MVC路由探寻,涉及路由的惯例、自定义片段变量、约束、生成链接和URL等
2020-12-13 16:35
标签:style class blog code http tar 引子 URL匹配的特点: 本篇涉及的方面包括: 路由惯例 □ 当URL中对应的controller,action根本不存在,报404错误。 □ 当URL中对应的controller,action存在,而路由规则的片段数量和URL的片段数量不等,报404错误。 □ 当URL中对应的controller,action存在,路由规则中设置了默认值,URL中的某些片段可省略。 □ 当路由规则中设置了静态片段,即使在路由规则中设置了默认值,URL的片段数量必须和路由规则中的动态片段数量一致,不能缺省。
□ 当路由中设置了静态片段,并且在路由规则中只为一个动态片段赋了默认值,那么这个赋值是有效的,URL中动态片段数量还是必须和路由规则中的动态片段数量一致。 □ 当路由规则中设置了混合片段,URL中的片段数量必须和路由规则片段数量一致,且URL片段中同时包含静态和动态
□ 路由的添加是有顺序的 在下面的路由,会添加到RouteCollection的结尾处。 □ 路由的匹配是有顺序的 从上到下开始匹配。 □ 路由的优先顺序是有讲究的 一般把具体的路由规则放在上面,把宽泛的路由规则放在下面。
自定义片段变量 →什么是自定义片段变量 →从RouteDate.Values中取出自定义片段变量并显示 在路由中添加一个自定义变量id,并附上初始值:
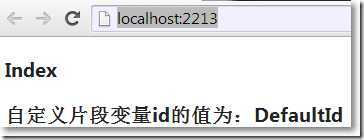
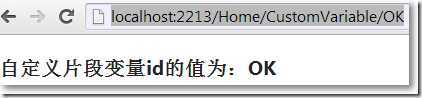
在Home/Index.cshtml中: 在Home/CustomVariable.cshtml中: 输入:http://localhost:2213/,在Home/Index.cshtml中显示自定义片段变量的默认值: 输入:http://localhost:2213/Home/CustomVariable/OK,在Home/CustomVariable.cshtml中显示自定义片段变量的新值: →MVC默认模型绑定机制把自定义片段变量赋值给方法参数 →把自定义片段变量设置为可选 →把自定义片段变量设置为可变长
设置路由规则搜寻的命名空间和控制器的优先顺序 →如果想让路由规则优先搜寻某个命名空间和控制器,可以这样设置:
→如果想让路由规则优先搜寻某些命名空间和控制器,应该写多条路由,并且有先后顺序,可以这样设置: →如果想让路由规则只搜寻某个命名空间,可以这样设置: 路由约束 →正则表达式约束路由 →指定值约束路由 →HTTP方式约束路由 →自定义约束,实现IRouteConstraint接口 路由允许对静态文件的请求 →在项目根目录下创建static.html。 →把RoutingExistingFiles设置为true: →输入http://localhost:2213/static.html: 生成链接 →使用默认路由规则,Html.ActionLink()生成链接 @Html.ActionLink("关于我们","About") →添加含有静态片段变量的路由规则,Html.ActionLink()生成链接 @Html.ActionLink("关于我们","About") →Html.ActionLink()带控制器名重载生成链接
先把路由改回: @Html.ActionLink("关于我们","About",new {id="MyID"}) →当在Html.ActionLink()方法中路由匿名函数的变量名与路由规则中的片段变量不一致,路由匿名函数的变量值作为查询字符串追加到输出URL上 →Html.ActionLink()指定输出链接的标签属性 →Html.ActionLink()生成绝对路径链接 →Html.RouteLink()根据路由数据生成链接 →Html.RouteLink()根据路由名称生成链接 生成URL Url.Action()的重载和Html.ActionLink()类似,除此之外还包括: →使用Url.Action()在控制器方法中生成URL →使用Url.RouteUrl()在控制器方法中生成URL →使用RedirecToAction()在控制器方法中重定向到一个URL →使用RedirecToRoute()在控制器方法中重定向到一个URL 来自Jeffery Zhao的生成自定义链接的几种方法 有这样的一个Model: ArticleController: →Article/Index.cshtml中使用拼接字符串生成链接 生成的链接为:查看详细 在Article/Index.cshtml视图中: 参考资料: MVC路由探寻,涉及路由的惯例、自定义片段变量、约束、生成链接和URL等,搜素材,soscw.com MVC路由探寻,涉及路由的惯例、自定义片段变量、约束、生成链接和URL等 标签:style class blog code http tar 原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/darrenji/p/3800384.html
在了解MVC路由之前,必须了解的概念是"片段"。片段是指除主机名和查询字符串以外的、以"/"分隔的各个部分。比如,在http://site.com/Home/Index中,包含2个片段,第一个片段是Home,第二个片段是Index。
● 保守的:URL中的片段数量必须和路由规则中的片段数量一致(路由规则没有设置默认值的前提下)
● 宽松的:在满足片段数要求的前提下,URL中的片段内容是宽松的
1、路由惯例
2、自定义片段变量
3、设置路由规则搜寻的命名空间和控制器的优先顺序
4、路由约束
5、路由允许对静态文件的请求
6、生成链接
7、生成URLroutes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}");
http://localhost:2213/Demo/Index 报404错误 因为还没有创建Demo控制器
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}");
http://localhost:2213/ 报404错误
http://localhost:2213/Home 报404错误
http://localhost:2213/Home/Index/Index 报404错误
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}",new {action = "Index"});
http://localhost:2213/Home 可以,因为设置了默认的action值
http://localhost:2213/Home/Index 当然也可以
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" }
);
routes.MapRoute(
name:"",
url:"Category/{controller}/{action}",
defaults: new {controller = "Home", action = "Index"}
);
在第二条路由规则中,Category是静态片段,{controller}和{action}是2个动态片段。以上,当给这2个动态片段同时赋默认值,由于URL中的动态片段数量也必须是2个,所以这里的动态片段赋默认值,赋不赋都无所谓了,即动态片段默认值是无效的。http://localhost:2213/Category/ 报404错误,因为 第二条路由要求2个片段变量
http://localhost:2213/Category/Home/Index 可以
routes.MapRoute(
name:"Shop",
url:"Shop/{action}",
defaults:new {controller = "Home"}
);
http://localhost:2213/Shop 报404错误,因为必须至少一个片段变量
http://localhost:2213/Shop/Index 可以,显式Home/Index.cshtml的内容,个动态片段{controller}赋的默认值起作用了。
routes.MapRoute(
name:"",
url:"X{controller}/{action}"
);
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" }
);
routes.MapRoute(
name:"Category",
url:"Category/{controller}/{action}",
defaults: new {controller = "Home", action = "Index"}
);
在第一条路由股则中,X{controller}是混合片段。http://localhost:2213/XHome/ 报404错误
http://localhost:2213/XHome/Index 可以
如果把具体的路由规则放在下面,把宽泛的路由规则放在上面。routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" }
);
routes.MapRoute(
name: "",
url: "X{controller}/{action}"
);
http://localhost:2213/XHome/Index 报404错误,因为对第一条宽泛的路由规则而言,XHome控制器是不存在的。
如果说controller和action是MVC固有的片段变量,我们同样可以自定义片段变量。所有的片段变量,包括自定义片段变量都是以键值对的形式放在RouteDate.Values中的,key就是片段变量名。routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = "DefaultId" }
);
在HomeController中:
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewBag.c = RouteData.Values["id"];
return View();
}
public ViewResult CustomVariable()
{
ViewBag.c = RouteData.Values["id"];
return View();
}
Index
自定义片段变量id的值为:@ViewBag.c
自定义片段变量id的值为:@ViewBag.c
public ViewResult CustomVariable(string id)
{
ViewBag.c = id;
return View();
}
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
即在URL中,自定义片段变量id后面的片段都赋给catchall变量。
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
constraints:new[]{"UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers"}
);
这样,路由规则优先搜寻UrlsAndRoutes命名空间下的控制器,然后再搜寻其它可用的命名空间。
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default1",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
constraints: new[] { "Additional.Controllers" }
);
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
constraints:new[]{"UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers"}
);
Route r = routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default1",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
constraints: new[] { "Additional.Controllers" }
);
r.DataTokens["UserNamespaceFallback"] = false;
routes.MapRoute(
"Default",
"{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
new{ controller = "^H.*"},
new[]{"UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers"}
);
routes.MapRoute(
"Default",
"{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
new{ controller = "^H.*", action = "^Index$|^About$"},
new[]{"UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers"}
);
routes.MapRoute(
"Default",
"{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
new{ controller = "^H.*", action = "^Index$|^About$", httpMethod = new HttpMethodConstraint("GET","POST")},
new[]{"UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers"}
);
using System.Web.Routing;
namespace UrlsAndRoutes.Extension
{
public class UserAgentConstraint : IRouteConstraint
{
private string requiredAgent;
public UserAgentConstraint(string agent)
{
this.requiredAgent = agent;
}
public bool Match(System.Web.HttpContextBase httpContext, Route route, string parameterName, RouteValueDictionary values, RouteDirection routeDirection)
{
return httpContext.Request.UserAgent != null && httpContext.Request.UserAgent.Contains(requiredAgent);
}
}
}
routes.MapRoute(
"Default",
"{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
new
{
controller = "^H.*",
action = "^Index$|^About$",
httpMethod = new HttpMethodConstraint("GET","POST"),
customConstraint = new UserAgentConstraint("IE")
},
new[]{"UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers"}
);
routes.RouteExistingFiles = true;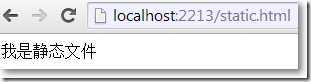
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
关于我们routes.MapRoute(
"NewRoute",
"App/Do{action}",
new {controller = "Home"}
);
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
关于我们@Html.ActionLink("关于我们","About","MyController")
"/MyController/About">关于我们
因为含有2个片段变量的值,所以符合第二条路由规则。
→Html.ActionLink()传递额外的值
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
关于我们@Html.ActionLink("关于我们","About",new {id="MyID", myVariable = "MyValue"})
"/Home/About/MyID?myVariable=MyValue">关于我们
@Html.ActionLink("关于我们","About","Home",new {id="MyID", myVariable = "MyValue"},new {@class = "MyClass"})
class="MyClass" href="/Home/About/MyID?myVariable=MyValue">关于我们
@Html.ActionLink("关于我们","About","Home",
"https",
"myserver.mydomain.com",
"myFragmentName",
new {id="MyID", myVariable = "MyValue"},
new {@class = "MyClass"})
class="MyClass" href="https://myserver.mydomain.com/Home/About/MyID?myVariable=MyValue#myFragmentName">关于我们
@Html.RouteLink("关于我们",new {controller = "Home", action = "About", id = "MyID"})
"/Home/About/MyID">关于我们
@Html.RouteLink("关于我们", "Default", new {action = "About"})
"/Home/About">关于我们
public ViewResult SomeAction()
{
string url = Url.Action("Index", new {id = "MyID"})
}
public ViewResult SomeAction()
{
string url = Url.RouteUrl(new {controller = "Home", action = "Index"});
}
public ActionResult SOmeAction()
{
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
public ActionResult SOmeAction()
{
return RedirectToRoute(new {controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = "MyID"});
}
namespace MvcApplication1.Models
{
public class Article
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
}
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View(GetArticles());
}
private List GetArticles()
{
return new List()
{
new Article(){Id = 1, Title = "This is an article"},
new Article(){Id = 2, Title = "We are the champion"}
};
}
@model IEnumerable
@foreach (var item in Model)
{
}
@item.Id
@item.Title
"/article/@item.Id-@Url.Encode(item.Title.Replace(‘ ‘,‘-‘))">查看详细
→通过扩展UrlHelper生成链接using System.Web.Mvc;
using MvcApplication1.Models;
namespace MvcApplication1.Extension
{
public static class ArticleUrlExtension
{
public static string ToArticle(this UrlHelper helper, Article article)
{
return "/article/" + article.Id + "-" + helper.Encode(article.Title.Replace(‘ ‘, ‘-‘));
}
}
}
@using MvcApplication1.Extension
@model IEnumerable
@foreach (var item in Model)
{
}
@item.Id
@item.Title
@*"/article/@item.Id-@Url.Encode(item.Title.Replace(‘ ‘,‘-‘))">查看详细*@
"@Url.ToArticle(item)">查看详细
http://blog.zhaojie.me/2009/10/several-ways-of-generating-url.html
精通ASP.NET MVC3框架(第三版)
上一篇:Java基础面试题及答案(三)
下一篇:jQuery之属性过滤选择器
文章标题:MVC路由探寻,涉及路由的惯例、自定义片段变量、约束、生成链接和URL等
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/36304.html