LRU算法的实现
标签:key use map refresh 数据库查询 com return 问题 under
需求
随着公司的业务越来越复杂,需要提供一个用户系统,供各个业务系统来查询用户的基本信息。且业务方对用户信息的查询频率很高,设计的用户系统需要注意性能。
-
初始设计: 考虑到性能,可以在内存中创建一个哈希表作为缓存,每当查找一个用户时,会现在哈希表中进行查询,查询不到再去数据库查询。
-
初始设计存在的问题: 随着用户量不断增大,可能会因为哈希表逐渐增大导致内存某一天会被撑爆。
-
初始设计的优化:使用LRU算法(内存管理算法,Least Recently Used),最近最少使用的思想。算法基于一种假设:长期不被使用的数据,在未来被用到的几率也不大。因此,当数据所占内存达到一定阈值时,我们要移除掉最近最少被使用的数据。
LRU算法
在LRU算法中,使用一种叫作“哈希链表”的数据结构。哈希表由若干个key-value组成,逻辑上这些key-value是无所谓排序的。但在哈希链表中,这些key-value被一个链条串在一起,不再是无序的了,而是有 了固定的排列顺序。每一个key-value都有前驱key-value、后继key-value。所以我们可以把key-value按照最后使用的时间来进行排序。链表的尾部是最近被使用的,头部是最近被使用最少甚至没有被使用过的key-value。所以,当缓存容量达到上限时,会先删除链表最左端的值,再把新的值插入到链表的最右端。
LRU算法实现
哈希链表的结构:
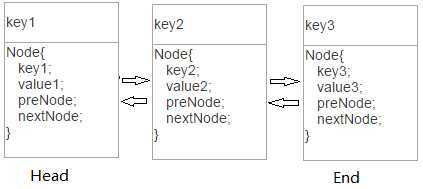
注意点: 删除节点的同时,记得把节点的key也要从hashMap中删除
1 package blogSrc;
2
3 import java.util.HashMap;
4
5 public class LRUCache {
6 private Node head;
7 private Node end;
8
9 private HashMap hashMap;
10 private int limit; //缓存上限
11
12 public LRUCache(int limit){
13 this.limit = limit;
14 this.hashMap = new HashMap();
15 }
16
17 //向链表中添加节点
18 public void addNode (Node node){
19 if (head == null){ //空链
20 head = node;
21 }
22
23 if(end != null) { //节点添加到尾部
24 end.next = node;
25 node.pre = end;
26 node.next = null;
27 }
28 end = node;
29 }
30
31 //从链表中移除节点
32 public String removeNode(Node node){
33 if(head == end && node == head){ //链表只有一个节点
34 head = null;
35 end = null;
36 }else if (node == end){ //node为最后一个节点
37 end.pre.next = null;
38 end = end.pre;
39 }else if (node == head){ //node为第一个节点
40 head.next.pre = null;
41 head = head.next;
42 }else { //node为中间节点
43 node.pre.next = node.next;
44 node.next.pre = node.pre;
45 }
46 return node.key;
47 }
48
49 //刷新链表,将最近使用的节点放置到链表末尾
50 public void refreshNode(Node node){
51 if (node == end){
52 return;
53 }
54 removeNode(node); //删除节点
55 addNode(node); //添加节点
56 }
57
58 //根据节点的key值,获取链表中该节点的value值
59 public String get(String key){
60 Node node = hashMap.get(key);
61 if (node == null){
62 return null;
63 }
64 refreshNode(node);
65 return node.value;
66 }
67
68 //向链表上添加key-value
69 public void put(String key, String value){
70 Node node = hashMap.get(key);
71 if (node == null){
72 if (hashMap.size() >= limit){
73 String oldKey = removeNode(head); //删除节点
74 hashMap.remove(oldKey); //同时需要把节点的key也从hashmap中删除
75 }
76 node = new Node(key,value);
77 addNode(node);
78 hashMap.put(key,node);
79 }else {
80 node.value = value;
81 refreshNode(node);
82 }
83 }
84
85 //从链表上删除指定key的数据
86 public void remove(String key){
87 Node node = hashMap.get(key);
88 if (node == null){
89 return ;
90 }
91 removeNode(node);
92 hashMap.remove(key);
93 }
94
95 class Node {
96 public Node next;
97 public Node pre;
98 public String key;
99 public String value;
100 Node(String key, String value){
101 this.key = key;
102 this.value = value;
103 }
104
105 public String getNextKey() {
106 return next.getKey();
107 }
108
109 public String getPreKey() {
110 return pre.getKey();
111 }
112
113 public String getKey() {
114 return key;
115 }
116
117 public String getValue() {
118 return value;
119 }
120 }
121
122
123 public static void main(String[] args){
124 LRUCache lruCache = new LRUCache(10);
125 lruCache.put("001","用户1信息");
126 lruCache.put("002","用户2信息");
127 lruCache.put("003","用户3信息");
128 lruCache.put("004","用户4信息");
129 lruCache.get("003");
130 System.out.println("Now End Node Key is: " + lruCache.end.getKey()+ ",Value is: " +lruCache.end.getValue());
131 lruCache.put("002","用户2信息更新");
132 System.out.println("Now End Node Key is: " + lruCache.end.getKey() + ",Value is: " +lruCache.end.getValue() );
133 lruCache.put("006","用户6信息");
134 System.out.println("Now End Node Key is: " + lruCache.end.getKey()+ ",Value is: " +lruCache.end.getValue());
135 }
136 }
结果:
Now End Node Key is: 003,Value is: 用户3信息
Now End Node Key is: 002,Value is: 用户2信息更新
Now End Node Key is: 006,Value is: 用户6信息
LRU算法的实现
标签:key use map refresh 数据库查询 com return 问题 under
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zldmy/p/11568544.html
文章来自:
搜素材网的
编程语言模块,转载请注明文章出处。
文章标题:
LRU算法的实现
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/34428.html
评论
