Window窗口布局 --- DecorView浅析
2020-12-13 14:44
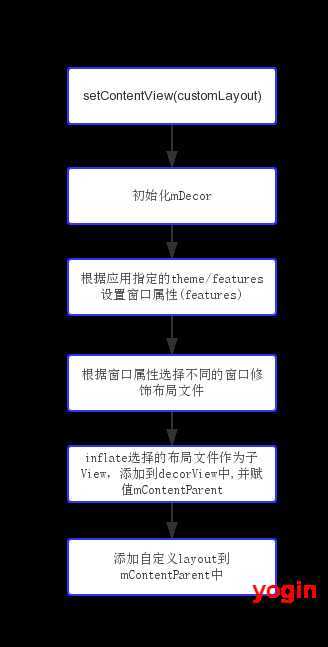
标签:des android style blog http io color os ar 开发中,通常都是在onCreate()中调用setContentView(R.layout.custom_layout)来实现想要的页面布局,我们知道,页面都是依附在窗口之上的,而DecorView即是窗口最顶层的视图。Android frameworks中,与窗口视图处理相关的类,主要是Window及其实现类PhoneWindow DecorView其实是PhoneWindow中的一个内部类,本质上也是一个View,其只是扩展了FrameLayout的实现 页面layout被添加至窗口Window的流程大致如下: 1,Activity中调用setContentView(R.layout.custom_layout), 具体实现为PhoneWindow中的同名方法 2, PhoneWindow执行setContentView(int layoutResource) 3, PhoneWindow.installDecor() 4, PhoneWindow.generateLayout(DecorView decor) 从上述步骤中,可以看出为什么在代码中必须要在setContentView(...)之前才能执行requestWindowFeature(...) 5, 最后页面中设置的自定义layout会被添加到mContentParent中 所以,Window窗口的布局层次结构(features不同,可能标题栏不存在, 这种情况下,窗口修饰视图区域与mContentParent内容区域重叠)如下所示: 示例: Activity代码: activity_decor.xml: Window窗口布局 --- DecorView浅析 标签:des android style blog http io color os ar 原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yogin/p/4061050.htmlpublic class PhoneWindow extends Window implements MenuBuilder.Callback {
//...
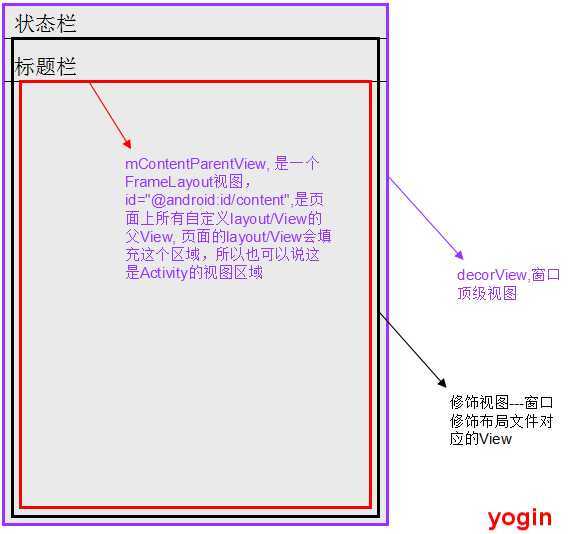
//窗口顶层View
private DecorView mDecor;
//所有自定义View的根View, id="@android:id/content"
private ViewGroup mContentParent;private final class DecorView extends FrameLayout implements RootViewSurfaceTaker {
//...
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
//getWindow()获取的即是PhoneWindow对象
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
}public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
//初始,mContentParent为空
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
//inflate自定义layout, 并将mContentParent作为其根视图
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent); private void installDecor() {
if (mDecor == null) {
//new一个DecorView
mDecor = generateDecor();
mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true);
if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) {
mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable);
}
}
if (mContentParent == null) {
//这一步会设置窗口的修饰文件,并将id为ID_ANDROID_CONTENT的view find出来作为返回值赋值给mContentParent
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
//4.1,获取, 节点指定的themes或者代码requestWindowFeature()中指定的Features, 并设置
TypedArray a = getWindowStyle();
//...
//4.2,获取窗口Features, 设置相应的修饰布局文件,这些xml文件位于frameworks/base/core/res/res/layout下
int layoutResource;
int features = getLocalFeatures();
if ((features & ((1 ) {
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(com.android.internal.R.attr.dialogTitleIconsDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
layoutResource = com.android.internal.R.layout.screen_title_icons;
}
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
} else if ((features & ((1 ) {
layoutResource = com.android.internal.R.layout.screen_progress;
//...
mDecor.startChanging();
//4.3, 将上面选定的布局文件inflate为View树,添加到decorView中
View in = mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);
decor.addView(in, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
//将窗口修饰布局文件中id="@android:id/content"的View赋值给mContentParent, 后续自定义的view/layout都将是其子View
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
if (contentParent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Window couldn‘t find content container view");
}
//...mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
//设置窗口无标题栏
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_decor);
}
RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".DecorActivity">
TextView
android:text="@string/hello_world"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
TextView
android:text="@string/hello_world"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"/>
RelativeLayout>
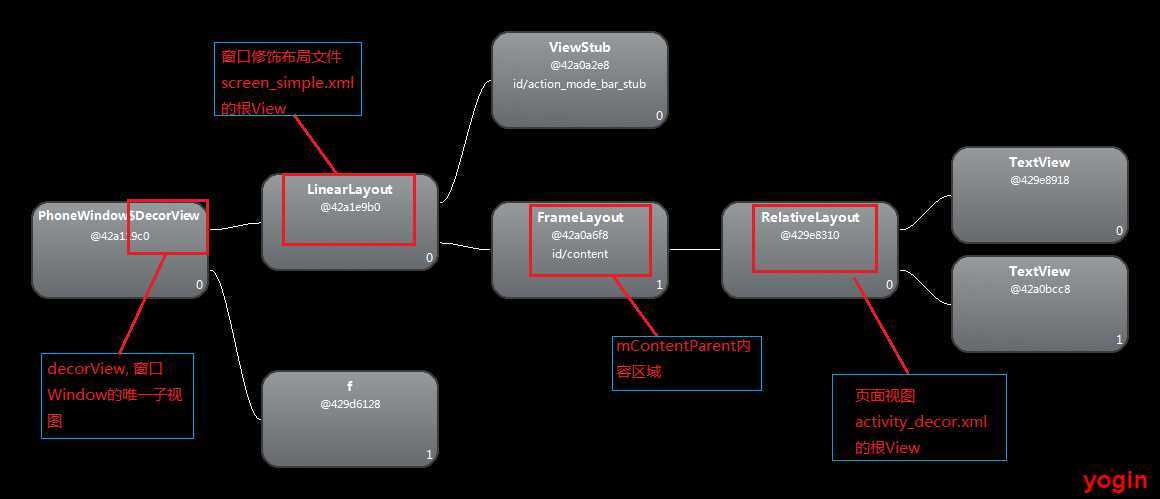
onCreate()中设置的Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE对应的窗口修饰布局文件为screen_simple.xml, 源码如下,LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
android:orientation="vertical">
ViewStub android:id="@+id/action_mode_bar_stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/action_mode_bar"
android:layout="@layout/action_mode_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundInsidePadding="false"
android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top"
android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" />
LinearLayout>
源码中id为"@android:id/content"的FrameLayout就是内容区域,在整个流程中,其会赋值给PhoneWindow类中的属性mContentParent, 运行应用后,使用SDK提供的hierarchyviewer工具查看页面的ViewTree结构,可以看到结构如下:
参考资料:
http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning/article/details/7226787
http://grepcode.com/file/repository.grepcode.com/java/ext/com.google.android/android/4.4.2_r1/android/view/Window.java?av=f
http://grepcode.com/file/repository.grepcode.com/java/ext/com.google.android/android/4.4.2_r1/com/android/internal/policy/impl/PhoneWindow.java?av=f
http://grepcode.com/file/repository.grepcode.com/java/ext/com.google.android/android/4.4.2_r1/frameworks/base/core/res/res/layout/screen_simple.xml?av=f
http://grepcode.com/file/repository.grepcode.com/java/ext/com.google.android/android/4.4.2_r1/android/app/Activity.java?av=f