startActivity(action='android.intent.action.INSERT',
mimetype='vnd.android.cursor.dir/contact',
extras = {'name':'user1501488', 'phone':'123-15489'})
google了半天网上根本找不到这种方法的使用样例,倒是stackOverFlow上有人建议用Shell来达到相同的效果。
targetDevice.shell("am start -a android.intent.action.INSERT -t vnd.android.cursor.dir/contact -e name 'Donald Duck' -e phone 555-1234").
所以可见这种方法并没有多少人在用,原因应该是它全然能够用上面介绍的两个方法替代。
3. void startActivity
(string uri, string action, string data, string mimetype, iterable categories dictionary extras, component component, flags)
3.1 演示样例
targetDevice.startActivity(action='android.intent.action.VIEW',
mimetype='vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.google.note')
使用component来启动一个Activity:
targetDevice.startActivity(component="com.example.android.notepad/com.example.android.notepad.NotesList")
使用action,mimetype和指定extras參数来启动一个Activity:
targetDevice.startActivity(action='android.intent.action.INSERT',
mimetype='vnd.android.cursor.dir/contact',
extras = {'name':'user1501488', 'phone':'123-15489'})
3.2 分析
4. void drag (tuple start, tuple end, floatduration, integer steps)
这种方法的目的是按住一个控件然后把她拖动到其它位置
4.1 实例
viewer = targetDevice.getHierarchyViewer()
note = viewer.findViewById('id/text1')
point = viewer.getAbsoluteCenterOfView(note)
startX = point.x
startY = point.y
targetDevice.drag((startX,startY),(startX,startY),1)
targetDevice.press('KEYCODE_BACK', MonkeyDevice.DOWN_AND_UP)
4.2 分析和建议
以上演示样例是通过drag的方法来模拟LongPress,仅仅要把參数中的起始坐标和目标坐标都设置成相同一个值,然后时常设置成一个有效的值就好了。
5 Object getProperty (string key)
通过环境变量的key来获得其相应的值。下面是官方提供的可用化境变量列表
|
Property Group |
Property |
Description |
Notes |
|
build |
board |
Code name for the device‘s system board |
See Build |
|
brand |
The carrier or provider for which the OS is customized. |
|
|
|
device |
The device design name. |
|
|
|
fingerprint |
A unique identifier for the currently-running build. |
|
|
|
host |
|
|
|
|
ID |
A changelist number or label. |
|
|
|
model |
The end-user-visible name for the device. |
|
|
|
product |
The overall product name. |
|
|
|
tags |
Comma-separated tags that describe the build, such as "unsigned" and "debug". |
|
|
|
type |
The build type, such as "user" or "eng". |
|
|
|
user |
|
|
|
|
CPU_ABI |
The name of the native code instruction set, in the form CPU type plus ABI convention. |
|
|
|
manufacturer |
The product/hardware manufacturer. |
|
|
|
version.incremental |
The internal code used by the source control system to represent this version of the software. |
|
|
|
version.release |
The user-visible name of this version of the software. |
|
|
|
version.sdk |
The user-visible SDK version associated with this version of the OS. |
|
|
|
version.codename |
The current development codename, or "REL" if this version of the software has been released. |
|
|
|
display |
width |
The device‘s display width in pixels. |
SeeDisplayMetricsfor details. |
|
height |
The device‘s display height in pixels. |
|
|
|
density |
The logical density of the display. This is a factor that scales DIP (Density-Independent Pixel) units to the device‘s resolution. DIP is adjusted so that 1 DIP is equivalent to one pixel on a 160 pixel-per-inch display. For example, on a 160-dpi screen, density = 1.0, while on a 120-dpi screen, density = .75. The value does not exactly follow the real screen size, but is adjusted to conform to large changes in the display DPI. See density for more details. |
|
|
|
am.current |
package |
The Android package name of the currently running package. |
The am.currentkeys return information about the currently-running Activity. |
|
action |
The current activity‘s action. This has the same format as the name attribute of the action element in a package manifest. |
|
|
|
comp.class |
The class name of the component that started the current Activity. See comp.package for more details. |
|
|
|
comp.package |
The package name of the component that started the current Activity. A component is specified by a package name and the name of class that the package contains. |
|
|
|
data |
The data (if any) contained in the Intent that started the current Activity. |
|
|
|
categories |
The categories specified by the Intent that started the current Activity. |
|
|
|
clock |
realtime |
The number of milliseconds since the device rebooted, including deep-sleep time. |
SeeSystemClock for more information. |
5.1演示样例
displayWidth =targetDevice.getProperty ('display.width')
printdisplayWidth.encode('utf-8')
displayHight =targetDevice.getProperty('display.width')
printdisplayHight.encode('utf-8')
5.2 分析和建议
以上演示样例的目的是获得目标设备的长和高,当我们使用坐标点来操作控件的时候,调试的时候在一台机器上通过了,可是假设换了另外一个屏幕大小不一样的机器的话就会失败,由于控件的坐标点位置可能就变了。这个时候我们就须要用到演示样例中的连个属性来动态计算控件在不同屏幕大小的设备上面的坐标点了。
这里须要注意參数应该填写的格式是以上列表中前两列的组合PropertyGroup.Property
6. Object getSystemProperty (string key)
6.1 演示样例
displayWidth = targetDevice.getSystemProperty ('service.adb.tcp.port')
print displayWidth.encode('utf-8')
6.2 分析和建议
依据官网的描写叙述,这个函数和getProperty函数应该有相同的功能(Synonym for getProperty().),使用的属性表也如上面的属性列表一样。可是依照我的实践并不是如此,只是它确实如官方描写叙述的等同于命令“adb
shell getprop
以上的样例是获取adb这个服务所打开的TCP端口,等同于例如以下的shell命令:“adb shell getprop service.adb.tcp.port“
假设我尝试使用以下的方法去获得设备的长度,返回的结果事实上会是None
displayWidth = targetDevice.getSystemProperty ('display.width')
print displayWidth.encode('utf-8')
7 Boolean installPackage (string path)
7.1演示样例
if True == targetDevice.installPackage('D:\\Projects\\Workspace\\PythonMonkeyRunnerDemo\\apps\\MPortal.apk'):
print "Installationfinished successfully"
else:
print "Failedto install the apk"
7.2 分析和建议
这里有两点须要注意的:
- 官方站点描写叙述的这个API是没有返回值的(见背景中的表),而最新版本号的API里面是Boolean值。
- 參数输入的应该是PC端这边的Local路径而非目标系统的Local路径。
注意这里碰到一个路径问题,假设我的路径写成:
‘D:\Projects\Workspace\PythonMonkeyRunnerDemo\apps\MPortal.apk‘
那么会出现下图这种错误:
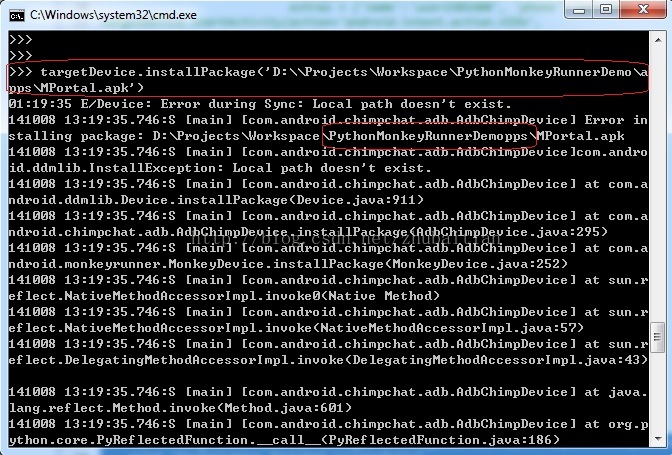
假设在“apps”前面加多个转义符就没有问题:
‘D:\Projects\Workspace\PythonMonkeyRunnerDemo\\apps\MPortal.apk‘
所以这里MonkeyRunner处理路径字串应该是存在Bug的,可是时间问题就先不去研究,建议全部路径的话“\“都加上转义符就好了
‘D:\\Projects\\Workspace\\PythonMonkeyRunnerDemo\\apps\MPortal.apk‘
8 boolean removePackage(string package)
8.1 演示样例
if True == targetDevice.removePackage('com.majcit.portal'):
print "Succeed toremove the package"
else:
print "Failedto remove teh package"
8.2 注意事项
· 如上面的installPackageAPI一样,官网描写叙述的该API是没有返回值的,而最新的是返回boolean值
9. dictionary instrument (string className, dictionary args)
9.1 演示样例
仅仅指定第一个參数(将会跑全部指定Component下的全部case+ NotePad项目本身的使用了Instrumentation的用例,详细意思请看下一节的分析)
dict = targetDevice.instrument('com.example.android.notepad.tryout/android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner')
print dict
指定仅仅跑当中的一个Case:
dict = dict = targetDevice.instrument('com.example.android.notepad.tryout/android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner',
{'class':'com.example.android.notepad.tryout.TCCreateNote'})
print dict
9.2 分析
这里首先须要看下官方的描写叙述
Runs the specifiedcomponent under Android instrumentation, and returns the results in adictionary whose exact format is dictated by the component being run. Thecomponent must already be present on this device
这里重点是第一句“Runs the specified component under Android instrumentation“,剩下的是说返回值依据模块不一样而有所区别。那么第一句翻译过来就是”执行使用了Anroid Instrumentation的指定模块“。那么到底什么是使用了Android Instrumentation的指定模块呢?事实上假设你实用过Robotium的话应该知道,脚本的每一个case都是从Instrumentation相关的类中继承下来的。
下面是本人之前写的一个Robotium的測试case(详细请查看本人之前的一篇《Robotium创建一个Note的实例》,能够看到它是继承于“ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2”的,事实上它就满足了刚才的描写叙述“使用了Anroid Instrumentation的指定模块“
package com.example.android.notepad.tryout;
import com.robotium.solo.Solo;
import android.test.ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2;
import android.app.Activity;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public class TCCreateNote extends ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2{
private static Solo solo = null;
public Activity activity;
private static final int NUMBER_TOTAL_CASES = 2;
private static int run = 0;
private static Class> launchActivityClass;
//相应re-sign.jar生成出来的信息框里的两个值
private static String mainActiviy = "com.example.android.notepad.NotesList";
private static String packageName = "com.example.android.notepad";
static {
try {
launchActivityClass = Class.forName(mainActiviy);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public TCCreateNote() {
super(packageName, launchActivityClass);
}
@Override
public void setUp() throws Exception {
//setUp() is run before a test case is started.
//This is where the solo object is created.
super.setUp();
//The variable solo has to be static, since every time after a case's finished, this class TCCreateNote would be re-instantiated
// which would lead to soto to re-instantiated to be null if it's not set as static
if(solo == null) {
TCCreateNote.solo = new Solo(getInstrumentation(), getActivity());
}
}
@Override
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
//Check whether it's the last case executed.
run += countTestCases();
if(run >= NUMBER_TOTAL_CASES) {
solo.finishOpenedActivities();
}
}
public void testAddNoteCNTitle() throws Exception {
solo.clickOnMenuItem("Add note");
solo.enterText(0, "中文标签笔记");
solo.clickOnMenuItem("Save");
solo.clickInList(0);
solo.clearEditText(0);
solo.enterText(0, "Text 1");
solo.clickOnMenuItem("Save");
solo.assertCurrentActivity("Expected NotesList Activity", "NotesList");
solo.clickLongOnText("中文标签笔记");
solo.clickOnText("Delete");
}
public void testAddNoteEngTitle() throws Exception {
solo.clickOnMenuItem("Add note");
solo.enterText(0, "English Title Note");
solo.clickOnMenuItem("Save");
solo.clickInList(0);
solo.clearEditText(0);
solo.enterText(0, "Text 1");
solo.clickOnMenuItem("Save");
solo.assertCurrentActivity("Expected NotesList Activity", "NotesList");
solo.clickLongOnText("English Title Note");
solo.clickOnText("Delete");
}
}
那么我们先在目标机器上运行命令“pm list instrumentation”看能否列出这个“Component”:
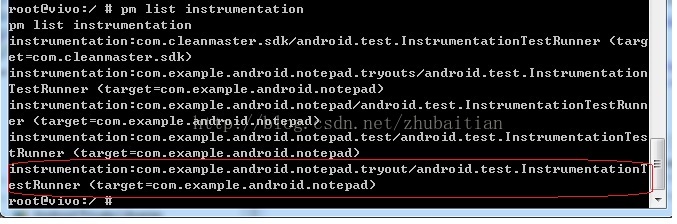
这当中哪一个是我们想要的呢?这要看我们的Robotium測试项目中的AndroidManifest.xml的定义了,依据下图的packageName再对比上图的输出我们就定位到我们想要的Component了:
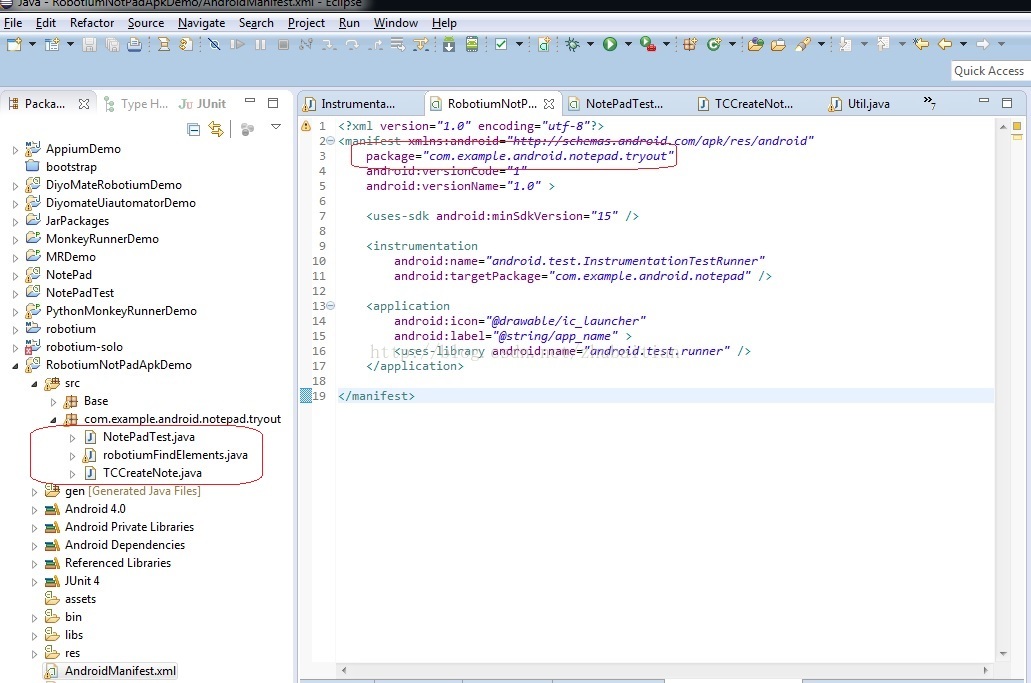
假设我们调用这种方法的时候仅仅是填写了第一个參数的话,上图处在”com.example.andriod.notepad.tryout”这个Component下的全部三个方法都会运行。但在我的測试中,发现除了跑这个Case之外,它还跑多了一些步骤,就是额外的多创建了一个Note1。我查了半天,发现原来我之前除了编写了基于ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2的Robotium的这个项目之外,还在NoetePad这个项目上直接用InstrumentationTestCase写了一个基于Instrumentation的測试用例,做得事情就是添加一个Note1,详细请看本人另外一篇blog《SDK Instrumentation创建一个Note的实例》
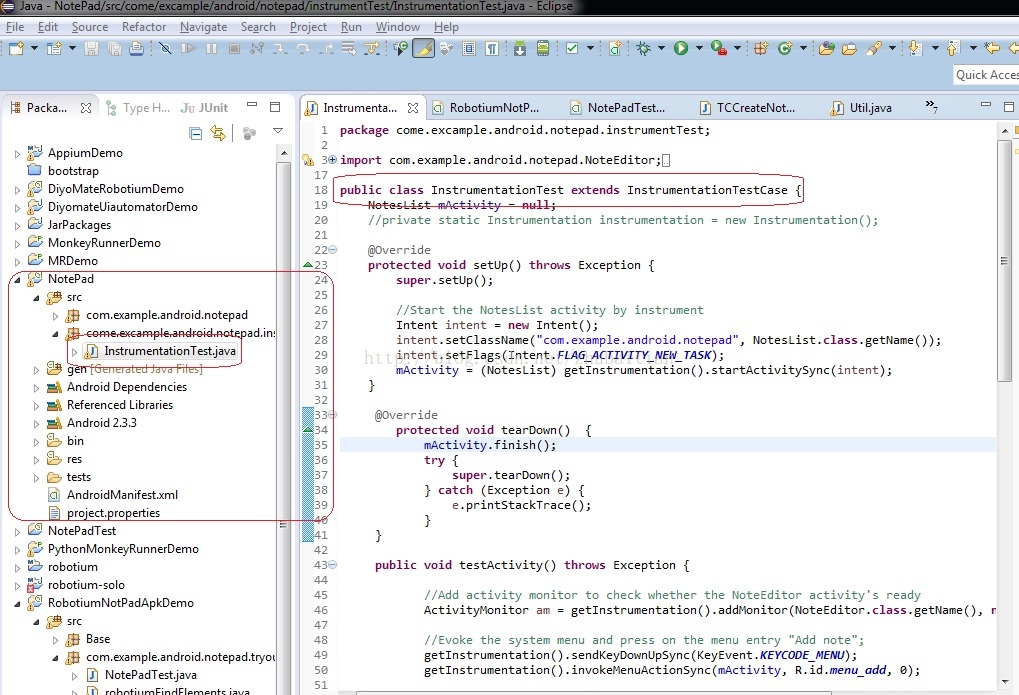
事实上调用这种方法相当于在shell脚本上运行例如以下的命令:
am instrument -w -r -e class com.example.android.notepad.tryout.TCCreateNote com.example.android.notepad.tryout/android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner
最后提一下的是,我们的脚本在运行演示样例的时候大概5秒左右就会失败,但其实在设备端全部的指定component的測试用例已经在运行的了。要解决问题须要又一次编译源代码,这里就免了,详细请查看:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/4264057/android-cts-is-showing-shellcommandunresponsiveexception-on-emulator
这里尝试做一个简单的总结
- 调用此方法之前先要找到第一个參数怎么写:运行命令“pm list instrumentation”
- 调用次方法假设不指定第一个參数会运行指定Component以下的全部測试脚本和目标应用包中全部用到Instrumentation的測试用例
- 调用此方法终于其实是在目标机器上依据指定的參数运行“am instrument xxxx”
10 void press (string name, integer type)
10.1 演示样例
targetDevice.press('KEYCODE_BACK',MonkeyDevice.DOWN_AND_UP)
10.2 分析
这种方法的目的是发送一个指定的Key事件到Android设备以触发对应的动作,比方演示样例中发送“KEYCODE_BACK”这个key到设备端去触发”返回“键的按下和升起(也就是点击)的动作。
详细Key的Code请查看:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/KeyEvent.html
第二个參数是指导该Key应该怎样Behave,比方先按下去,休眠一秒再弹起来(事实上就相当于一个长按的动作)。详细支持behavior在本MonkeyDevice这个类的成员变量里有定义好:
|
Type |
Constants |
Notes |
Comment |
|
int(官网是string,下同) |
DOWN |
Use this with the type argument of press() or touch() to send a DOWN event. |
|
|
int |
UP |
Use this with the type argument of press() or touch() to send an UP event. |
|
|
int |
DOWN_AND_UP |
Use this with the type argument of press() or touch() to send a DOWN event immediately followed by an UP event. |
|
|
int |
MOVE |
TBD |
官网没有列出来 |
11. void touch (integer x,integer y, integer type)
11.1 演示样例
viewer = targetDevice.getHierarchyViewer()
note = viewer.findViewById('id/text1')
point = viewer.getAbsoluteCenterOfView(note)
startX = point.x
startY = point.y
targetDevice.touch(startX,startY,MonkeyDevice.DOWN_AND_UP)
11.2 分析
这个和上面的press方法在结果上有点类似,可是本方法是接受坐标进行点击的,而上面方法接受的是keycode。
第二个參数同上。
12. void type (string message)
viewer =targetDevice.getHierarchyViewer()
note = viewer.findViewById(‘id/text1‘)
point = viewer.getAbsoluteCenterOfView(note)
startX = point.x
startY = point.y
targetDevice.touch(startX,startY,MonkeyDevice.DOWN_AND_UP)
MonkeyRunner.sleep(3)
targetDevice.type(‘NewContent‘)
12.1 演示样例
viewer = targetDevice.getHierarchyViewer()
note = viewer.findViewById('id/text1')
point = viewer.getAbsoluteCenterOfView(note)
startX = point.x
startY = point.y
targetDevice.touch(startX,startY,MonkeyDevice.DOWN_AND_UP)
MonkeyRunner.sleep(3)
targetDevice.type('NewContent')
12.2 分析
指定一串字符串进行模拟键盘输入,等同于调用press方法依照一个一个的keycode用MonkeyDevice的DOWN_AND_UP进行输入。
尝试时发现中文不支持,鉴于项目不须要用到这样的手机键盘,所以节省时间暂不研究。
13. Wake()
13.1演示样例
targetDevice.wake()
13.2 分析
注意这里仅仅是唤醒屏保,假设手机已经锁屏的话你是不能唤醒的。所以尝试这个API的时候要注意把锁屏功能先关闭掉。
14. MonkeyImange takeSnapshot()
14.1 演示样例
#Connect to the target targetDevice
targetDevice = MonkeyRunner.waitForConnection()
easy_device = EasyMonkeyDevice(targetDevice) #touch a button by id would need this
targetDevice.startActivity(component="com.example.android.notepad/com.example.android.notepad.NotesList")
#invoke the menu options
MonkeyRunner.sleep(6)
#targetDevice.press('KEYCODE_MENU', MonkeyDevice.DOWN_AND_UP);
'''
public ViewNode findViewById(String id)
* @param id id for the view.
* @return view with the specified ID, or {@code null} if no view found.
'''
#MonkeyRunner.alert("Continue?", "help", "Ok?")
pic = targetDevice.takeSnapshot()
pic = pic.getSubImage((0,38,480,762))
newPic = targetDevice.takeSnapshot()
newPic = newPic.getSubImage((0,38,480,762))
print (newPic.sameAs(pic,1.0))
newPic.writeToFile('./shot1.png','png')
14 object shell(string cmd)
14.1 演示样例
res = targetDevice.shell('ls /data/local/tmp|grep note')
print res
14.2 分析
这个命令等同于你直接在命令行上“adb shell $command”
15 void reboot(string into)
其它參数没实用到所以也就没有尝试,只尝试了不带參数的情况,结果就是直接reboot目标设备了
targetDevice.reboot()这里有点须要提下的是,假设你是在MonkeyRunner命令行下运行这条命令的话,就算目标机器重新启动,整个MonkeyRunner的环境还是依旧有效的。也就是说你假设继续打进一条"targetDevice.reboot()",你的设备就会再重新启动一次。
上一篇:c#分页读取GB文本文件