Keras高层API之Metrics
2021-01-15 05:13
标签:res for zip variables cat style col image class 在tf.keras中,metrics其实就是起到了一个测量表的作用,即测量损失或者模型精度的变化。metrics的使用分为以下四步: step1:Build a meter step2:Update data step3:Get Average data 清除缓存: 实战: Keras高层API之Metrics 标签:res for zip variables cat style col image class 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zdm-code/p/12244043.htmlacc_meter = metrics.Accuracy()
loss_meter = metrics.Mean()
loss_meter.update_state(loss)
acc_meter.update_state(y,pred)
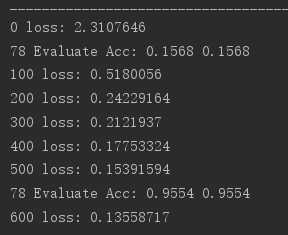
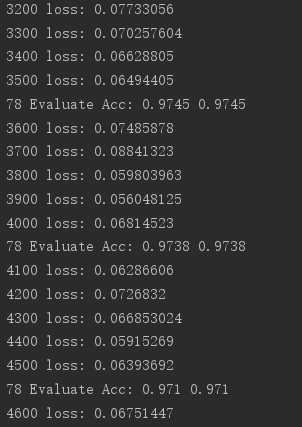
print(step,‘loss:‘,loss_meter.result().numpy())
print(step,‘Evaluate Acc:‘,total_correct/total,acc_meter.result().numpy())
if step % 100 == 0:
print(step,‘loss:‘,loss_meter.result().numpy())
loss_meter.reset_states()
if step % 500 ==0:
total,total_correct = 0.,0
acc_meter.reset_states()
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, Sequential, metrics
def preprocess(x, y):
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x,y
batchsz = 128
(x, y), (x_val, y_val) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
print(‘datasets:‘, x.shape, y.shape, x.min(), x.max())
db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y))
db = db.map(preprocess).shuffle(60000).batch(batchsz).repeat(10)
ds_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val, y_val))
ds_val = ds_val.map(preprocess).batch(batchsz)
network = Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation=‘relu‘),
layers.Dense(128, activation=‘relu‘),
layers.Dense(64, activation=‘relu‘),
layers.Dense(32, activation=‘relu‘),
layers.Dense(10)])
network.build(input_shape=(None, 28*28))
network.summary()
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01)
acc_meter = metrics.Accuracy()
loss_meter = metrics.Mean()
for step, (x,y) in enumerate(db):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28*28))
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
out = network(x)
# [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10)
# [b]
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, out, from_logits=True))
loss_meter.update_state(loss)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, network.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, network.trainable_variables))
if step % 100 == 0:
print(step, ‘loss:‘, loss_meter.result().numpy())
loss_meter.reset_states()
# evaluate
if step % 500 == 0:
total, total_correct = 0., 0
acc_meter.reset_states()
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(ds_val):
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28*28))
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
out = network(x)
# [b, 10] => [b]
pred = tf.argmax(out, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
# bool type
correct = tf.equal(pred, y)
# bool tensor => int tensor => numpy
total_correct += tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, dtype=tf.int32)).numpy()
total += x.shape[0]
acc_meter.update_state(y, pred)
print(step, ‘Evaluate Acc:‘, total_correct/total, acc_meter.result().numpy())
上一篇:云平台发展前沿报告 微软云平台——Windows Azure
下一篇:Get Window Size关键字——获取当前页面窗口的大小,会返回窗口的宽和高,先返回宽,再返回高——不需要接收任何参数