python中文件操作
2020-12-13 16:16
标签:rename lib 序列 nal 读取 close 访问 error 设置 1.创建和打开文件 (1)打开模式: r:以只读模式打开;r+:以读写模式打开;w:以只写模式打开(重写文件,不存在则创建) w+:以读/写模式打开;a:只写模式(只允许在末尾追加);a+以读/写模式打开 >>> fo=open(‘test.txt‘) >>> fo=open(‘test.txt‘,‘w‘) >>> fo.close() (2)写文件(write()写入字符串、writelines()写入字符串序列) >>> fo=open(‘test.txt‘,‘w‘) >>> fo=open(‘test.txt‘,‘w+‘) >>> fo.writelines([‘I\n‘,‘learn\n‘,‘python\n‘]) >>> fo.read() (3)保存和关闭文件(close()和flush()) a.结合异常机制确保文件关闭 >>> try: b.with语句自动管理上下文资源 >>> with open(‘test.txt‘,‘w+‘) as f: (4)读文件 read(),读取并返回整个文件; >>> with open(‘test.txt‘,‘r‘) as f: readline(),只返回一行结果; >>> with open(‘test.txt‘,‘r‘) as f: readlines(),一次读取所有,返回一个列表 >>> with open(‘test.txt‘,‘r‘) as f: 2.文件读写位置 (1)tell(),返回文件当前位置 >>> fo=open(‘test.txt‘) (2)seek(),移动文件读取指针到指定位置,实现文件随机读写 >>> fo.seek(5,0) 3.文件迭代器 每读取一行加载到内存中 >>> fo=open(‘test.txt‘) stestt >>> fo=open(‘test.txt‘) stestt 4.copy模块(在定义类时,通过定义__copy__和__deepcopy__方法,可改变copy默认行为) (1)浅拷贝copy.copy(只复制对象本身,未复制该对象所引用的对象) >>> import copy >>> a >>> c[3][0]=‘g‘ (2)深拷贝copy.deepcopy(复制对象及该对象所引用的对象) >>> d=copy.deepcopy(b) 5.os模块 (1)创建目录(mkdir()/makedirs()) >>> import os (2)删除目录(rmdir()\removedirs()) >>> os.rmdir(‘test‘) (3)创建/删除文件(mknod()/remove()) >>> os.mknod(‘test.txt‘) >>> os.remove(‘test.txt‘) (4)获取当前路径(getcwd()) >>> os.getcwd() (5)切换目录(chdir()) >>>os.chdir(‘/‘) (6)列出目录下的所有目录和文件(listdir()) >>> os.listdir(‘.‘) (7)文件重命名(rename(old,new) >>> os.rename(‘test.txt‘,‘a.txt‘) (8)获取文件/文件夹名 >>> os.path.basename(‘c:\test.txt‘) ‘test.txt‘ (9)获取文件/文件夹路径 >>> os.path.dirname(‘c:\test.txt‘) ‘C:\\‘ (10)遍历树生成文件名(os.walk(top[,topdown=True[,onerror=None[,followlinks=False]]])) top - 以目录为根的每个目录产生3元组,即(dirpath,dirnames,filenames)。dirpath为目录的路径,为一个字符串。 dirnames列出了目录路径下面所有存在的目录的名称。 filenames列出了目录路径下面所有文件的名称。 topdown - 如果可选参数topdown为True或未指定,则从上到下扫描目录。如果topdown设置为False,则会自下而上扫描目录,不懂的话可以看下图的结果就明白了 onerror - 这可能会显示错误以继续行走,或者引发异常以中止行走。 followlinks - 如果设置为true,则访问符号链接指向的目录。 python中文件操作 标签:rename lib 序列 nal 读取 close 访问 error 设置 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/CSXZ/p/11618849.html
>>> fo
>>> fo.read()
‘123‘
>>> fo
>>> fo.write(‘english id ‘)
‘I\nlearn\npython\n‘
... f=open(‘test.txt‘,‘w+‘))
... f.write(‘test‘)
... except BaseException as e:
... print(e)
... finally:
... f.close()
... f.write(‘testtest‘)
... s=f.read()
... print(s)
...
testt\nest\ntest\ntes\nttesttest\nttttt
stesttesttestsstesttesttests\n
stesttesttestsstesttesttests\n
stesttesttests
... line=f.readline()
... print(line)
...
testt\nest\ntest\ntes\nttesttest\nttttt
... content=f.readlines()
... print(content)
...
[‘testt\\nest\\ntest\\ntes\\nttesttest\\nttttt\n‘, ‘stesttesttestsstesttesttests\\n\n‘, ‘stesttesttestsstesttesttests\\n\n‘, ‘stesttesttests‘]
>>> fo.tell()
0L
>>> print(fo.read(5))
testt
>>> fo.tell()
5L
>>> fo.tell()
5L
>>> print(fo.read())
\nest\ntest\ntes\nttesttest\nttttt
stesttesttests
>>> for line in fo:
... print(line)
...
testt\nest\ntest\ntes\nttesttest\nttttt
>>> for line in fo.readlines():
... print(line)
...
testt\nest\ntest\ntes\nttesttest\nttttt
>>> a=[1,2,3,[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘]]
>>> b=a
>>> c=copy.copy(a)
>>> c
[1, 2, 3, [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘],‘e‘]
[1, 2, 3, [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘],‘e‘]
>>> c
[1, 2, 3, [‘g‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘], ‘e‘]
>>> a
[1, 2, 3, [‘g‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘], ‘e‘]
>>> b
[1, 2, 3, [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘], ‘e‘]
>>> d
[1, 2, 3, [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘], ‘e‘]
>>> d[3][1]=‘f‘
>>> d
[1, 2, 3, [‘a‘, ‘f‘, ‘c‘], ‘e‘]
>>> b
[1, 2, 3, [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘], ‘e‘]
>>> os.mkdir(‘test‘)
>>> os.mkdirs(‘a/b/c‘)
>>> os.removedirs(‘a/b/c‘)
‘C:\\Python‘
[‘3.py‘, ‘a.py‘, ‘chromedriver.exe‘, ‘DLLs‘, ‘Doc‘, ‘include‘, ‘Lib‘, ‘libs‘, ‘LICENSE.txt‘, ‘NEWS.txt‘, ‘python.exe‘, ‘pythonw.exe‘, ‘README.txt‘, ‘Scripts‘, ‘tcl‘, ‘test1‘, ‘Tools‘]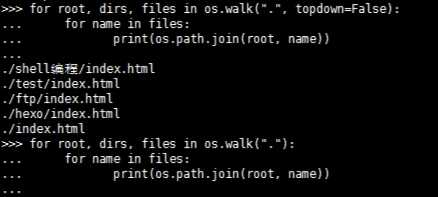
下一篇:python 虚拟环境