JavaSE集合基础总览
2021-05-17 18:29
标签:for string name ima 实现 集合类 api 问题: remove Java集合,也称之为容器。基本上你写所有的Java程序,都必须要用到一个包。该API基本都位于java.util工具类包中,是JavaSE中的重中之重。 大部分容器类,都必须实现Collection接口,而实现该接口必须实现其的iterator方法。 JavaSE集合基础总览 标签:for string name ima 实现 集合类 api 问题: remove 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/byuc/p/9744060.htmlJava集合
简单可以总结为“1136”,分别是一个图,一个类,三个知识点,六个接口。下面逐个剖析。1.一个图
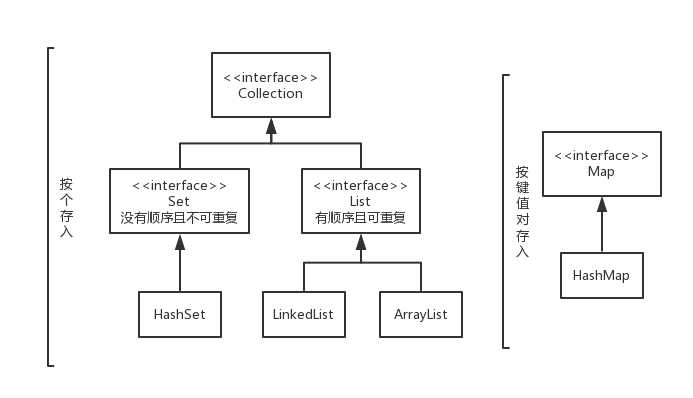
备注:
(1)六个接口:Collection接口
1 import java.util.*;
2
3 public class CollectionTest {
4 public static void main(String[] args) {
5 // 父类引用,指向子类对象
6 // 为求方便更换其他子类的实现
7 Collection c = new ArrayList();
8 // 可以放入不同类型的对象
9 c.add("hello");
10 c.add("f1");
11 c.add(new Integer(100));
12 System.out.println(c.size()); // 3
13 System.out.println(c); // [hello,f1,100]
14 }
15 }
(2)六个接口:Iterator接口
iterator方法的作用就是,所有实现Collection接口方法的容器子类,不管其具体的实现、使用的数据结构,其必须提供一个iterator方法用以进行统一的遍历数据方式。
(举个栗子,我不管你馒头店具体是怎么去做馒头,存储馒头的,反正你做馒头必须要实现卖馒头的方法,我去到按照金钱交易的方式一定能得到馒头)
所以:
1 import java.util.*;
2
3 public class IteratorTest {
4 public static void main(String[] args) {
5 Collection c = new HashSet();
6 c.add(new Name("f1", "l1"));
7 c.add(new Name("f2", "l2"));
8 c.add(new Name("f3", "l3"));
9 Iterator i = c.iterator();
10 while (i.hasNext()) {
11 //next()的返回值为Object,需要转换为相应类型
12 Name = n = (Name) i.next();
13 System.out.println(n.getName());
14 // 因为set没有顺序,所以返回[f2,f1,f3,l1,l2,l3]
15 }
16 }
17 }
(3)六个接口:Set接口
示例: 1 import java.util.*;
2
3 /**
4 * 求交集 去重
5 */
6 public class SetTest {
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 Set s1 = new HashSet();
9 Set s2 = new HashSet();
10 s1.add("a");s1.add("b");s1.add("c");
11 s2.add("d");s2.add("a");s2.add("b");
12 //Set和List容器类都具有Constructor(Constructor c)
13 //构造方法用以初始化容器类
14 Set sn = new HashSet(s1);
15 sn.retainAll(s2);
16 Set su = new HashSet(s1);
17 su.addAll(s2);
18 System.out.println(sn);// [a,b]
19 System.out.println(su);// [d,a,c,b]
20 }
21 }
(4)六个接口:List接口
一个类:Collections类
其余的方法可以具体去看API文档,再给个示例: 1 import java.util.*;
2 /**
3 * 举例部分Collections的算法排序,具体看API
4 */
5 public class Collections {
6 public static void main(String[] args) {
7 List l1 = new LinkedList();
8 for (int i = 0; i ) {
9 l1.add("a" + i);
10 }
11 /**
12 * 目前l1的值排序为: [a0,a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6,a7,a8,a9]
13 */
14 Collections.reverse(l1);// 逆序排序
15 System.out.println(l1);// [a9,a8,a7,a6,a5,a4,a3,a2,a1,a0]
16 Collections.shuffle(l1);// 随机排序
17 System.out.println(l1);// [a1,a3,a8,a9,a4,a6,a5,a2,a0,a7]
18 Collections.sort(l1);// 正序排序
19 System.out.println(l1);// [a0,a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6,a7,a8,a9]
20 System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(l1, "a5"));// 6
21 }
22 }
(5)六个接口:Comparable接口
(6)六个接口:Map接口
泛型
总结